Grade 12 Exam > Grade 12 Notes > Economics for Grade 12 > Demand
Demand | Economics for Grade 12 PDF Download
Introduction to Demand
- Demand is the amount of a good/service that a consumer is willing & able to purchase at a given price in a given time period
- If a consumer is willing to purchase a good, but cannot afford to, it is not effective demand
- A demand curve is a graphical representation of the price & quantity demanded (QD) by consumers
- If data were plotted, it would be an actual curve. Economists, however, use straight lines so as to make analysis easier
Individual & Market Demand
- Market demand is the combination of all the individual demand for a good/service
- It is calculated by adding up the individual demand at each price level

- It is calculated by adding up the individual demand at each price level
- Individual & market demand can also be represented graphically
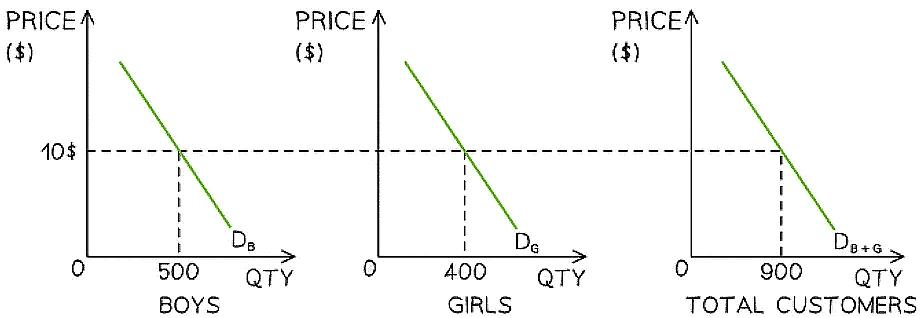
Market demand for children's swimwear in July is the combination of boys & girls demand
Diagram Analysis
- A shop sells both boys & girls swimwear
- In July, at a price of $10, the demand for boys swimwear is 500 units & girls is 400 units
- At a price of $10, the shops market demand during July is 900 units
Movements Along a Demand Curve
- If price is the only factor that changes (ceteris paribus), there will be a change in the quantity demanded (QD)
- This change is shown by a movement along the demand curve
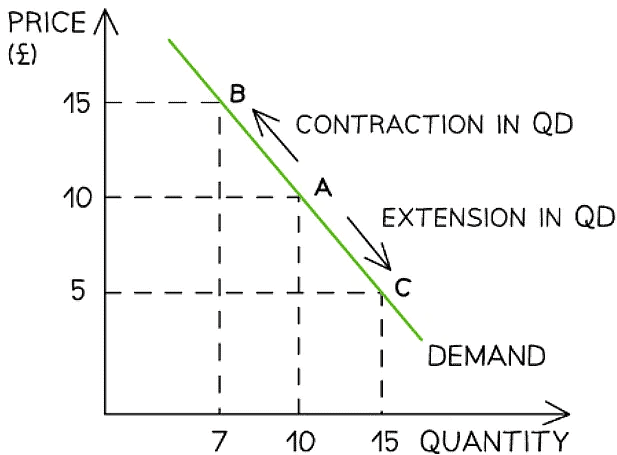
- This change is shown by a movement along the demand curve
A demand curve showing a contraction in quantity demanded (QD) as prices increase & an extension in quantity demanded (QD) as prices decrease
Diagram Analysis
- An increase in price from £10 to £15 leads to a movement up the demand curve from point A to B
