DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 2 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
Objective Questions (Level 2)
Single Correct Option
Ques 1: When a man moves down the inclined plane with a constant speed 5 ms-1 which makes an angle of 37° with the horizontal, he finds that the rain is falling vertically downward. When he moves up the same inclined plane with the same speed, he finds that the rain makes an angle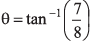 with the horizontal. The speed of the rain is
with the horizontal. The speed of the rain is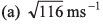
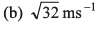
(c) 5 ms-1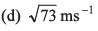
Ans: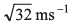
Sol: Applying sine for mula in Δ AOB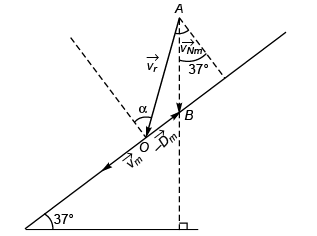
Applying sine formula in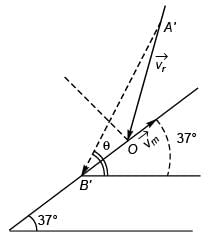
Δ AOB'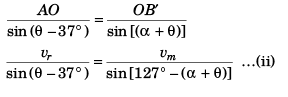
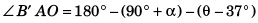
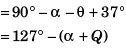
Comparing Eqs. (i) and (ii)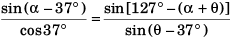
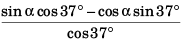
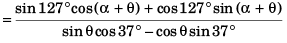
sin α - cos α tan 37°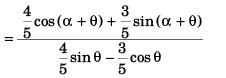
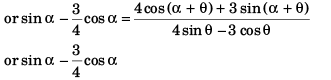
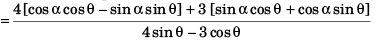
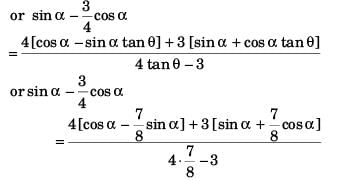
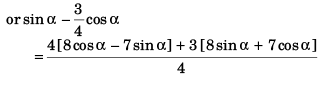
or 4 sin α - 3 cos α = 32 cos α - 28 sin α + 24 sin α + 21 cos α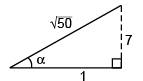
or 32 cos α + 21 cos α + 3 cos α = 28 sin α - 24 sin α + 4 sin α
or 56 cos α = 8 sin α
tan α = 7/1
From Eq. (i)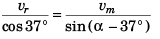
∴ 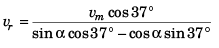
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 2: Equation of motion of a body is dv/dt = -4v + 8 where v is the velocity in ms-1 and t is the time in second.
Initial velocity of the particle was zero. Then
(a) the initial rate of change of acceleration of the particle is 8 ms-2
(b) the terminal speed is 2 ms-1
(c) Both (a) and (b) are correct
(d) Both (a) and (b) are wrong
Ans: the terminal speed is 2 ms-1
Sol: 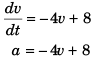
At the time the body acquires terminal speed its acceleration (a) must be zero.
Thus
- 4v + 8 = 0
v = 2 m/s
Terminal speed = 2 m/s.
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 3: Two particles A and B are placed in gravity free space at (0, 0, 0)m and (30, 0, 0)m respectively. Particle A is projected with a velocity 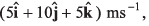 while particle B is projected with a velocity
while particle B is projected with a velocity 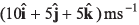
simultaneously. Then
(a) they will collide at (10, 20, 10)m
(b) they will collide at (10, 10, 10) m
(c) they will never collide
(d) None of the above
Ans: they will never collide
Sol: Particles will collide if
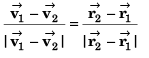
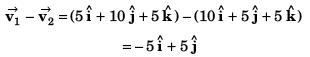
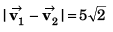
∴ 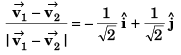
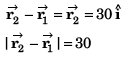
∴ 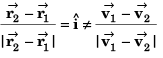
∴ Option (c) is correct.
