UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Notes > Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce > Demand and the determinants of demand
Demand and the determinants of demand | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Defining Demand |

|
| Factors Influencing Demand |

|
| Categories of Demand |

|
| The Principle of Demand |

|
Defining Demand
- Demand is essentially the desire of a consumer to purchase goods and services, coupled with their willingness to pay the specified price.
- In simple terms, demand represents the quantity of a particular product that consumers are ready to buy at different prices within a certain time frame.
- Demand is rooted in preferences and choices, influenced by factors like cost, potential benefits, profit, and other variables.
- The quantity of goods consumers decide to purchase largely depends on the product's price, the cost of other products, the consumer's income, and their personal preferences and tastes.
- The specific quantity of a product that a consumer is willing to buy, based on their financial ability and preferences, is referred to as the demand for that product.
- The demand curve is a graphical representation illustrating the relationship between the price of a product or service and the quantity demanded over a specific period.
- Typically, price is shown on the vertical axis, while the quantity demanded is plotted on the horizontal axis in the demand curve.
Factors Influencing Demand
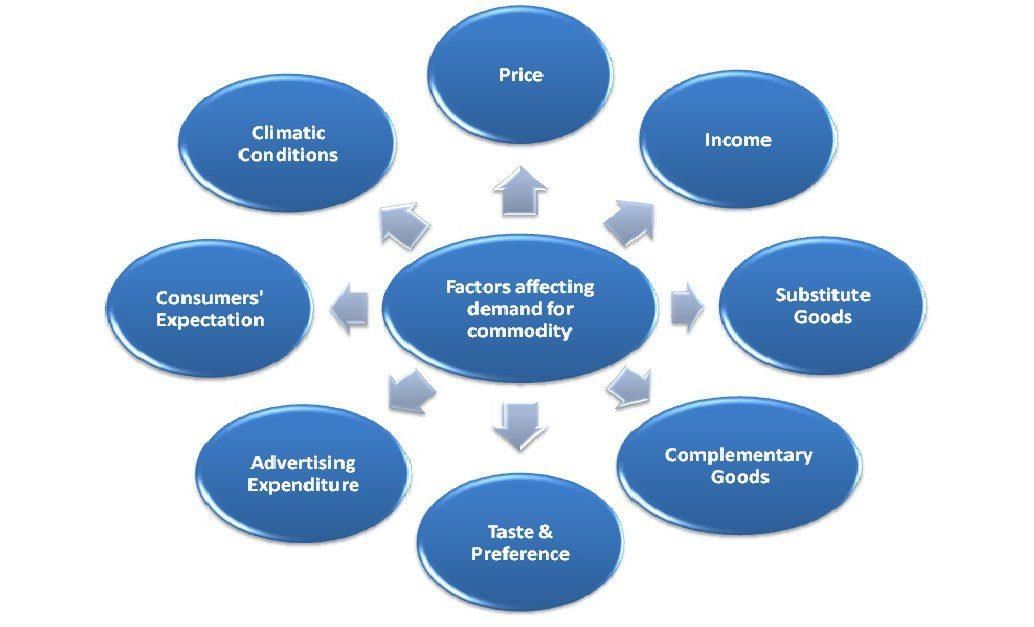 There are various factors that can impact demand significantly. Here, we will delve into the top five influencers:
There are various factors that can impact demand significantly. Here, we will delve into the top five influencers:
Price of the Product:
- The demand for a product tends to shift with alterations in its price. Generally, if all other factors remain constant, the decision to purchase a product will stay consistent.
Consumer's Income:
- With a rise in income, the demand for goods typically increases as well. Conversely, a decrease in income usually results in a decrease in demand for goods.
Prices of Related Goods and Services:
- The prices of related goods and services play a significant role. For complementary products, an increase in the price of one can lead to a decrease in demand for its complement. For example, if the price of potatoes rises, the demand for potato chips may fall. Similarly, a price increase in one product can trigger an increase in demand for a substitute product. For instance, if the price of coffee goes up, the demand for tea may rise.
Consumer Expectations:
- Consumer expectations, such as high income expectations or anticipation of a price hike, can result in increased demand. Conversely, low income expectations or expectations of price decreases can lead to reduced demand for a product.
Number of Buyers:
- An increase or decrease in the number of buyers for a product will lead to a shift in demand.
Question for Demand and the determinants of demandTry yourself: What factor can significantly impact the demand for a product if all other factors remain constant?View Solution
Categories of Demand
- Price Demand: This type involves varying quantities of a product or service that a consumer is willing to purchase at a specific price, assuming other factors remain constant.
- Income Demand: Different quantities of a product or service that a consumer is willing to buy at various income levels, assuming other factors remain constant.
- Cross Demand: Indicates that the demand for a product is influenced not by its own price, but by the prices of related products.
- Direct Demand: Arises when a product or service directly fulfills a consumer's needs.
- Derived or Indirect Demand: Occurs when a product or service is essential for producing other goods that indirectly satisfy consumer needs.
- Joint Demand: Happens when multiple items are necessary to produce a product. For instance, in baking a cake, ingredients like flour, eggs, and sugar are jointly demanded.
- Composite Demand: This type of demand appears when a product or service serves multiple purposes. For example, electricity can be utilized for lighting, heating, and powering appliances.
The Principle of Demand
- The principle of demand asserts that when the price of a product rises, the quantity demanded decreases, provided all other factors remain constant.
- Essentially, as a product's price goes up, consumers tend to buy less of it. This occurs because the opportunity cost for the consumer increases, prompting them to either choose a substitute product or avoid the purchase altogether.
- Exploring the principle of demand and its exceptions is fascinating.
- The theory of consumer preference sheds light on the combination of two products that a consumer is likely to purchase, considering the market prices of the products and the consumer's budget constraints.
- What makes this concept particularly interesting is the actual quantity of a product that a consumer decides to buy. In microeconomics, this is effectively explained through the demand function.
The document Demand and the determinants of demand | Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce is a part of the UGC NET Course Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce.
All you need of UGC NET at this link: UGC NET
|
214 videos|236 docs|166 tests
|
FAQs on Demand and the determinants of demand - Crash Course for UGC NET Commerce
| 1. What are the factors influencing demand in economics? |  |
Ans. Factors influencing demand in economics include price of the product, consumer preferences, income levels, price of related goods, and future expectations.
| 2. What are the categories of demand in economics? |  |
Ans. The categories of demand in economics include individual demand, market demand, derived demand, composite demand, competitive demand, joint demand, and autonomous demand.
| 3. How is demand defined in economics? |  |
Ans. Demand in economics refers to the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a specific price and time.
| 4. What is the principle of demand in economics? |  |
Ans. The principle of demand in economics states that there is an inverse relationship between the price of a product and the quantity demanded, assuming all other factors remain constant.
| 5. How does demand and the determinants of demand relate in economics? |  |
Ans. Demand and the determinants of demand are closely related as the determinants such as price, consumer preferences, income levels, and future expectations influence the overall demand for a product or service in the market.
Related Searches















