DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Projectile Motion- 1 | DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics PDF Download
Subjective Questions (Level 1)
Projectile Motion from Ground to Ground
Ques 1: A particle is projected from ground with initial velocity u = 20√2 m/s at θ = 45°.
Find: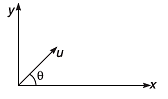
(a) R, Hand T,
(b) velocity of particle after 1 s
(c) velocity of particle at the time of collision with the ground (x-axis).
Ans: (a) 80 m, 20 m, 4 s Sol:
Sol: 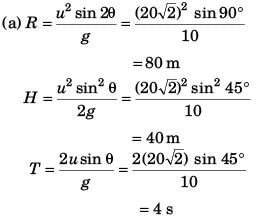
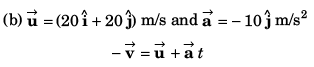
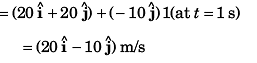
(c) Time of flight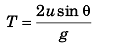
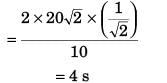
(c) ∴ Velocity of particle at the time of collision with ground.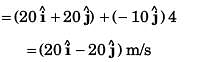
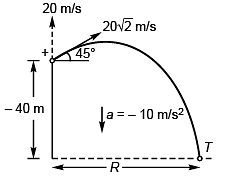
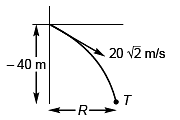
Ques 2: In the figures shown, three particles are thrown from a tower of height 40 m as shown in figure. In each case find the time when the particles strike the ground and the distance of this point from foot of tower.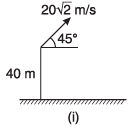
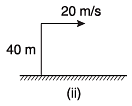
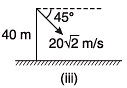
Ans: 5.46 s, 2.83 s, 1.46 s, 109.2 m, 56.6 m, 29.2 m
Sol: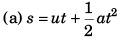
∴ 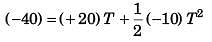
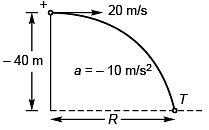
or 5T2 - 20T - 40 = 0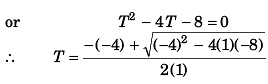
Leaving - ive sign which is not positive.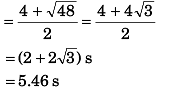
R = 20 x 5.46 = 109.2 m 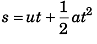
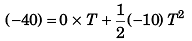
⇒ 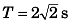
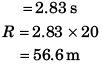
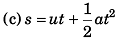
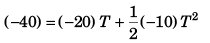
or 5T2 + 20T - 40 = 0
or T2 + 4T - 8 = 0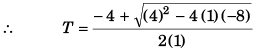
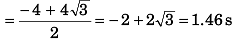
∴ R = 20 x 1.46
= 29.2 m
Ques 3: A particle is projected from ground at angle 45° with initial velocity 20√2 m/s.
Find:
(a) change in velocity,
(b) magnitude of average velocity in a time interval from t = 0 to t = 3 s.
Ans: (a) 30 ms-1 (vertically downwards)
(b) 20.62 ms-1
Sol: (a) Change in velocity (vc) = Change in vertical velocity
(as horizontal velocity does not change).
= (u sin θ - gt) - (u sin θ)
= - gt = - (10 x 3) m/s
= - 30 m/s
= 30 m/s (downward)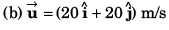
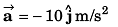
∴ Displacement at time t (= 3 s)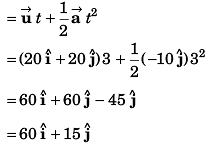
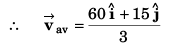
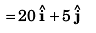
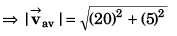
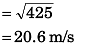
Ques 4: The coach throws a baseball to a player with an initial speed of 20 m/s at an angle of 45° with the horizontal. At the moment the ball is thrown, the player is 50 m from the coach. At what speed and in what direction must the player run to catch the ball at the same height at which it was released? (g = 10 m/s2)
Ans: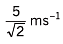
Sol: R + vT = 50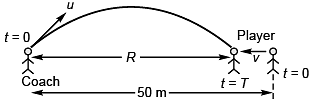
⇒ 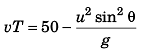
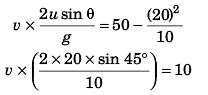
∴ 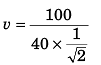
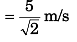
Ques 5: At time t = 0 a small ball is projected from point A with a velocity of 60 m/s at 60° angle with horizontal. Neglect atmospheric resistance and determine the two times t1 and t2 when the velocity of the ball makes an angle of 45° with the horizontal x-axis.