Ques 4: Velocity of the river with respect to ground is given by v0. Width of the river is d. A swimmer swims (with respect to water) perpendicular to the current with acceleration a = 2t (where t is time) starting from rest from the origin O at t = 0. The equation of trajectory of the path followed by the swimmer is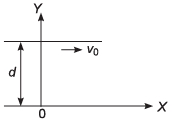
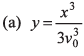
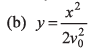
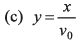
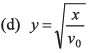
Ans: 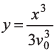
Sol: Displacement along y-axis at time t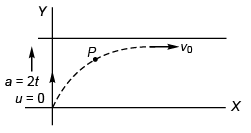
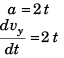
or ∫ dvy = ∫ 2t dt
or vy = t2 + C1
At t = 0, vy = 0 (given)
∴ C1 = 0
∴ vy = t2
⇒ 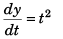
or ∫ dy = ∫ t2 + C2
or 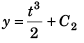
At t = 0, Y = 0 (given)
∴ 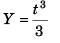 …(i)
…(i)
Displacement along x-axis at time t:
x = v0t
or 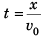
Substituting above value of t in Eq. (i)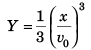
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 5: The relation between time t and displacement x is t = αx2 + βx where α and β are constants. The retardation is
(a) 2αv3
(b) 2βv3
(c) 2αβv3
(d) 2β2v3
Ans: 2αv3
Sol: t = ax2 + bx
Differentiating w.r.t. time t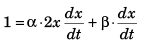
or v (β + 2α × x ) = 1
or v = (β + 2α × x )-1
∴ 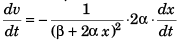
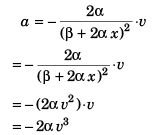
∴ Retardation = 2αv3
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 6: A street car moves rectilinearly from station A to the next station B with an acceleration varying according to the law f = a — bx, where a and b are constants and x is the distance from station A. The distance between the two stations and the maximum velocity are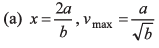
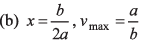
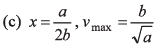
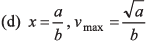
Ans: 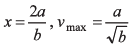
Sol: f = a - bx
∴ 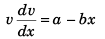
or
or
As at x = 0 car is at rest C = 0
∴ 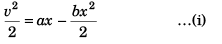
For v to be maximum.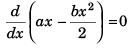
i.e., a - bx = 0
or x = a/b
Substituting x = a/b in Eq. (i),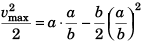
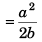
∴ 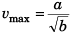
Car will come to rest when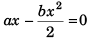
x = 2a/b
∴ Distance between two stations = 2a/b
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 7: A particle of mass m moves on positive x-axis under the influence of force acting towards the origin given by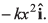 If the particle starts from rest at x = a, the speed it will attain when it crosses the origin is
If the particle starts from rest at x = a, the speed it will attain when it crosses the origin is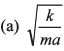
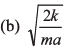
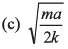
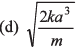
Ans: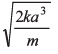
Sol: Force = - kx2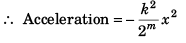
⇒ 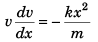
or 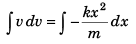
or 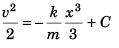
Now at x = a, v = 0
∴ 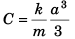
Thus 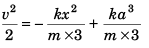
∴ Velocity at x = 0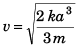
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 8: A particle is moving mX-Y plane such that vx = 4 + 4t and vy = 4t. If the initial position of the particle is (1, 2). Then the equation of trajectory will be
(a) y2 = 4x
(b) y = 2x
(c) x2 = y/2
(d) None of these
Sol: 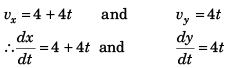
or ∫ dx = ∫(4 + 4t) dt
and ∫ dy = ∫ 4t dt
or x = 4t + 2t2 + C1
∴ C1 = 1
Thus x = 4t + 2t2 + 1 …(i)
and y = 2t2 + C2
At t = 0 x = 1
and at t = 0, y = 2
∴ C2 = 0
Thus y = 2t2 + 2 …(ii)
Substituting value of t in Eq. (i) in terms of y using Eq. (ii) we won’t get relationship as mentioned in option (a), (b) or (c).
∴ Option (d) is correct.
