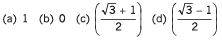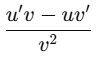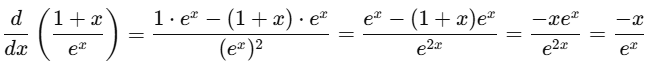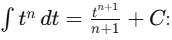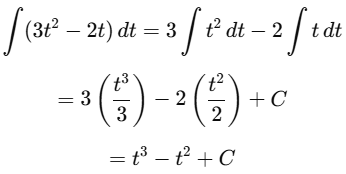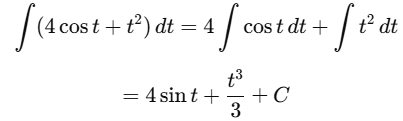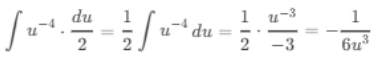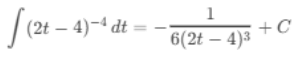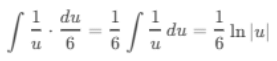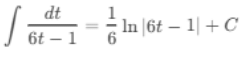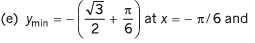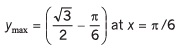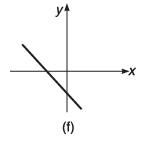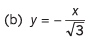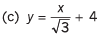DC Pandey Solutions: Basic Mathematics | Physics Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Subjective Questions |

|
| Calculus |

|
| Graphs |

|
| Significant Figures |

|
| Error Analysis |

|
| Vernier Callipers and Screw Gauge |

|
The DC Pandey Solutions for Physics is a crucial book for Class 11 and 12 students. In the JEE physics community, DC Pandey is well-known among writers like HC Verma and Igor Irodov. Toppers of JEE exam also recommend this book. The book is divided into theory and numerical sections with solved examples and various practice questions. However, this book's primary emphasis is on the numerical side, and students are given a variety of practice problems to choose from. Additionally, every chapter of this book has problems of varying degrees of difficulty. EduRev provides solutions for all chapters of DC Pandey.
Section-II
Subjective Questions
Trigonometry
Q1. Find the value of
(a) cos 120°
Ans:120° is in the second quadrant where cosine is negative.
cos 120° = -cos(180° -120°) = -COS 60° = -1/2
(b) sin 240°
Ans:240° is in the third quadrant where sine is negative.
sin 240° = -sin(240° - 180°) = -sin 60° = -√3/2
(c) tan (-60°)
Ans:Tangent is an odd function, so tan(-θ) = -tan θ.
tan (-60°) = -tan 60° = -√3
(d) cot 300°
Ans:300° is in the fourth quadrant where cotangent is negative.
cot 300° = -cot(360° - 300°) = -cot 60° = -1/√3
(e) tan 330°
Ans:330° is in the fourth quadrant where tangent is negative.
tan 330° = -tan(360° - 330°) = -tan 30° = -1/√3
(f) cos (-60°)
Ans:Cosine is an even function, so cos[-θ) = cos θ.
cos (-60°) = cos 60° = 1/2
(g) sin (-150°)
Ans:Sine is an odd function, sin sin(-θ) = -sin θ.
sin (-150°) = -sin 150°
150° is in the second quadrant where sine is positive.
sin 150° = sin(180° - 150°) = sin 30° = 1/2
Thus, sin (-150°) = -1/2
(h) cos (-120°)
Ans:Cosine is an even function, so cos[-θ) = cos θ.
cos (-120°) = cos 120°
120° is in the second quadrant where cosine is negative.
cos 120° = -cos (180° -120°) = -cos 60° = -1/2
Q2. Find the value of
(a) sec2θ - tan2θ
(b) cosec2θ - cot2θ - 1
(c) 2 sin 45°cos 45°
(d) 2sin 15°cos 45°
Ans.
