Definitions - Phase Diagram, Soil Mechanics | Soil Mechanics Notes- Agricultural Engineering PDF Download
Void Ratio
Void ratio (e) of a soil is the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solid. Thus,
\[e={{{V_v}} \over {{V_s}}}\] (2.1)
The void ratio is greater than zero (as soil has to contain some voids), but there is no upper limit to the value of void ratio. As this the ratio of two volumes, it is unit less.
Porosity
The porosity (n) of a soil is the ratio of the volume of voids to the total volume of the soil. Thus,
\[n={{{V_v}} \over V} \times 100\] (2.2)
The porosity cannot be greater than 100%. As this the ratio of two volumes, it is unit less.
Water content
The water content or moisture content (w) of a soil is the ratio of weight of water to the weight of solids present in the soil. Thus,
\[w={{{w_w}} \over {{w_s}}} \times 100\] (2.3)
The water content is greater than or equal to zero, but there is no upper limit to the value of water content. As this the ratio of two weights, it is unit less.
Degree of saturation
The degree of saturation (S) is the ratio of the volume of water to the volume of voids. Thus,
\[S={{{V_w}} \over {{V_v}}} \times 100\] (2.4)
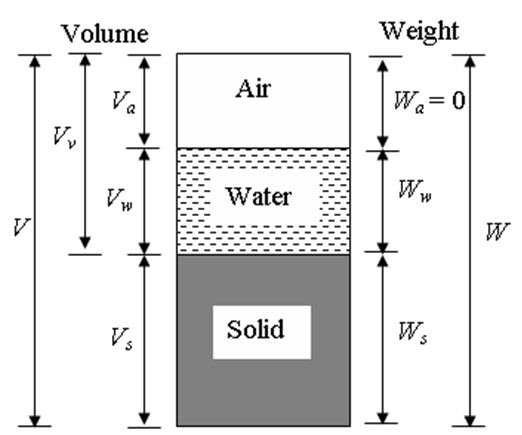 Module 1 Lesson 2 Fig.2.1(a)
Module 1 Lesson 2 Fig.2.1(a)
(a) Partially saturated soil (Three-phase system)

(b) Completely saturated soil (Two-phase system)
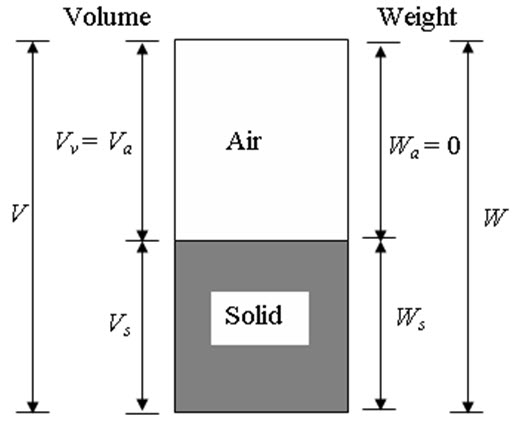
(b) Completely dry soil (Two-phase system)
Figure 2.1. Phase diagrams.
For fully saturated soil, Vv = Vw, Thus, S = 100% or 1. Similarly, for completely dry soil, Vw = 0, Thus, S = 0. For partially saturated soil, S value can be in between 0 to 100%. As this the ratio of two volumes, it is unit less.
Unit weight
Depending upon the state of the soil, the unit weight of the soil also changes. Bulk unit weight ( \[{\gamma _{bulk}}\] or \[{\gamma _t}\] ) of the soil is defined as the total weight of the soil mass per unit of total volume. The bulk unit weight is the unit weight of the soil in its natural condition. In SI unit, it is expressed as ‘kN/m3’. Thus,
\[{\gamma _t}={W \over V}={{{W_s} + {W_w}} \over {{V_s} + {V_w} + {V_a}}}\] (2.5)
Saturated unit weight ( \[{\gamma _{sat}}\] ) of the soil is defined as the total weight of the soil when it is fully saturated per unit of total volume. This is the unit weight of soil under completely saturated condition. Thus,
\[{\gamma _{sat}}={{{W_{sat}}} \over V}\] (2.6)
Dry unit weight ( \[{\gamma _d}\] ) of the soil is defined as the weight of soil solids per unit of total volume. This is the unit weight of soil under completely dry condition. Thus,
\[{\gamma _d}={{{W_s}} \over V}\] (2.7)
Submerged unit weight ( \[\gamma '\] ) of the soil is equal to the saturated unit weight of soil minus unit weight of the water ( \[{\gamma _w}\] ). The unit weight of water is taken to be 9.8 kN/m3 or approximately 10 kN/m3. Thus,
Unit weight of solids ( \[{\gamma _s}\] ) is the ratio of weight of solid to the volume of solids. Thus,
\[{\gamma _s}={{{W_s}} \over {{V_s}}}\] (2.9)
Specific gravity
The specific gravity (Gs) of the soil is defined as the ratio of the weight of a given volume of solid to the weight of an equivalent volume of water at 4°C. Thus,
\[{G_s}={{{W_s}} \over {{V_s}{\gamma _w}}}={{{\gamma _s}} \over {{\gamma _w}}}\] (2.10)
The specific gravity of the soil varies in between 2.65 to 2.80 (Ranjan and Rao, 2000). Specific gravity is also a unit less quantity.
FAQs on Definitions - Phase Diagram, Soil Mechanics - Soil Mechanics Notes- Agricultural Engineering
| 1. What is a phase diagram in soil mechanics? |  |
| 2. How is a phase diagram useful in agricultural engineering? |  |
| 3. What are the different phases represented in a phase diagram of soil mechanics? |  |
| 4. How does a phase diagram help in evaluating soil stability? |  |
| 5. Can a phase diagram be used to determine the composition of soil? |  |



















