Consumer Buying Process - Consumer Behaviour, Principles of Marketing | Principles of Marketing - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Consumer Buying Behavior |

|
| Types of Consumer Buying Behaviour |

|
| Stages in Buying Behaviour Process |

|
| Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Behavior |

|
| Market Segmentation |

|
Understanding Consumer Buying Behavior
Consumer buying behavior refers to the decision processes and actions of individuals involved in purchasing and using products. It is crucial to comprehend why consumers make certain purchases, what factors influence their buying decisions, and how these factors are changing in society.
Importance of Analyzing Buying Behavior:
- Buyers' reactions to a firm's marketing strategy significantly impact the firm's success.
- The marketing concept emphasizes creating a Marketing Mix (MM) that satisfies customers, necessitating an analysis of what, where, when, and how consumers buy.
- Understanding buying behavior helps marketers predict consumer responses to marketing strategies more accurately.
Types of Consumer Buying Behaviour
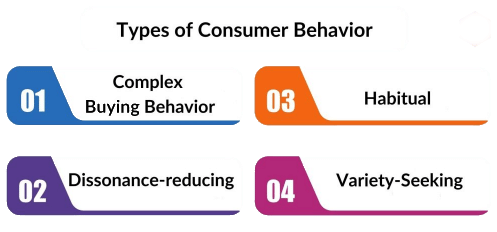
Types of consumer buying behaviour are determined by: Level of Involvement in purchase decision. Importance and intensity of interest in a product in a particular situation.
Buyers level of involvement determines why he/she is motivated to seek information about a certain products and brands but virtually ignores others.
High involvement purchases --Honda Motorbike, high priced goods, products visible to others, and the higher the risk the higher the involvement.
Types of Risk:
- Personal risk
- Social risk
- Economic risk
The four types of consumer buying behavior are:
1. Routine Response/Programmed Behavior
- Buying low involvement frequently purchased low cost items
- Need very little search and decision effort
- Purchased almost automatically
- Examples include soft drinks, snack foods, milk etc.
2. Limited Decision Making
- Buying product occasionally
- Need to obtain information about unfamiliar brand in a familiar product category
- Requires a moderate amount of time for information gathering
- Examples include Clothes—know product class but not the brand
3. Extensive Decision Making/Complex
- High involvement, unfamiliar, expensive and/or infrequently bought products
- High degree of economic/performance/psychological risk
- Examples include cars, homes, computers, education
- Spend a lot of time seeking information and deciding
- Information from the companies MM; friends and relatives, store personnel etc.
- Go through all six stages of the buying process
4. Impulse Buying
- No conscious planning
- The purchase of the same product does not always elicit the same Buying Behavior
- Product can shift from one category to the next
Example:
- Going out for dinner for one person may be extensive decision making (for someone that does not go out often at all)
- Limited decision making for someone else
- The reason for the dinner, whether it is an anniversary celebration, or a meal with a couple of friends will also determine the extent of the decision making
Diagram of Consumer Buying Behaviour Process
Stages in Buying Behaviour Process
Six Stages to the Consumer Buying Decision Process (For complex decisions)
- Actual purchasing is only one stage of the process.
- Not all decision processes lead to a purchase.
- All consumer decisions do not always include all 6 stages, determined by the degree of complexity...discussed next.
- The 6 stages are:
Problem Recognition (awareness of need)
- The difference between the desired state and the actual condition.
- A deficit in the assortment of products.
- For example, hunger stimulates your need to eat. Marketers can stimulate this recognition by providing product information, such as through commercials.
- For instance, seeing a commercial for a new pair of shoes might trigger your awareness that you need a new pair of shoes.
Information Search
Internal Search: This involves recalling information from memory about past experiences with products or services.
External Search: If more information is needed, external sources are consulted, including:
- Friends and Relatives: Word of mouth recommendations.
- Marketer-Dominated Sources: Advertisements and promotional materials.
- Comparison Shopping: Online and offline platforms that compare products and prices.
- Public Sources: Reviews, ratings, and other publicly available information.
A successful information search results in the evoked set, which is a list of possible alternatives. For example, when hungry and thinking about going out to eat, the evoked set might include:
- Chinese Food
- Indian Food
- Burger King
- Klondike Kate's
Evaluation of Alternatives