Calculus
Q3. Differentiate the following functions with respect to x
(a) x4 + 3x2 - 2x
Ans:Using the power rule for differentiation:
d/dx (x4) = 4x3, d/dx (3x2) = 6x, d/dx (-2x) = - 2
So,
d/dx (x4 + 3x2 - 2x) = 4x3 + 6x - 2
(b) x2 cos x
Ans:Using the product rule: d/dx (u. v) = u'. v + u. v'
Let u = x2 and v = cos x:
u'= 2x, v' = -sinx
So,
d/dx (x2 cosx) = 2x cosx + x2 (-sin x) = 2x cosx - x2 sin x
(c) (6x + 7 )4
Ans:Using the chain rule: d/dx [f (g(x))] = f' (g(x)) .g'(x)
Let f(u) = u4 and g(x) = 6x + 7:
f'(u) = 4u3, g'(x) = 6
So,
d/dx [(6x + 7)4] = 4 (6x + 7)3 . 6 = 24(6x + 7)3
(d) ex. 5
Ans: Since 5 is a constant, the derivative of ex - 5 is:
d/dx (ex · 5) = 5 · d/dx (ex) = 5ex
(e) (1 + x) / ex
Ans:Using the quotient rule: d/dx (u/v) =
Let u=1+xand v=ex:
u'=1,v'=ex
So,
Q4. Integrate the following functions with respect to t
(a) ∫(3t2 - 2t)dt
Ans:Using the power rule
(b) ∫(4 cos t + t2) dt
Ans:Using
(c) ∫(2t - 4)-4 dt
Ans:Let u = 2t - 4, then du = 2 dt or dt = du/2:
Substitute back u = 2t - 4:
(d) ∫ dt / (6t - 1)
Ans:Let u = 6t - 1, then du = 6 dt or dt = du/6:
Substitute back u = 6t - 1:
Q5. Integrate the following functions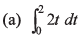
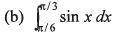
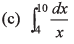
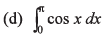
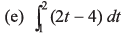
Ans.
(a) 4
(b) (√3 - 1) / 2
(c) In (5/2)
(d) Zero
(e) - 1
Q6. Find maximum/minimum value of y in the functions given below
(a) y = 5 - (x - 1)2
(b) y = 4x2 - 4x + 7
(c) y = x3 - 3x
(d) y = x3 - 6x2 + 9x+ 15
(e) v = (sin 2x - x),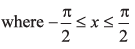
Ans.
(a) ymax = 5 at x = 1
(b) ymin = 6 at x = 1/2
(c) ymin = - 2 at x = 1 and ymax = 2 at x = - 1
(d) ymin = 15 at x = 3 and ymax = 19 at x = 1
Graphs
Q7. Draw the graphs corresponding to the equations
(a) y = 4x
(b) y = - 6x
(c) y = x + 4
(d) y = -2x + 4
(e) y = 2x - 4
(f) y = -4x - 6
Ans.
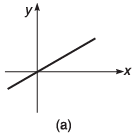
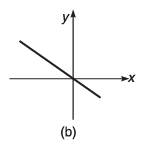
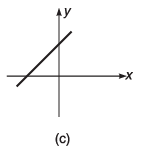
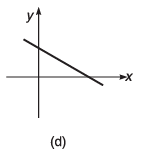
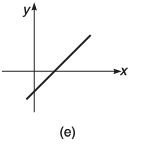
Q8. For the graphs given below, write down their x-y equations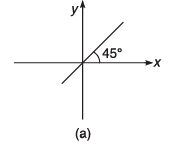
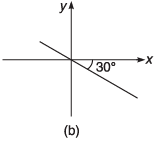
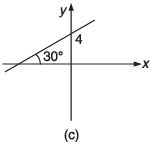
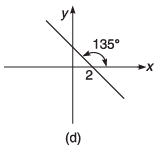
Ans.
(a) y = x
(d) y = - x + 2
Q9. For the equations given below, tell the nature of graphs.
(a) y = 2x2
(b) y = -4x2 +6
(c) y = 6e -4x
(d) y = 4 (1 - e -2x)
(e) y = 4/x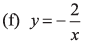
Ans.