Ques 9: A particle is moving along a straight line whose velocity-displacement graph is as shown in the figure. What is the magnitude of acceleration when displacement is 3 m?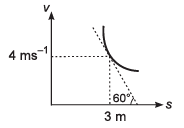
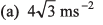
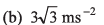
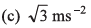
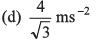
Ans: 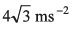
Sol:
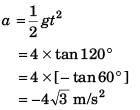
∴ Magnitude of acceleration 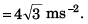
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 10: A particle is falling freely under gravity. In first t second it covers distance x1 and in the next t second it covers distance x2, then t is given by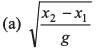
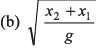
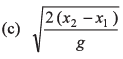
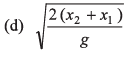
Ans: 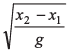
Sol: 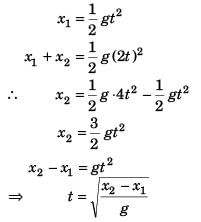
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 11: A rod AB is shown in figure. End A of the rod is fixed on the ground. Block is moving with velocity 2 ms-1 towards right. The vertical com ponent of velocity of end B of rod at the instant shown in figure is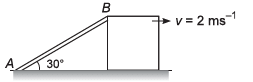
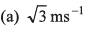
(b) 2 ms-1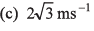
(d) 4 ms-1
Ans: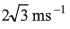
Sol: y2 + x2 = l2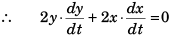
or 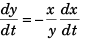
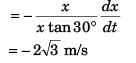
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 12: A thief in a stolen car passes through a police check post at his top speed of 90 kmh-1. A motorcycle cop, reacting after 2 s, accelerates from rest at 5 ms-2. His top speed beingl 08 kmh-1. Find the maximum separation between policemen and thief.
(a) 112.5 m
(b) 115 m
(c) 116.5 m
(d) None of these
Ans: 112.5 m
Sol: Maximum separation (xmax) between the police and the thief will be at time t (shown in figure)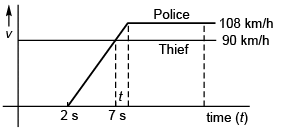
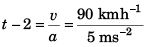
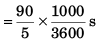
i.e., t = 7 s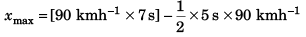
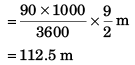
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 13: Sachin (S) hits a ball along the ground with a speed u in a direction which makes an angle 30° with the line joining him and the fielder Prem (P). Prem runs to intercept the ball with a speed 2u/3. At what angle θ should he run to intercept the ball ?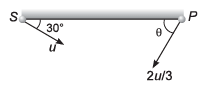
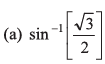
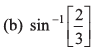
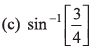
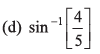
Ans: 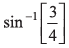
Sol: If meeting time is t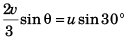
i.e., sin θ = 3/4
or 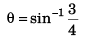
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 14: A car is travelling on a straight road. The maximum velocity the car can attain is 24 ms-1. The maximum acceleration and deceleration it can attain are 1 ms-2 and 4 ms-2 respectively. The shortest time the car takes from rest to rest in a distance of 200 m is,
(a) 22.4 s
(b) 30 s
(c) 11.2s
(d) 5.6 s
Ans: 22.4 s
Sol: 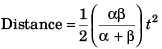
∴ 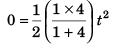
⇒ 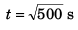
= 22.36 s
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 15: A car is travelling on a road. The maximum velocity the car can attain is 24 ms 1 and the maximum deceleration is 4 ms-2. If car starts from rest and comes to rest after travelling 1032 m in the shortest time of 56 s, the maximum acceleration that the car can attain is
(a) 6 ms-2
(b) 1.2 ms-2
(c) 12 ms-2
(d) 3.6 ms-2
Ans: 1.2 ms-2
Sol: Let BC = t'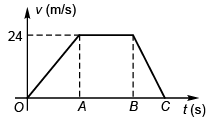
∴ 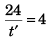
⇒ t' = 6 s
∴ OB = 50 s
Let OA = t