Ans: t1= 2.19 s, t2 = 8.20 s
Sol: Horizontal compnent of velocity at
P = Horizontal component of velocity at O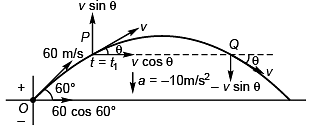
∴ v cos θ = 60 cos 60°
⇒ v cos 45° = 60 cos 60°
⇒ 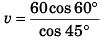
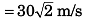
For point P:
v sin 45° = 60 sin 60° + (-10) t1
or 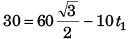
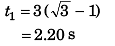
For point Q:
- v sin 45° = 60 sin 60° + (-10) t2
∴ t2 = 3 (√3 + 1)
= 8.20 s
Ques 6: A particle moves in the xy-plane with constant acceleration a directed along the negative y-axis. The equation of path of the particle has the form y = bx - cx2, w here b and c are positive constants. Find the velocity of the particle at the origin of coordinates.
Ans: 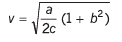
Sol: Y = bx - cx2
Differentiating above equation w.r.t. time t
∴ 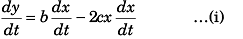
⇒ 
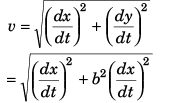
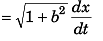 …(ii)
…(ii)
Differentiating Eq. (i) w.r.t. time t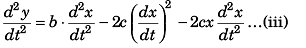
Acceleration of particle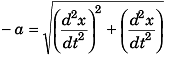
∴ 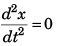
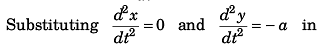
Eq. (iii)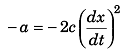
i.e., 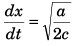
Substituting above value of 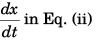
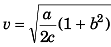
Ques 7: A ball is shot from the ground into the air. At a height of 9.1 m, its velocity is observed to be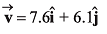 in metre per second
in metre per second
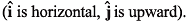
Give the approximate answers.
(a) To what maximum height does the ball rise?
(b) What total horizontal distance does the ball travel?
What are:
(c) the magnitude and
(d) the direction of the ball’s velocity just before it hits the ground?
Ans: (a) 11 m
(b) 23 m
(c) 16.6 ms-1
(d) tan-1
(2) below horizontal
Sol: 
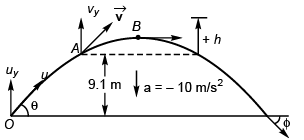
∴ Initial vertical velocity at 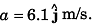
Final vertical velocity at B (highest point)
= 0 m/s
Using v2 = u2 + 2as (Between A and B)
02 = (6.1)2 + 2 (-10) (+ h)
⇒ 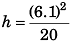
= 1.86 m
∴ Maximum height attained by ball
= 9.1 + 1.86
= 10.96 m
(b) Let magnitude of vertical velocity at O (point of projection) = uy
Using v2 = u2 + 2as (Between O and A)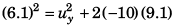
⇒ 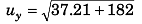
= 14.8
Angle of projection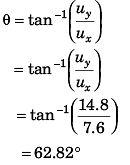
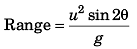
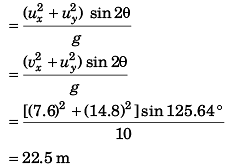
(c) Magnitude of velocity just before the ball hits ground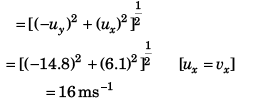
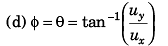
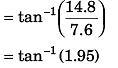
Ques 8: Two particles move in a uniform gravitational field with an acceleration g. At the initial moment the particles were located over a tower at one point and moved with velocities = 3 m/s v1 and v2 = 4 m/s horizontally in opposite directions. Find the distance between the particles at the moment when their velocity vectors become mutually perpendicular.
