DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 3 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
More than One Correct Options
Ques 1: particle having a velocity v = v0 at t = 0 is decelerated at the rate 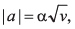 where α is a positive constant.
where α is a positive constant.
(a) The particle comes to rest at 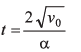
(b) The particle will come to rest at infinity.
(c) The distance travelled by the particle before coming to rest is 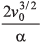
(d) The distance travelled by the particle before coming to rest is 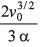
Ans: (a, d)
Sol: ∵ 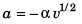 …(i)
…(i)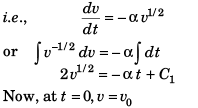
∴ 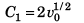
⇒ 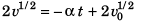
i.e., the particle will stop at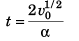
Option (a) is correct.
Option (b) is incorrect.
From Eq. (i),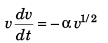
or 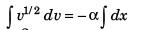
or 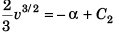
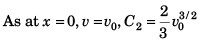
∴ 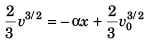
i.e., when the particle stops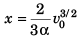
Option (d) is correct.
Option (c) is incorrect.
Ques 2: At time t = 0, a car moving along a straight line has a velocity of 16 ms-1. It slows down with an acceleration of - 0.5t ms-2, where t is in second. Mark the correct statement (s).
(a) The direction of velocity changes at t = 8 s
(b) The distance travelled in 4 s is approximately 58.67 m
(c) The distance travelled by the particle in 10 s is 94 m
(d) The speed of particle at t = 10 s is 9 ms-1
Ans: (all)
Sol: a = - 0.5 t (m/s2)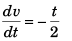
or 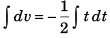
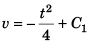
At t = 0, v = 16 m/s
∴ 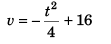 …(i)
…(i)
From above relation v is zero at t = 8 s
Options (a) is correct.
From relation (i),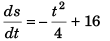
∴ 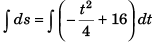
i.e., 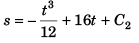
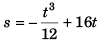 [As at t = 0, s = 0]
[As at t = 0, s = 0]
At t = 4 s
s = 58.67 m
Option (b) is correct.
The particle returns back at t = 8 s
From relation (ii)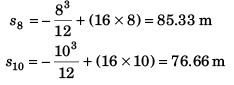
Distance travelled in 10 s
= s8 + (s8 - s10) = (2 x 85.33 ) - 76.66
= 94 m
Option (c) is correct.
Velocity of particle at t = 10 s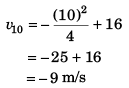
∴Speed of particle at t = 10 s is 9 m/s.
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 3: An object moves with constant acceleration 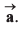 Which of the following expressions are also constant ?
Which of the following expressions are also constant ?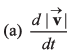
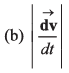
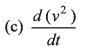
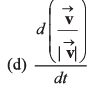
Ans: (b)
Sol: 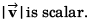
∴ Option (a) is incorrect.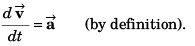
∴ Option (b) is correct.
v2 is scalar.
∴ Option (c) is incorrect.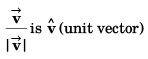
∴ 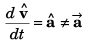
∴ Option (d) is incorrect.
Ques 4: Ship A is located 4 km north and 3 km east of ship B. Ship A has a velocity of 20 kmh-1 towards the south and ship B is moving at 40 kmh-1 in a direction 37° north of east. X and 7-axes are along east and north directions, respectively
(a) Velocity of A relative to B is 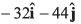
(b) Position of A relative to B as a function of time is given by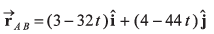
(c) Velocity of A relative to B is 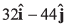
(d) Position of A relative to B as a function of time is given by 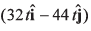
Ans: (a, b)
Sol: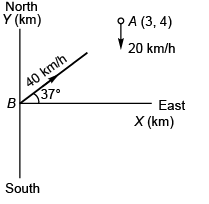
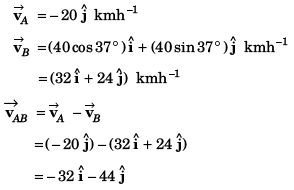
Option (a) is correct.
Option (c) is incorrect.
At any time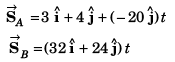
Position of A relative to B: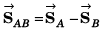
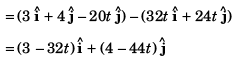
Option (b) is correct.
Option (d) is incorrect.