∴ AB = 56 - t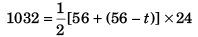
⇒ t = 20 s
∴ maximum acceleration 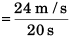
= 1.2 m/s2
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 16: Two particles are moving along two long straight lines, in the same plane with same speed equal to 20 cms-1. The angle between the two lines is 60° and their intersection point is O. At a certain moment, the two particles are located at distances 3m and 4m from O and are moving towards O. Subsequently, the shortest distance between them will be
(a) 50 cm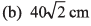
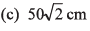
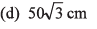
Ans: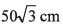
Sol: From Δ OAB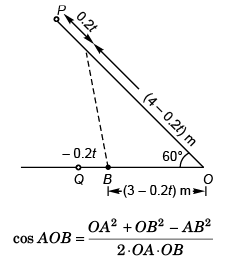
∴ OA2 + OB2 - AB2 = OA × OB
i.e., AB2 = OA2 + OB2 - OA × OB
= (4 - 0.2t)2 + (3 - 0.2t)2 + (4 - 0.2t) (3 - 0.2t)
or AB2 = 16 + 0.04t2 - 1.6t + 9 + 0.04t2 - 1.2t + 12 - 1.4t + 0.04t2
or AB2 = 0.12t2 - 4.2t + 37
For AB to be minimum
0.24t - 4.2 = 0
or t = 17.5 s
∴ (AB)2min = 0.12(17.5)2 - 4.2 × (17.5) + 37
= 36.75 - 73.5 + 37
(AB)2min = 0.75 m2
= 7500 cm2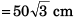
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 17: An elevator without a ceiling is ascending up with an acceleration of 5 ms-2. A boy on the elevator shoots a ball in vertical upward direction from a height of 2 m above the floor of elevator. At this instant the elevator is moving up with a velocity of 10 ms-1, and floor of the elevator is at a height of 50 m from the ground. The initial speed of the ball is 15 ms-1 with respect to the elevator. Consider the duration for which the ball strikes the floor of elevator in answering following questions, (g = 10 ms-2)
The time in which the ball strikes the floor of elevator is given by
(a) 2.13 s
(b) 2.0 s
(c) 1.0 s
(d) 3.12 s
Ans: 2.13 s
Sol: Velocity of ball w.r.t. elevator = 15 m/s
Acceleration of ball w.r.t. elevator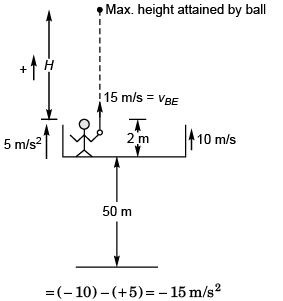
Final displacement of ball w.r.t. elevator = - 2m
∴ 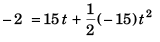
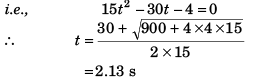
= 2.13 s
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 18: An elevator without a ceiling is ascending up with an acceleration of 5 ms-2. A boy on the elevator shoots a ball in vertical upward direction from a height of 2 m above the floor of elevator. At this instant the elevator is moving up with a velocity of 10 ms-1, and floor of the elevator is at a height of 50 m from the ground. The initial speed of the ball is 15 ms-1 with respect to the elevator. Consider the duration for which the ball strikes the floor of elevator in answering following questions, (g = 10 ms-2)
The maximum height reached by ball, as measured from the ground would be
(a) 73.65 m
(b) 116.25 m
(c) 82.56 m
(d) 63.25 m
Ans: 82.56 m
Sol: Velocity of ball w.r.t. ground (vBE)
= (15 + 10) m/s
= 25 m/s
Now v2 = u2 + 2as
∴ 02 = (25)2 + 2(- 10) H
or H = 31.25 m
Maximum height by ball as measured from ground = 31.25 + 2 + 50
= 83.25 m
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 19: An elevator without a ceiling is ascending up with an acceleration of 5 ms-2. A boy on the elevator shoots a ball in vertical upward direction from a height of 2 m above the floor of elevator. At this instant the elevator is moving up with a velocity of 10 ms-1, and floor of the elevator is at a height of 50 m from the ground. The initial speed of the ball is 15 ms-1 with respect to the elevator. Consider the duration for which the ball strikes the floor of elevator in answering following questions, (g = 10 ms-2)
Displacement of ball with respect to ground during its flight would be
(a) 16.25 m
(b) 8.76 m
(c) 20.24 m
(d) 30.56 m
Ans: 30.56 m
Sol: Displacement of ball w.r.t. ground during its flight = H = 31.25 m