- Due to the increase in price, the QD has fallen from 10 to 7 units
- This movement is called a contraction in QD
- A decrease in price from £10 to £5 leads to a movement down the demand curve from point A to point C
- Due to the decrease in price, the QD has increased from 10 to 15 units
- This movement is called an extension in QD
- The law of demand captures this fundamental relationship between price and QD
- It states that there is an inverse relationship between price and QD
- When the price rises the QD falls
- When prices fall the QD rises
Shifts of the Demand Curve
- There are numerous factors that will change the demand for a good/service, irrespective of the price level. Collectively these factors are called the conditions of demand
- Changes to each of the conditions of demand, shifts the entire demand curve (as opposed to a movement along the demand curve)
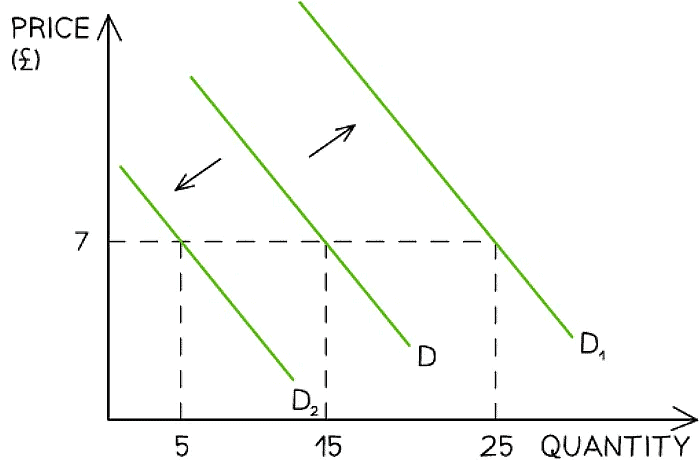
A graph that shows how changes to any of the conditions of demand shifts the entire demand curve left or right, irrespective of the price level
- For example, if a firm increases their Instagram advertising, there will be an increase in demand as more consumers become aware of the product
- This is a shift in demand from D to D1. The price remains unchanged at £7 but the demand has increased from 15 to 25 units
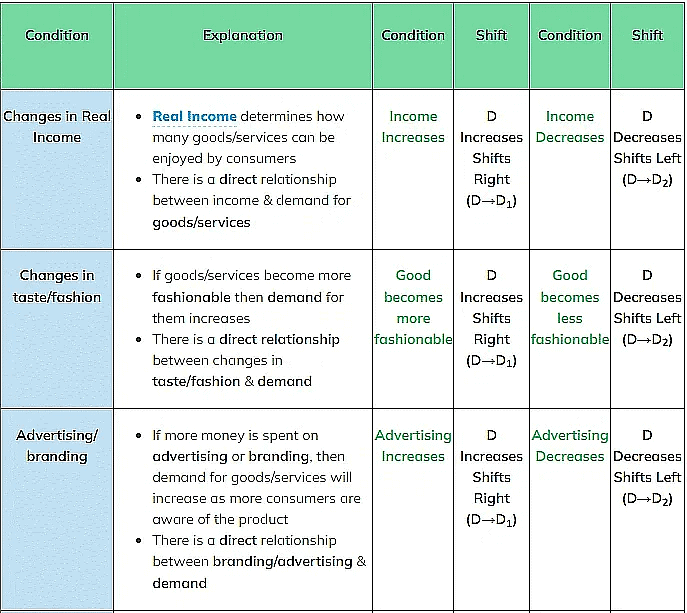
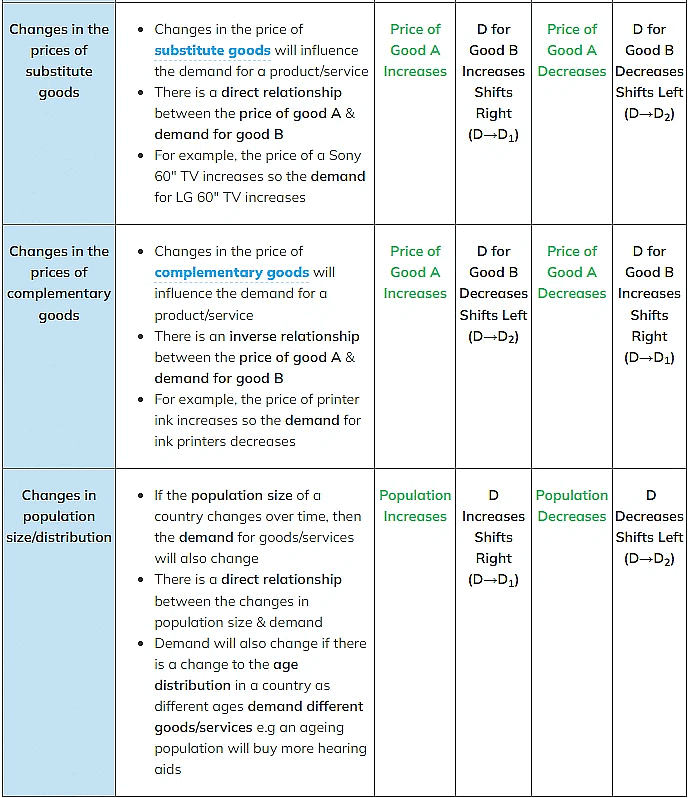
An Explanation of How Each of the Conditions of Demand Shifts the Entire Demand
Curve at Every Price Level
The document Demand | Economics for Grade 12 is a part of the Grade 12 Course Economics for Grade 12.
All you need of Grade 12 at this link: Grade 12
|
23 videos|22 docs|1 tests
|
Related Searches




