Ques 5: Starting from rest a particle is first accelerated for time t1 with constant acceleration a1 and then stops in time t2 with constant retardation a2. Let v1 be the average velocity in this case and s1 the total displacement. In the second case it is accelerating for the same time tx with constant acceleration 2a1 and come to rest with constant retardation a2 in time t3. If v2 is the average velocity in this case and s2 the total displacement, then
(a) v2 = 2v1
(b) 2v1 < v2 < 4v1
(c) s2 = 2s1
(d) 2s1 <s2 < 4s1
Ans: (a, d)
Sol: Case I.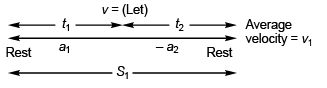
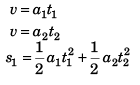
Case II.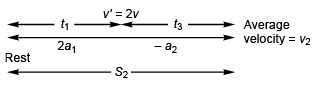
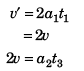
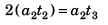
⇒ 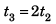
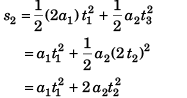
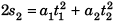
∴ 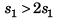 …(i)
…(i)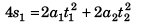
∴ 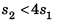 …(ii)
…(ii)
Combining Eqs. (i) and (ii),
2s1 < s2 < 4s1
Option (d) is correct.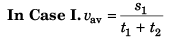
i.e., 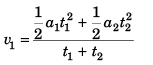
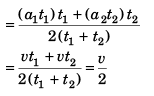
In Case II.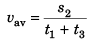
i.e., 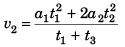
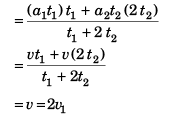
Option (a) is correct.
Option (b) is incorrect.
Ques 6: A particle is moving along a straight line. The displacement of the particle becomes zero in a certain time (t > 0) The particle does not undergo any collision.
(a) The acceleration of the particle may be zero always
(b) The acceleration of the particle may be uniform
(c) The velocity of the particle must be zero at some instant
(d) The acceleration of the particle must change its direction
Ans: (b, c)
Sol: If the particle’s initial velocity is + ive and has some constant - ive acceleration the particle will stop somewhere and then return back to have zero displacement at same time t (> 0).
Also if particle’s initial velocity is - ive and has some constant + ive acceleration the particle will stop somewhere and then return back to have zero displacement at same time t (> 0).
∴ Options (b) and (c) are correct.
and options (a) and (d) are incorrect.
Ques 7: A particle is resting over a smooth horizontal floor. At t = Q a horizontal force starts acting on it. Magnitude of the force increases with time according to law F = at, where a is a positive constant. From figure, which of the following statements are correct ? 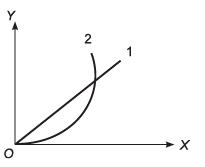
(a) Curve 1 can be the plot of acceleration against time
(b ) Curve 2 can be the plot of velocity against time
(c) Curve 2 can be the plot of velocity against acceleration
(d) Curve 1 can be the plot of displacement against time
Ans: (a, b)
Sol: F = α t
⇒ ma = α t
or 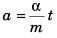 …(i)
…(i)
∴ Graph between a (acceleration) and time (t) will be as curve 1.
∴ Option (a) is correct.
From equation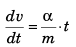
∴ 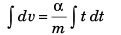
i.e., 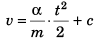
∴ Graph between velocity (v) and time (t) will be as curve 2.
Option (b) is correct.
Ques 8: A train starts from rest at S = 0 and is subjected to acceleration as shown
(a) velocity at the end of 10 m displacement is 20 ms-1
(b) velocity of the train at S = 10m is 10 ms-1
(c) The maxim um velocity attained b y train is 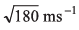
(d) The maximum velocity attained by the train is 15 ms-1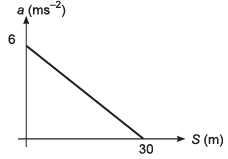
Ans: (b, c)
Sol: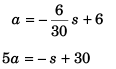
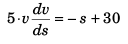
or 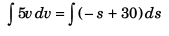
or 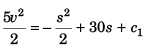
or 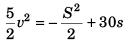 …(i)
…(i)
[C1 = 0 as at s = 0 particle is at rest]
Substituting s = 10 m in Eq. (i),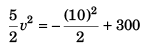
i.e., v = 10 m/s
∴ Option (b) is correct.
From Eq. (i) v to be maximum
- s + 30 = 0
s = 30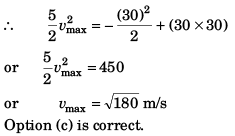
Ques 9: For a moving particle which of the following options may be correct?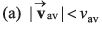
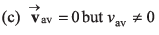
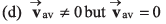
Ans: (a, c)
Sol: If particle’s path is
(i) straight with backward motion
(ii) not straight somewhere.
Distance moved will be greater than the modulus of displacement
∴ 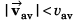
Option (a) is correct.
If particle returns to its initial position, the value of 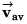 will be zero while its average speed (vav) will not be zero.
will be zero while its average speed (vav) will not be zero.
∴ Option (c) is correct.
Ques 10: Identify the correct graph representing the motion of a particle along a straight line with constant acceleration.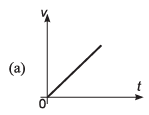
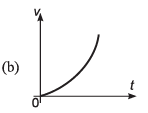
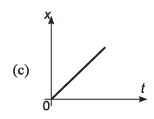
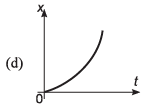
Ans: (a, d)
Sol: If u = 0, v = at and 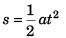
∴ v-t graph will be as shown in (a).
s-t graph will be as shown in (d).
Ques 11: A man who can swim at a velocity v relative to water wants to cross a river of width b, flowing with a speed u.
