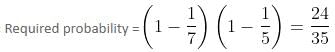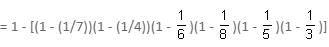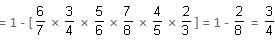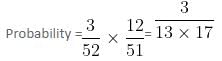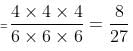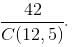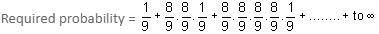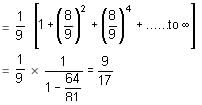This EduRev document offers 10 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) from the topic Probability (Level - 1). These questions are of Level - 1 difficulty and will assist you in the preparation of CAT & other MBA exams. You can practice/attempt these CAT Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) and check the explanations for a better understanding of the topic.
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:Tickets numbered from 1 to 20 are mixed up together and then a ticket is drawn at random. What is the probability that the drawn ticket contains a number, which is a multiple of 3 or 7?
Explanation
Favourable cases = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 7, 14
Probability = 8/20 = 2/5
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:A husband and a wife appear in an interview for the same post. The probability of husband's selection is 1/7 and that of wife's selection is 1/5. What is the probability that none of them will be selected?
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:A piece of work is given to 6 men and their probabilities for doing the work are 1/7, 1/4, 1/6, 1/8, 1/5 and 1/3. Find the probability that the work is done.
Explanation
Probability that the work is done
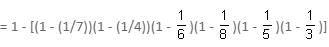
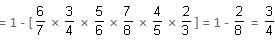
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:Two cards are drawn from a pack of 52 cards. The probability that one of the cards drawn is an ace and the other is a spade but none of the cards drawn is an ace of spades is
Explanation
Number of Ace except ace of spade = 4 - 1 = 3
Number of spade except ace of spade = 13 - 1 = 12
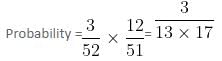
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:Two dice are rolled. What is the probability that the total score is not a prime number?
Explanation
S = sample space.
n(S) = 36.
E = event of getting a prime number = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 4), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 3), (2, 5), (3, 2), (3, 4), (4, 1), (4, 3), (5, 2), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 5)}.
n(E) = 15.
P(not a prime number) = (1 - (15/36)) = 21/36 = 7/12.
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:A die is rolled thrice. Find the probability of getting a number less than 5 in each case.
Explanation
Total cases = 63
Favorable cases = 43
Probability of getting a number less than 5 in each case
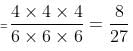
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:A purse contains two 50 paisa coins, four 25 paisa coins and six 10 paisa coins. If 5 coins are taken out from the purse at random, what is the probability that the sum taken out is at least Rs. 1.50?
Explanation
5 coins can be selected at random as 2 + 4 + 6 = 12 coins in C(12, 5) ways.
They will amount to at least Rs. 1.50 if two 50 paisa and three 25 paisa coins are selected or one 50 paisa and four 25 paisa coins are selected or two 50 paisa coins, two 25 paisa coins and one 10 paisa coin are selected.
This can be done in 2C2 × 4C3 + 2C1 × 4C4 + 2C2 × 4C2 × 6C1 = (4 + 2 + 36) = 42 ways.
Thus, required probability is
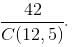
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:If a card is drawn at random from 100 cards numbered 1 to 100, find the probability that the number on the card drawn is a perfect square.
Explanation
Favourable cases = 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100
Number of favourable cases = 10
Required probability = 10/100 = 1/10
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:Two persons throw a pair of dice alternately till, one gets a total of 9 and wins the game. If A takes the first throw, then the probability that A wins the game is
Explanation
P(win) = 4/36 = 1/9
P(loss) = 8/9
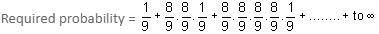
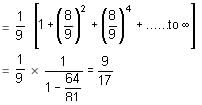
Report a problem
Question for Practice Questions Level 1: Probability - 1
Try yourself:A coin is tossed (m + n) times (m > n). The probability of getting at least m consecutive heads is
Explanation
Let the value of m = 2 and n = 1
Total outcomes will be 8, and probability of getting two consecutive outcomes will be
HHT, HHH and THH, i.e.3/8, only option 3 satisfies for m = 2 and n = 1
Report a problem