DC Pandey Solutions: Motion in One Dimension - 2 | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Introductory Exercise 3.2
Ques 1: A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Which quantity remains constant among, speed, kinetic energy, velocity and acceleration?
Ans: acceleration
Sol: Acceleration (due to gravity).
Ques 2: Equation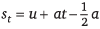 does not seem dimensionally correct, why?
does not seem dimensionally correct, why?
Ans: 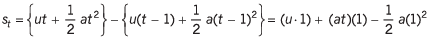
Sol: 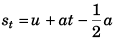 is physically correct as itgives the displacement of the particle in tth second (or any time unit).
is physically correct as itgives the displacement of the particle in tth second (or any time unit).
st = Displacement in t seconds - displacement in (t - 1) seconds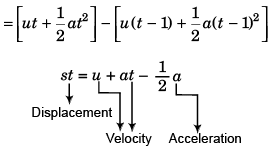
Therefore, the given equation is dimensionally incorrect.
Ques 3: Can the speed of a particle increase as its acceleration decreases? If yes give an example.
Ans: Yes, in simple harmonic motion
Sol: Yes. When a particle executing simple harmonic motion returns from maximum amplitude position to its mean position the value of its acceleration decreases while speed increases.
Ques 4: The velocity of a particle moving in a straight line is directly proportional to 3/4th power of time elapsed. How does its displacement and acceleration depend on time?
Ans: t7/4, t-1/4
Sol: v = t3/4 (given)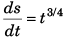 …(i)
…(i)
∴ 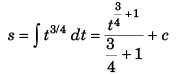
or 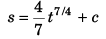
i.e., s ∝ t7/4
Differentiating Eq. (i) w.r.t. time t,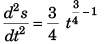
⇒ a ∝ t-1/4
Ques 5: A particle is projected vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Find the displacement and distance covered by the particle in 6 seconds. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 60 m, 100 m
Sol: Displacement (s) of the particle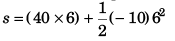
= 240 - 180
= 60 m (in the upward direction)
Distance covered (D) by the particle
Time to attain maximum height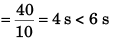
It implies that particle has come back after attaining maximum height (h) given by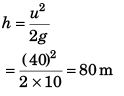
∴ D = 80 + (80 - 60)
= 100 m
Ques 6: Velocity of a particle moving along positive x-direction is v = (40 - 101) m/s. Here, t is in seconds. A t time t = 0, the x coordinate of particle is zero. Find the time when the particle is at a distance of 60 m from origin.
Ans: 2 s, 6 s, 2 (2 + √7) s
Sol: v = 40 - 10t
∴ 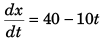
or dx = (40 - 10t) dt
or x = ∫ (40 - 10t) dt
or x = 40t - 5t2 + c
As at t = 0 the value of x is zero.
c = 0
∴ x = 40t - 5t2
For x to be 60 m.
60 = 40t - 5t2
or t2 - 8t + 12 = 0
∴ t = 2 s or 6 s
Ques 7: A particle moves rectilinearly with initial velocity u and a constant acceleration a. Find the average velocity of the particle in a time interval from t = 0 to t = t second of its motion.
Ans: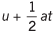
Sol: 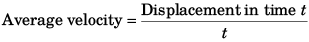
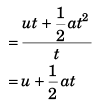
Ques 8: A particle moves in a straight line with uniform acceleration. Its velocity at time t = 0 is v1 and at time t = t is v2. The average velocity of the particle in this time interval is 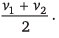 Is this statement true or false?
Is this statement true or false?
Ans: True
Sol: v2 = v1 + at
∴ at = v2 - v1 
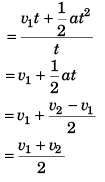
Ques 9: Find the average velocity of a particle released from rest from a height of 125 m over a time interval till it strikes the ground, g = 10 m/s2.
Ans: 25 m/s (downwards)
Sol: 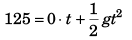
⇒ t = 25 s
Average velocity = 125 m/5 s (downwards)
= 25 m/s (downwards)
Ques 10: Velocity of a particle moving along x-axis varies with time as, v = (10 + 5t - t2) At time t = 0, x = 0.
Find
(a) acceleration of particle at t = 2 s
(b) x-coordinate of particle at t = 3 s
Ans: (a) 1 m/s2
(b) 43 .5 m
Sol: v = 10 + 5t - t2 … (i)
∴ 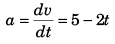
At t = 2 s
a = 5 - 2 x 2
= 1 m/s2
From Eq. (i),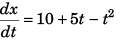
∴ x = ∫ (10 + 5t - t2) dt
or
As, at t = 0 the value of x is zero
c = 0
∴ 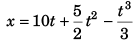
Thus, at t = 3 s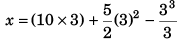
= 30 + 22.5 - 9
= 43.5 m
Ques 11: Velocity of a particle at time t = 0 is 2 m/s. A constant acceleration of 2 m/s2 acts on the particle for 2 seconds at an angle of 60° with its initial velocity. Find the magnitude of velocity and displacement of particle at the end of t = 2 s.