Ans: 2.5 m
Sol: As initial vertical velocities of both particles will be zero and both fall under same acceleration (g), at anytime t, the vertical displacement of both will be same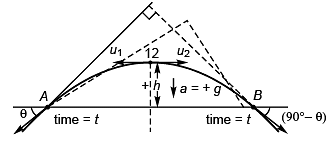
i.e., both will always remain in the same horizontal line as shown in figure.
At time t:
Vertical velocity of A
= Vertical velocity of B
= 0 + (+ g) t
= gt
At A: 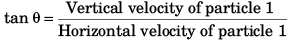
or 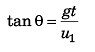 …(i)
…(i)
At B:
or 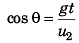 …(ii)
…(ii)
Multiplying Eq. (i) by Eq. (ii),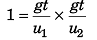
∴ 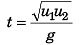
Distance between A and B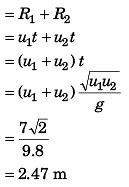
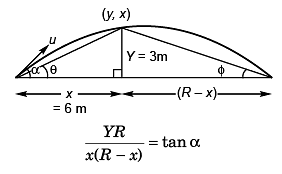
Ques 9: A ball is thrown from the ground to clear a wall 3 m high at a distance of 6 m and falls 18m away from the wall. Find the angle of projection of ball.
Ans: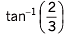
Sol: 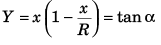
or 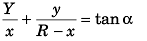
or tan θ + tan φ = tan α
(Students to remember this formula)
⇒ 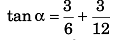
= 9/12
⇒ 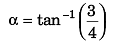
Ques 10: A particle is projected with velocity 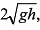 so that it just clears two walls of equal height h which are at a distance of 2h from each other. Show that the time of passing between the walls is
so that it just clears two walls of equal height h which are at a distance of 2h from each other. Show that the time of passing between the walls is 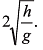
[Hint: First find velocity at height h. Treat it as initial velocity and 2h as the range.]
Sol: On the trajectory there be two points P and Q at height h from ground.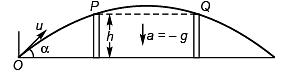
If particle takes t time to reach point A
(i.e., vertical displacement of + h)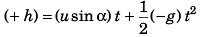
or gt2 - 2 (u sin α) t + 2h = 0 …(i)
The above equation is quadratic in t. Two values of t will satisfy Eq. (i). One having lower value will be time (= t1) to reach point P while the higher value will be the time (= t2) to reach point Q.
∴ Time to reach point Q from point P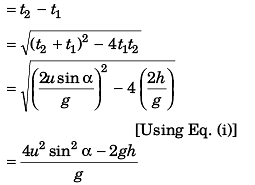
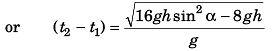
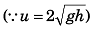
Distance between P and Q:
2h = (u cos α) (t2 - t1)
∴ 4 h2 = u2 cos2 α (t2 - t1)2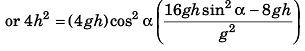
or 1 = cos2 (16 sin2 α - 8)
or 1 = cos2 α [16 (1 - cos2 α) - 8]
or 1 = cos2 α [8 - 16 cos2 α]
or 16 cos4 α - 8 cos2 α + 1 = 0
⇒ (4 cos2 α - 1)2 = 0
⇒ 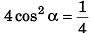
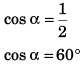
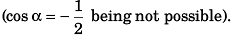
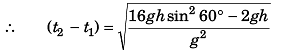
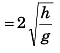 (Proved)
(Proved)
Ques 11: A particle is projected at an angle of elevation α and after t second it appears to have an elevation of β as seen from the point of projection. Find the initial velocity of projection.
