Crystallization process - Class 7 PDF Download
Define the crystallization methods of separation of mixture with an example each ?
Ref: https://edurev.in/question/619987/Define-the-crystallization-methods-of-separation-of-mixture-with-an-example-each-
Crystallization is a technique used for the purification of substances. A separation technique to separate solids from a solution.
On adding a solid substance in a liquid and stirring it, the solid dissolves in the fluid. But when added more and more solid to the liquid, a point comes after which no more solid dissolves in the liquid. This point is called saturation point and the fluid is called saturation solution.
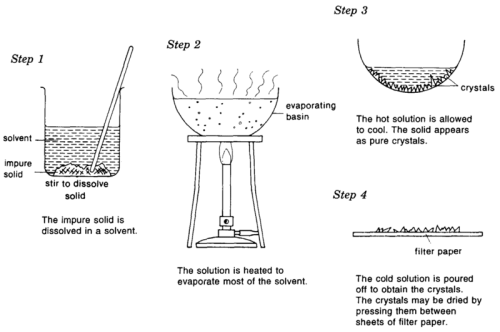
Crystallization process
- The solution is heated in an open container
- The solvent molecules start evaporating, leaving behind the solutes
- When solution cools, crystals of solute start accumulating on the surface of the solution
- Crystals are collected and dried as per the product requirement
- The undissolved solids in the liquid are separated by the process of filtration
- The size of crystals formed during this process depends on the cooling rate.
- Large number of tiny crystals are formed, if the solution is cooled at a fast rate
- Large crystals are formed at slow cooling rates
Separation technique of substance by Crystallization
Activity:
Here is an experiment to understand crystallization clearly:
Step 1: Take 50 ml water in a beaker
Step 2: Add sugar in it and stir it
Step 3: Now heat the solution
Step 4: Repeat the process continuously
Step 5: After some time there will be a point at which no more sugar can be dissolved in water. This stage is the saturation point, and the solution is referred as a saturated solution
Step 6 : Now filter the sugar with the help of a filter paper
Step 7: Collect the filtrate in a glass bowl and cool it
Step 8: We will observe that some fine crystals are formed in the bowl
Step 9: The process of filtration can separate these crystals. The liquid left after the removal of crystals is known as mother liquor
Application of crystallization:
- Purification of seawater
- Separation of alum crystals from impure samples
- In the pharmaceutical industry, crystallization is used as a separation and purification process for the synthesis and isolation of co-crystals, pure active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), controlled release pulmonary drug delivery, and separation of chiral isomers.
FAQs on Crystallization process - Class 7
| 1. What is crystallization? |  |
| 2. How does the crystallization process work? |  |
| 3. Why is crystallization important? |  |
| 4. What factors can influence the crystallization process? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of crystallization in daily life? |  |

