Ans: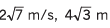
Sol: 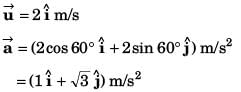
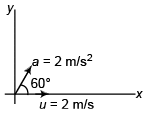
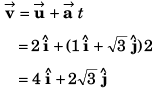
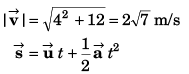
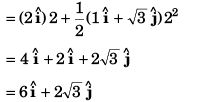
∴ 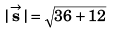
= 4√3 m
Ques 12: Velocity of a particle at any time t is 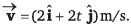 Find acceleration and displacement of particle at t = 1 s. Can we apply
Find acceleration and displacement of particle at t = 1 s. Can we apply 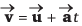 or not?
or not?
Ans: 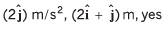
Sol: Part I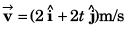 …(i)
…(i)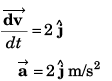
From Eq. (i),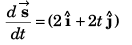
∴ 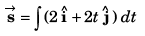
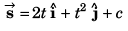
Taking initial displacement to be zero.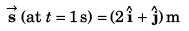
Part II
Yes. As explained below.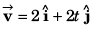 implies that initial velocity of the particle is
implies that initial velocity of the particle is 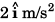 and the acceleration is
and the acceleration is 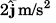
∴ 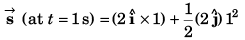
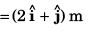
Ques 13: The coordinates of a particle moving in x-y plane at any time t are (21, t2)..
Find:
(a) the trajectory of the particle,
(b) velocity of particle at time t and
(c) acceleration of particle at any time t.
Ans: (a) x2 = 4y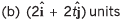
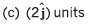
Sol: x = 2t and y = t2
∴ 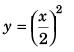
or, x2 = 4y
(The above is the equation to trajectory) x = 2t
∴ 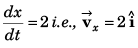
y = t2
∴ 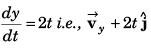
Thus,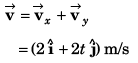
Introductory Exercise 3.3
Ques 1: Figure shows the displacement-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line. Find the signs of velocity and acceleration of particle at time t = t1 and t = t2.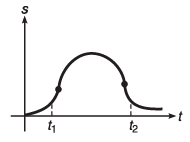
Ans: vt1, at1 and at2 are positive while vt2 is negative
Sol: At t = t1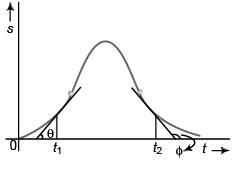
v = tan θ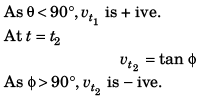
Corresponding v-t graph will be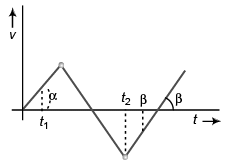
Acceleration at t = t1 : 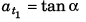
As α < 90°, a t1 is + ive constant.
Acceleration at t = t2
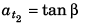
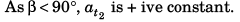
Ques 2: A particle of mass m is released from a certain height h with zero initial velocity. It strikes the ground elastically (direction of its velocity is reversed but magnitude remains the same). Plot the graph between its kinetic energy and time till it returns to its initial position.
Ans:
Sol: Let the particle strike ground at time t velocity of particle when it touches ground
would be gt. KE of particle will be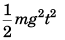 i.e., KE ∝ t2. While going up the velocity will get - ive but the KE will remain. KE will reduce to zero at time 2 t when the particle reaches its initial position.
i.e., KE ∝ t2. While going up the velocity will get - ive but the KE will remain. KE will reduce to zero at time 2 t when the particle reaches its initial position.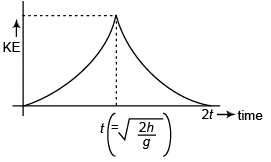
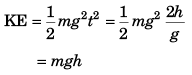
Ques 3: A ball is dropped from a height of 80 m on a floor. At each collision, the ball loses half of its speed. Plot the speed-time graph and velocity-time graph of its motion till two collisions with the floor. [Take g = 10 m/s2]
Ans: 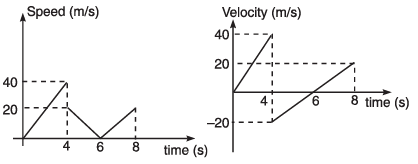
Sol: Speed of ball (just before making first collision with floor) 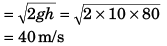
Time taken to reach ground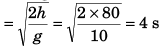
Speed of ball (just after first collision with floor)
= 40/2 = 20 m/s
Time to attain maximum height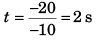
∴ Time for the return journey to floor = 2 s.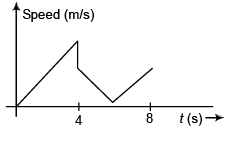
Corresponding velocity-time will be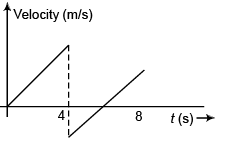
Ques 4: Figure shows the acceleration-time graph of a particle moving along a straight line. After what time the particle acquires its initial velocity?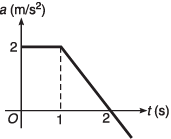
Ans: (2 + √3) s
Sol: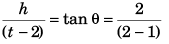
⇒ h = 2 (t - 2)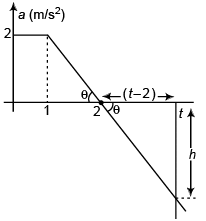
Particle will attain its initial velocity i.e., net increase in velocity of the particle will be zero when,
area under a-t graph = 0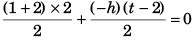
or 3 - (t - 2)2 = 0
or (t - 2)2 = 3
or t - 2 = ± √3
or t = 2 ± √3
At time t = 2 + √3 s
Introductory Exercise 3.4
Ques 1: Two balls A and B are projected vertically upwards with different velocities. What is the relative acceleration between them?