(a) The minimum time in which he can cross the river is b/v
(b) He can reach a point exactly opposite on the bank in time 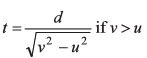
(c) He cannot reach the point exactly opposite on the bank if u > v
(d) He cannot reach the point exactly opposite on the bank if v > u
Ans: (a, b, c)
Sol: Swimmer will reach point B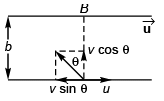
if v sin θ = u
i.e., v > u
Option (c) is correct.
Time to cross the river
Option (b) is correct.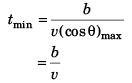
Option (a) is correct.
Ques 12: The figure shows the velocity (v) of a particle plotted against time (t).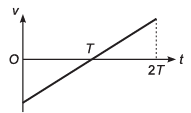
(a) The particle changes its direction of motion at some points
(b) The acceleration of the particle remains constant
(c) The displacement of the particle is zero
(d) The initial and final speeds of the particle are the same
Ans: (all)
Sol: At time T, particle’s velocity change from –ive to + ive.
Option (a) is correct.
As slope v-t is same throughout, particle’s acceleration is constant.
Option (b) is correct.
As net area under the curve is zero.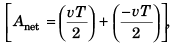 displacement of particle at time 2T is zero.
displacement of particle at time 2T is zero.
Option (c) is correct.
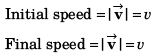
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 13: The speed of a train increases at α constant rate a from zero to v and then remains constant for an interval and finally decreases to zero at a constant rate β. The total distance travelled by the train is l. The time taken to complete the journey is t. Then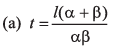
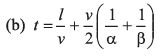
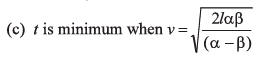
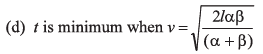
Ans: (b, d)
Sol: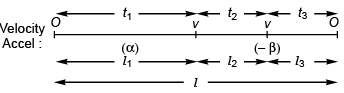
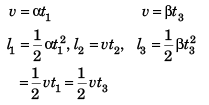
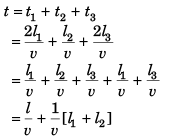
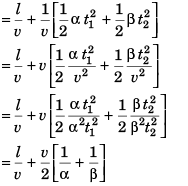
Option (b) is correct.
For t to be minimum.
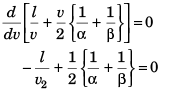
or 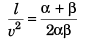
or 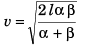
Option (d) is correct.
Ques 14: A particle moves in x-y plane and at time t is at the point (t2, t3 - 2t), then which of the following is/are correct?
(a) At t = 0, particle is moving parallel to y-axis
(b) At t = 0, direction of velocity and acceleration are perpendicular.
(c) 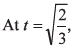 particle is moving parallel to x-axis.
particle is moving parallel to x-axis.
(d) At t = 0, particle is at rest.
Ans: (a, b, c)
Sol: 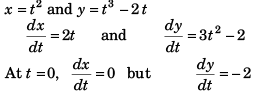
∴ at t = 0 particle is moving parallel to y-axis.
Option (a) is correct.
Option (d) is incorrect.
At t = 0, 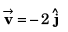
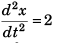
and 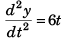
At t = 0, 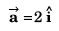
i.e., 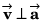
Option (b) is correct.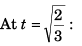
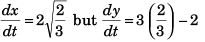
∴ Particle is moving parallel to x-axis.
Option (c) is correct.
Ques 15: A car is moving with uniform acceleration along a straight line between two stops X and Y. Its speed at X and 7 are 2 ms-1 and 14 ms-1, Then
(a) its speed at mid-point of X Y is 10 ms-1
(b) its speed at a point A such that XA : AY = 1 : 3 is 5 ms-1
(c) the time to go from X to the mid-point of X Y is double o f that to go from mid-point to Y
(d) the distance travelled in first half of the total time is half of the distance travelled in the second half of the time
Ans: (a, c)
Sol: 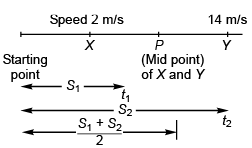
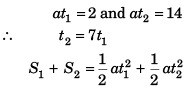
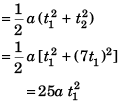
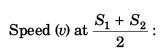
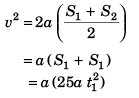
∴ v = 5a t1
or v = 10 m/s
Option (a) is correct.
Time t to reach P from T
10 = 2 + at
⇒ 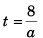 …(i)
…(i)
Time t' to reach Y from P
14 = 10 + at'
∴ 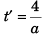 …(ii)
…(ii)
Comparing Eq. (i) and Eq. (ii),
t = 2t'
Option (c) is correct.
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Advance): Motion in One Dimension- 3 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. How to solve problems related to motion in one dimension in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between distance and displacement in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 3. How can you determine the average velocity in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 4. What is instantaneous velocity in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 5. How can you determine the acceleration in one-dimensional motion? |  |
