(a) parabola passing through origin
(b) parabola not passing through origin
(c) exponentially decreasing graph
(d) exponentially increasing graph
(e) Rectangular hyperbola in first and third quadrant
(f) Rectangular hyperbola in second and fourth quadrant
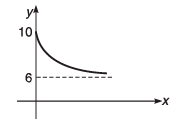
Q10. Value of y decreases exponentially from y = 10 to y = 6 Plot an x-y graph.
Ans.
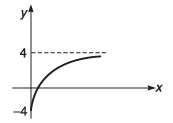
Q11. Value of y increases exponentially from y = -4 to y = +4. Plot an x- y graph.
Ans.
Q12. The graph shown in the figure is exponential. Write down the equation corresponding to the graph.
Ans.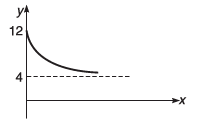
y = 4 + 8e -Kx Here, K is a positive constant
Q13. The graph shown in the figure is exponential. Write down the equation corresponding to the graph.
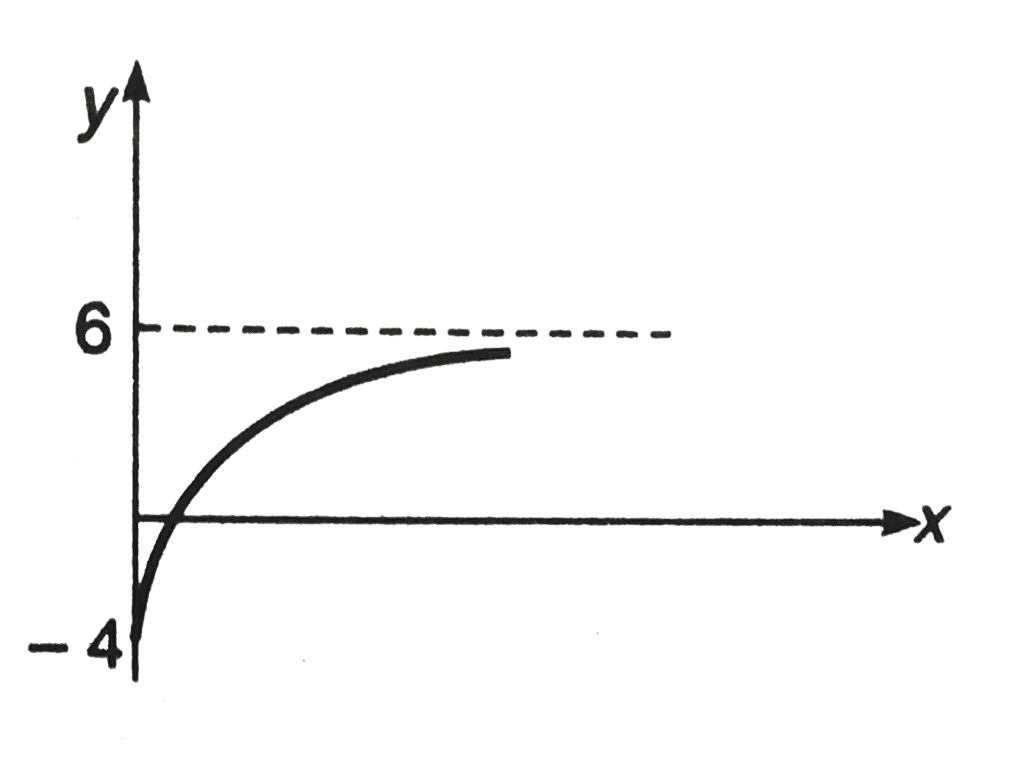
Ans.
y = - 4 + 10(1 - e-Kx)Here, K is positive constant
Significant Figures
Q14. Write down the number of significant figures in the following.
(a) 6428
(b) 62.00 m
(c) 0.0628 cm
(d) 1200 N
Ans.
(a) Four
(b) Four
(c) Three
(d) Four
Q15. Round off to four significant figures.
(a) 45.689
(b) 2.0082
Ans.
(a) 45.69
(b) 2.008
Q16. Add 6.75 x 103 cm and 4.52x 102 cm with due regards to significant figures.