Ans: 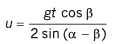
Sol: Initial vertical velocity = u sin α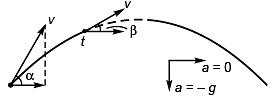
At time t vertical velocity = v sin β
∴ v sin β = u sin α = (- g) t …(i)
Now, as horizontal acceleration will be zero.
v cos β = u cos α
Thus, Eq. (i) becomes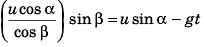
or u sin α cos β - u cos α sin β = gt cos β
or 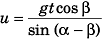
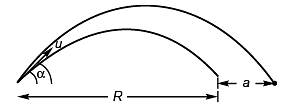
Ques 12: A projectile aimed at a mark, which is in the horizontal plane through the point of projection, falls a cm short of it when the elevation is α and goes b cm far when the elevation is β. Show that, if the speed of projection is same in all the cases the proper elevation is: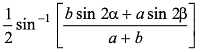
Sol: 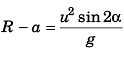
i.e., 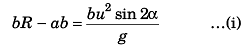
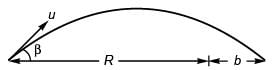
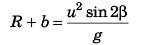
i.e., 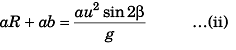
Adding Eqs. (i) and (ii), we have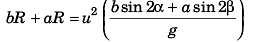
or 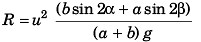
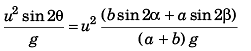
⇒  (Proved.)
(Proved.)
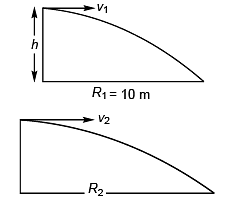
Ques 13: Two particles are simultaneously thrown in horizontal direction from two points on a riverbank, which are at certain height above the water surface. The initial velocities of the particles are v1=5 m/s and v2 = 7.5 m/s respectively. Both particles fall into the water at the same time. First particle enters the water at a point s = 10m from the bank.
Determine:
(a) the time of flight of the two particles,
(b) the height from which they are thrown,
(c) the point where the second particle falls in water.
Ans: (a) 2 s (b) 19.6 m (c) 15 m
Sol: 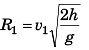
i.e., 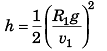
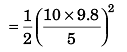
= 19.6 m
∴ 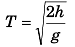
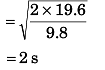
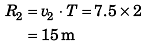
Ques 14: A balloon is ascending at the rate v = 12 km/h and is being carried horizontally by the wind at vw = 20 km/h. If a ballast bag is dropped from the balloon at the instant h = 50 m, determine the time needed for it to strike the ground. Assume that the bag was released from the balloon with the same velocity as the balloon. Also, find the speed with which bag the strikes the ground?
Ans: 3.55 s, 32.0 m/s
Sol: Vertical velocity of balloon (+ bag)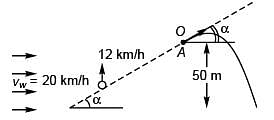
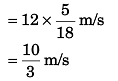
Horizontal velocity of balloon (+ bag)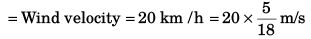
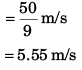
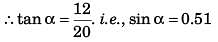
Bag is released at point A.
Let t be time, the bag takes from A to reach ground.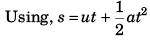
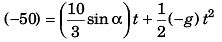
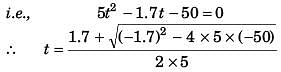
= 3.37 s
Vertical velocity of bag when it strikes ground
∴ Velocity of bag with which it strikes ground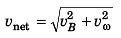
= 37.44 m/s
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions (JEE Main): Projectile Motion- 1 - DC Pandey Solutions for JEE Physics
| 1. What is projectile motion in physics? |  |
| 2. How is projectile motion different from linear motion? |  |
| 3. What are the key equations used to analyze projectile motion? |  |
| 4. How does air resistance affect projectile motion? |  |
| 5. How do you calculate the range of a projectile? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