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 20: An elevator without a ceiling is ascending up with an acceleration of 5 ms-2. A boy on the elevator shoots a ball in vertical upward direction from a height of 2 m above the floor of elevator. At this instant the elevator is moving up with a velocity of 10 ms-1, and floor of the elevator is at a height of 50 m from the ground. The initial speed of the ball is 15 ms-1 with respect to the elevator. Consider the duration for which the ball strikes the floor of elevator in answering following questions, (g = 10 ms-2)
The maximum separation between the floor of elevator and the ball during its flight would be
(a) 12 m
(b) 15 m
(c) 9.5 m
(d) 7.5 m
Ans: 12 m
Sol: Displacement of ball w.r.t. floor of elevator at time t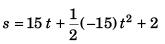
will be maximum, when
ds/dt = 0
i.e., 15 - 15t = 0
i.e., t = 1s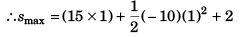
= 12 m
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 21: A situation is shown in which two objects A and B start their motion from same point in same direction. The graph of their velocities against time is drawn. uA and uB are the initial velocities of A and B respectively. T is the time at which their velocities become equal after start of motion. You can not use the data of one question while solving another question of the same set. So all the questions are independent of each other.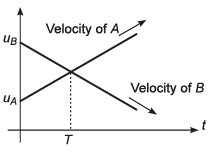
If the value of T is 4 s, then the times after which A will meet B is
(a) 12 s
(b) 6 s
(c) 8 s
(d) data insufficient
Ans: 8 s
Sol: Let the particles meet at time t
i.e., displacement of the particles are equal and which is possible when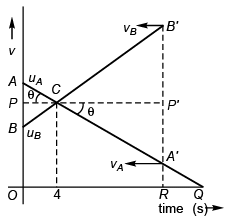
Area of Δ ACB = Area of Δ A' B' C
[Area OBCA' θO being common]
or Area of Δ APC = Area A' P' C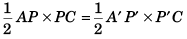
or AP × PC = A' P' × P' C
or (PC tan θ) PC = (P' C tan θ) P' C
or PC = P' C'
∴OR = PC + P' C' = 2 PC = 8 s.
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 22: A situation is shown in which two objects A and B start their motion from same point in same direction. The graph of their velocities against time is drawn. uA and uB are the initial velocities of A and B respectively. T is the time at which their velocities become equal after start of motion. You can not use the data of one question while solving another question of the same set. So all the questions are independent of each other.
Let vA and vB be the velocities of the particles A and B respectively at the moment A and B meet after start of the motion. If uA = 5 ms-1 and uB = 15 ms-1 , then the magnitude of the difference of velocities vA and vB is
(a) 5 ms-1
(b) 10 ms-1
(c) 15 ms-1
(d) data insufficient
Ans: 10 ms-1
Sol: Area of Δ A' B' O = Area of Δ ABO
∴ 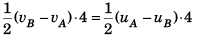
i.e., vB - vA = uA - uB
= 5 - 15 = - 10
⇒ vA - vB = 10 ms-1
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 23: A situation is shown in which two objects A and B start their motion from same point in same direction. The graph of their velocities against time is drawn. uA and uB are the initial velocities of A and B respectively. T is the time at which their velocities become equal after start of motion. You can not use the data of one question while solving another question of the same set. So all the questions are independent of each other.
After 10 s of the start of motion of both objects A and B, find the value of velocity of A if uA = 6 ms-1, uB = 12 ms-1 and at T velocity of A is 8 ms-1 and T = 4 s
(a) 12 ms-1
(b) 10 ms-1
(c) 15 ms-1
(d) None of these
Sol: uA = 6 ms-1, uB = 12 ms-1
and at t = 4 s common velocity = 8 ms-1
To find velocity of A at t = 10 s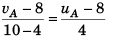
or 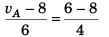
∴ vA = 5 ms-1
Option (d) is correct.
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 2 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is motion in one dimension? |  |
| 2. What is the JEE Advanced exam? |  |
| 3. Who is DC Pandey? |  |
| 4. What are the solutions provided by DC Pandey's book for JEE Advanced? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to motion in one dimension in the JEE Advanced exam? |  |





