Ans.7.20 x 103 cm
Q17. A thin wire has length of 21.7 cm and radius 0.46 mm. Calculate the volume of the wire to correct significant figures.
Ans.0.14 cm3
Q18. A cube has a side of length of 2.342 m. Find volume and surface area in correct significant figures.
Ans.Area= 5.485 m2, volume= 12.85 m3
Q19. Find density when a mass of 9.23 kg occupies a volume of 1.1m3. Take care of significant figures.
Ans.Density = 8.4 kg/m3
Q20. Length, breadth and thickness of a rectangular slab are 4.234 m, 1.005 m and 2.01 cm respectively. Find surface area and volume to correct significant figures.
Ans.Area= 4.255 m2, volume = 8.55 m3
Q21. Solve with due regards to significant figures
(4.0 x 10-4 -2.5 x 10-6)
Ans.4.0 x 10-4
Error Analysis
Q22. The refractive index (n) of glass is found to have the values 1.49, 1.50, 1.52,1.54 and 1.48. Calculate
(a) the mean value of refractive index
(b) absolute error is each measurement
(c) fractional error and
(d) percentage error
Ans.
(a) 1.51
(b) + 0.02,+ 0.01,- 0.01,- 0.03,+ 0.03
(c) ± 0.0132
(d) ± 1.32%
Q23. The radius of a sphere is measured to be (2.1 + 0.5)cm. Calculate its surface area with error limits.
Ans.
(55.4±26.4) cm2
Q24. Calculate focal length of a spherical mirror from the following observations. Object distance u = (50.1 + 0.5) cm and image distance v = (20.1 ± 0.2) cm.
Ans.(14.3 ± 0.4) cm
Q25. Find the percentage error in specific resistance given by 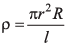 where r is the radius having value (0.2+ 0.02)cm, R is the resistance of (60 ± 2) ohm and l is the length of (150 ± 0.1)cm.
where r is the radius having value (0.2+ 0.02)cm, R is the resistance of (60 ± 2) ohm and l is the length of (150 ± 0.1)cm.
Ans.3.4%
Q26. A physical quantity ρ is related to four variables α, β, γ and η as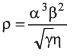
The percentage errors of measurements in α, β, γ and η are 1%, 3%, 4% and 2% respectively. Find the percentage error in ρ.
Ans.3%
Q27. The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is 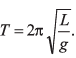 Length L is about 10 cm and is known to 1 mm accuracy. The period of oscillation is about 0.5 s. The time of 100 oscillations is measured with a wristwatch of 1 s time period. What is accuracy in the determination of g?
Length L is about 10 cm and is known to 1 mm accuracy. The period of oscillation is about 0.5 s. The time of 100 oscillations is measured with a wristwatch of 1 s time period. What is accuracy in the determination of g?
Ans.5%
Vernier Callipers and Screw Gauge
Q28. 19 divisions on the main scale of a vernier callipers coincide with 20 divisions on the vernier scale. If each division on the main scale is of 1 cm, determine the least count of instrument.
Ans.0.05 cm
Q29. The pitch of a screw gauge is 1 mm and there are 100 divisions on the circular scale. While measuring the diameter of a wire, the linear scale reads 1 mm and 47th division on the circular scale coincides with the reference line. The length of the wire is 5.6 cm. Find the curved surface area (in cm2) of the wire inappropriate number of significant figures.
Ans.2.6 cm2
Q30. The edge of a cube is measured using vernier callipers. [9 divisions of the main scale are equal to 10 divisions of vernier scale and 1 main scale division is 1 mm]. The main scale division reading is 10 and 1 division of the vernier scale was found to be coinciding with the main scale. The mass of the cube is 2.736 g. Calculate the density in g/cm3 upto correct significant figures.
Ans.2.66 g/cm3
|
96 videos|367 docs|98 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Basic Mathematics - Physics Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the basic concepts of calculus that I should understand for my exams? |  |
| 2. How do I interpret graphs in calculus? |  |
| 3. What are significant figures, and how do they apply in error analysis? |  |
| 4. How do I properly use Vernier callipers and screw gauges for measurements? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of error analysis in scientific measurements? |  |