Crude Distillation | Chemical Technology - Chemical Engineering PDF Download
5.1 Introduction
In this section, we present a brief overview of the crude distillation process.
The first essential task for the crude oil consisting of more than 108 compounds is to separate its major components based on boiling point differences. This principle is exploited in the crude distillation unit which involves energy intensive operation. Since crude distillation involves the processing of the entire feed, it remains as the most significant operation in a refinery.

Figure. 5.1: Process flowsheet-a conceptual diagram of the crude distillation unit (CDU) along with heat exchanger networks (HEN)
The conceptual process flowsheet for the petroleum refinery is shown in the Figure 5.1. It consists of the following important sub-processes:
- Crude desalte
- Furnace
- Pre-flash column
- Crude distillation column supplemented with side columns. These columns produce the desired products
- Pump around heat exchanger units
- Heat exchanger network that facilitates energy recovery from hot product and reflux streams to heat the crude oil.
- We next present the functional role of various sub-processes in the crude distillation unit.
5.1.1 Crude desalter
- The crude desalting unit is a separation process. Here, water along with other trace chemicals such as caustic and acid are allowed to enter a mixing unit along with the crude oil.
- The mixture of crude oil and water is subsequently passed through an electrostatic precipitator cum gravity settler. The electrostatic field enables the agglomeration of water droplets and aids faster gravity settling.
- An essential issue for the good performance of crude desalter is the temperature of the operation. . Usually, high efficiency of salt removal is possible between 100 – 300° F.
- Therefore, the crude oil is heated to about 250° F before it enters the desalter unit.
- The clean desalted crude oil flows from the top of the gravity settler and the water along with other dissolved impurities is removed as a bottom product from the gravity settler unit.
- A high degree of salt removal is desired (95 – 99% removal of the dissolved salt in the crude oil). Usually, a two stage desalting process is deployed. When higher salt removal efficiencies are desired, three stage units are deployed.
- Crude oil consists of dissolved salts and they tend to cause fouling and corrosion in various process equipments. Therefore, dissolved salts need to be removed using a separation process.
5.1.2 Furnace
- The furnace is an important constituent in the crude distillation unit
- Here, fuel oil and fuel gas (heavier products) obtained from the refining process itself are burnt to increase the crude oil temperature.
- Typically in refineries, the crude oil is heated to a temperature that enables overflash conditions in the main crude distillation column.
- The concept of overflash is that the crude is heated to such a temperature that enables an additional 5 % vaporization with respect to the residue product. In other words, the residue fraction vapors amounting to 5 % of the total volume of the crude oil are desired.
- Depending upon the quality of the crude, the desired temperature for the crude oil is about 600 -700°F.
5.1.3 Pre-flash column
- The crude oil enters the pre-flash column after leaving the furnace
- The pre-flash tower separates the lighter fractions of the already heated crude oil.
- The heavier fractions of the crude oil leave from the bottom section of the pre-flash tower.
- Both lighter and heavier streams emanating from the pre-flash tower are fed to the main crude distillation column at various sections
- Pre-flash column enables better refluxes in the main column by distributing the streams effectively between various processing zones of the crude oil.
- Pre-flash column may or may not be included i.e., it is optional. In other words, the pre-flash column can be avoided and the heated crude oil from the furnace can be fed to the main column directly.
5.1.4 Main and Secondary distillation columns
- The distillation columns consisting of both main and secondary crude distillation columns are one of the most complex circuitries in distillation.
- The complex arrangement of distillation columns is based on research carried out with pilot plants and simulation software.
- The crude distillation columns (both main and primary) are regarded to an indirect sequence of thermally coupled distillation sequences to obtain the desired products.
- Effective distribution of vapor and reflux in the main column is a serious issue.
- The effective distribution of vapor and reflux is aided through pump around heat exchanger units.
- Live steam is also used in the recent designs. The live steam is usually at about 50 psig.
- The basic principle of using live steam stems out from several facts. Firstly, upon condensation, oil and water are very easy to separate. Secondly, steam can take significant amount of heat in terms of enthalpy. Thirdly, steam enables enhancement in relative volatility, a principle that is used in steam distillation laboratory experimental set ups. These principles together are anticipated to provide good dividends technically.
- Live steam cannot be just fed at one section of the CDU. It needs to be fed at various sections to ensure both good heat distribution and reduce relative volatilities of the hydrocarbons at various sections of the main and secondary towers.
- Therefore, live steam will enable good product quality as lighter hydrocarbons with higher relative volatilities in the bottom heavy product liquid streams will be easily stripped and carried along with the vapor.
- The only condenser in the main column is a partial condenser to facilitate the production of both gas and naptha+water stream.
- The circuitry totally avoided the existence of reboilers by introducing live steam. Therefore, much fixed costs of the column have been reduced. However, higher operating costs due to higher steam utilization rates are evident.
5.1.5 Pump-around units
- Pump around units are most essential units in the crude distillation column.
- They are used to maintain good reflux conditions in the main column and therefore the desired product quality.
- They also provide a good heat source as the liquid streams are at higher temperatures. Therefore, they are also important units in the heat exchanger network.
- The cooled liquid is sent back to a section above.
- Usually two pump arounds are used in conventional designs. However, there are crude distillation units with even three pump around units.
The circuitry connections between primary and secondary towers along with relevant pump around units are presented in Figure 5.2. It can be seen that very complex interactions exists between the main and secondary columns.
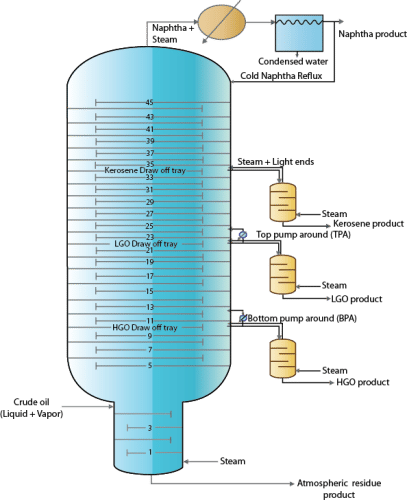
Figure 5.2: Design architecture of main and secondary columns of the CDU.
|
69 videos|121 docs
|
FAQs on Crude Distillation - Chemical Technology - Chemical Engineering
| 1. What is crude distillation? |  |
| 2. How does crude distillation work? |  |
| 3. What are the main fractions obtained from crude distillation? |  |
| 4. What factors affect crude distillation? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges in crude distillation? |  |






