Ans: zero
Sol: Relative acceleration of A w.r.t. B
αAB = (+ g) - (+ g) = 0
Ques 2: In the above problem what is the shape of the graph between distance between the balls and time before either of the two collide with ground?
Ans: straight line passing through origin
Sol: Velocity of A w.r.t. B = vA - vB
∴ Relative displacement (i.e., distance between A and B) would be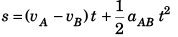
or s = (vA - vB) t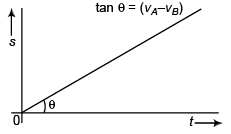
Ques 3: A river 400 m wide is flowing at a rate of 2.0 m/s. A boat is sailing at a velocity of 10.0 m/s with respect to the water in a direction perpendicular to the river.
(a) Find the time taken by the boat to reach the opposite bank.
(b) How far from the point directly opposite to the starting point does the boat reach the opposite bank?
Ans: (a) 40 s
(b) 80 m
Sol: In figure, u = speed of boat
v = speed of river flow
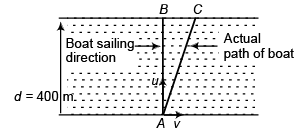
Time to cross river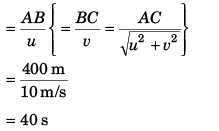
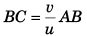
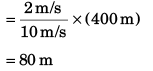
Ques 4: An aeroplane has to go from a point A to another point B, 500 km away due 30° east of north. Wind is blowing due north at a speed of 20 m/s. The air-speed of the plane is 150 m/s.
(a) Find the direction in which the pilot should head the plane to reach the point B.
(b) Find the time taken by the plane to go from A to B.
Ans: 
(b) 50 min
Sol: Let C be the point along which pilot should head the plane.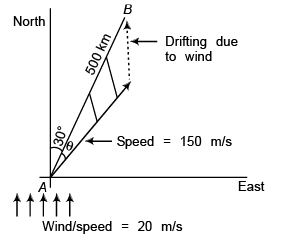
Apply sine formula in Δ ABC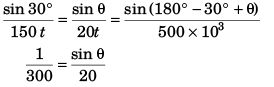
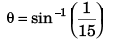
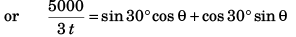
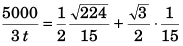
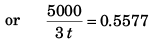
⇒ 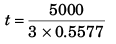
= 2989 s
= 50 min
Ques 5: Two particles A and B start moving simultaneously along the line joining them in the same direction with acceleration of 1 m/s2 and 2 m/s2 and speeds 3 m/s and 1 m/s respectively. Initially A is 10 m behind B. What is the minimum distance between them?
Ans: 8 m
Sol: αA = 1 m/s2 , αB = 2 m/s2
vA = 3 m/s, vB = 1 m/s
Acceleration of A w.r.t. B = 1 - 2 = - 1 m/s2
Velocity of A w.r.t. B = 3 - 1 = 2 m/s
Initial displacement of A w.r.t. B = - 10 m
At time relative displacement of A w.r.t. B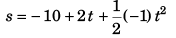
or s = - 10 + 2t - 0.5t2
For s to be minimum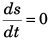
or 2 - (0.5 x 2t) = 0
i.e., t = 2 s
∴ smin = - 10 + (2 x 2) - 0.5 x (2)2
= - 10 + 4 - 2
= - 8 m
Minimum distance between A and B = 8 m.
|
268 videos|740 docs|171 tests
|
FAQs on DC Pandey Solutions: Motion in One Dimension - 2 - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is motion in one dimension? |  |
| 2. How is displacement different from distance in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 3. How can we calculate average velocity in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between speed and velocity in one-dimensional motion? |  |
| 5. How can we determine the acceleration in one-dimensional motion? |  |






