- During this stage, criteria for evaluation are established, including desired and undesired features. Alternatives are ranked or weighted based on these criteria. For instance, if craving something spicy, Indian food might receive the highest rank.
- If none of the alternatives are satisfactory, the search phase may be revisited. This could involve looking for other restaurants in directories like the Yellow Pages. It's important to note that information from different sources may be perceived differently, and marketers often try to influence perceptions by "framing" alternatives.
Purchase Decision
- This stage involves choosing the buying alternative, which includes decisions about the product, packaging, store, and method of purchase.
Purchase
- The actual purchase may differ from the decision made earlier. There can be a time lapse between the decision and the purchase, and factors like product availability can affect the outcome.
Post-Purchase Evaluation
- After the purchase, the outcome is assessed as either Satisfaction or Dissatisfaction. Cognitive Dissonance may occur, leading to questioning whether the right decision was made. This can be alleviated by warranties and after-sales communication. For example, after enjoying an Indian meal, one might wonder if a Chinese meal would have been a better choice.
Information Gathering Time: Moderate:
- Familiar with the product class but not the brand (e.g., clothes). Extensive: Involves high involvement, unfamiliar, expensive, or infrequently bought products (e.g., cars, homes, computers, education). These purchases carry a high degree of economic, performance, or psychological risk, leading to extensive information-seeking behavior.
Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Behavior
Consumer buying behavior is shaped by four main factors:
- Cultural
- Social
- Personal
- Psychological
These factors lead consumers to develop specific preferences for products and brands. While marketers cannot directly control many of these factors, understanding their influence is crucial for creating effective marketing strategies that resonate with the target audience.
Stages of the Consumer Decision Process
When buying a product, consumers typically go through a decision process that can involve up to five stages:
- Problem Recognition: Realizing there is a need or want.
- Information Search: Looking for information about potential solutions.
- Evaluation of Alternatives: Comparing different options.
- Purchase Decision: Making the decision to buy.
- Post-Purchase Behavior: Reflecting on the purchase and its outcomes.
The duration of this process can vary significantly. Additionally, consumers are often influenced by others during the purchase, and the number of people involved typically increases with the complexity and importance of the buying decision.
Social Factors:
Social factors encompass the influence of various groups and individuals on a consumer's purchasing decisions. This includes:
- Reference Groups: Groups that individuals look to for guidance, which can affect their preferences and choices.
- Aspirational Groups: Groups that consumers aspire to join, influencing their buying behavior to align with the group's standards.
- Member Groups: Groups to which consumers currently belong, impacting their purchasing decisions based on group norms and values.
Additionally, family, roles, and social status play a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior, highlighting the direct and indirect impact of others on individual purchase decisions.
Personal Factors:
Personal factors refer to individual characteristics that influence purchasing behavior. These include:
- Age and Lifecycle Stage: Different age groups and life stages have varying needs and preferences.
- Occupation:. person’s job can affect their buying habits and preferences.
- Economic Circumstances: Financial situations can impact what and how much consumers are willing to spend.
- Lifestyle: Activities, interests, opinions, and demographics shape individual preferences and buying behavior.
- Personality and Self-Concept: Individual personalities and how people perceive themselves can influence their choices.
Understanding these personal factors is essential as they explain why consumer preferences may change with different situations and contexts.
Psychological Factors:
Psychological factors play a significant role in influencing purchase decisions. These include:
- Motivation: Driven by needs, as outlined in Maslow's hierarchy of needs, which ranges from basic physiological needs to self-actualization.
- Perception: How consumers interpret information and form opinions about products.
- Learning: The process through which consumers acquire information and experiences that influence their future buying behavior.
- Beliefs and Attitudes: Preconceived notions and feelings towards a product that can significantly affect purchasing decisions.
Understanding these psychological factors helps marketers tailor their strategies to align with consumers' internal motivations and perceptions.
Influence of Others on Consumer Purchase Decisions
- Other individuals often play a crucial role in influencing a consumer's purchase decision. Marketers need to identify the people involved in the buying process and understand the role each person plays. This knowledge allows for the development of targeted marketing strategies aimed at these individuals as well.
Diagrams for Consumer Buying Behaviour Factors
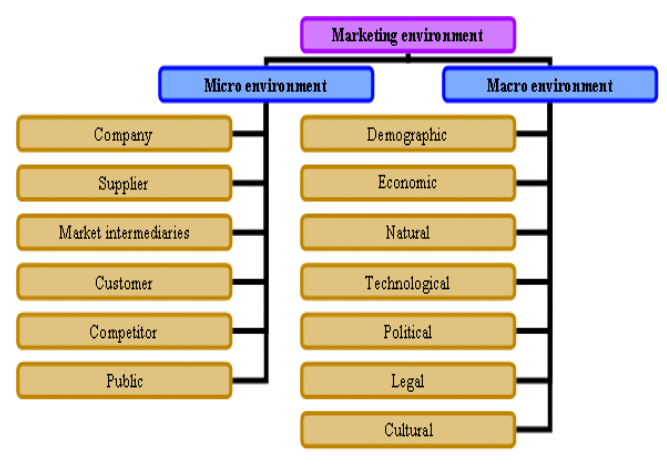
Factors Influencing Consumer Buying Behavior
Cultural Factors
- Culture: The set of values, ideas, and accepted behaviors that a group of people share. This is the most important factor as it shapes a person's wants and behaviors.
- Subculture:. group within a culture that has its own distinct values and behaviors, such as nationalities, religions, racial groups, and geographic regions.
- Social Class: Society's divisions based on factors like income, education, occupation, and wealth, which influence preferences and behaviors.
Social Factors
- Reference Groups: Groups that influence an individual's behavior, including friends, family, and coworkers. These groups can affect what a person buys and how they behave.
- Family: The family unit plays a crucial role in shaping buying behavior, as family members often influence each other's purchases.
- Roles and Status: The role a person plays in a group and their status within that group can impact their buying decisions.
Personal Factors
- Age and Life Cycle Stage:. person's age and the stage of their life cycle (such as single, married, or retired) can influence their purchasing habits.
- Occupation:. person's job can determine the types of products they buy. For example, a chef may buy different kitchen equipment than an office worker.
- Economic Situation: An individual's financial situation, including income, savings, and economic conditions, affects their buying capacity.
- Lifestyle:. person's lifestyle, including their activities, interests, and opinions, influences their buying choices.
- Personality and Self-Concept:. person's personality traits and self-image can affect their preferences and buying behavior.
Psychological Factors
- Motivation: The internal drive that compels a person to take action, such as the need for safety, belonging, or self-esteem.
- Perception: How a person interprets information and forms an opinion about a product or service, which can be influenced by marketing and personal experiences.
- Beliefs and Attitudes:. person's beliefs about a product or brand and their overall attitude towards it can significantly impact their buying decisions.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad market into smaller, more manageable groups of consumers or organizations that share common characteristics, such as needs or behaviors. This approach helps businesses tailor their marketing strategies to specific segments, making their efforts more effective.
Market segments can be defined in various ways, and one common method is by identifying preference segments. This involves grouping consumers based on their preferences and behaviors.
Types of Market Segmentation
1. Demographic Segmentation
- This type of segmentation divides the market based on demographic factors such as age, gender, income, education, occupation, and family size. For example, a company selling luxury cars may target high-income individuals, while a family-oriented brand might focus on households with children.
2. Psychographic Segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation considers the lifestyle, interests, values, and personality traits of consumers. This approach helps businesses understand the motivations behind consumer behavior. For instance, a fitness brand may target health-conscious individuals who prioritize exercise and nutrition.
3. Behavioral Segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation focuses on consumer behaviors, such as purchase frequency, brand loyalty, and usage patterns. This type of segmentation helps businesses identify and target specific behaviors. For example, an online retailer may offer discounts to frequent shoppers to encourage repeat purchases.
|
37 videos|59 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Consumer Buying Process - Consumer Behaviour, Principles of Marketing - Principles of Marketing - B Com
| 1. What is the consumer buying process? |  |
| 2. How does consumer behavior influence the buying process? |  |
| 3. What are the principles of marketing related to the consumer buying process? |  |
| 4. How does the information search stage of the consumer buying process affect purchasing decisions? |  |
| 5. Why is post-purchase evaluation important in the consumer buying process? |  |





















