Design of Columns | RCC & Prestressed Concrete - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Slenderness ratio (λ)
λ = effective length/least lateral dimension
If λ > 12 then the column is long.
Load carrying capacity for short column
P = σscAsc + σccAc
where, AC = Area of concrete, Ac = Ag - ASC
σSC Stress in compression steel
σCC Stress in concrete
Ag Total gross cross-sectional area
ASC Area of compression steel
Load carrying capacity for long column
P = Cr(σscAsc + σccAc)
where, Cr = Reduction factor
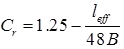
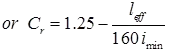
where, leff = Effective length of the column
B = Least lateral dimension
imin = Least radius of gyration and 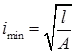
where, l = Moment of inertia and A = Cross-sectional area
Effective length of column
Effective length of Compression Members
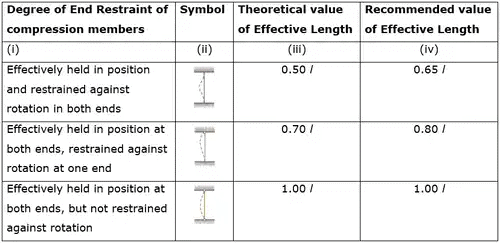
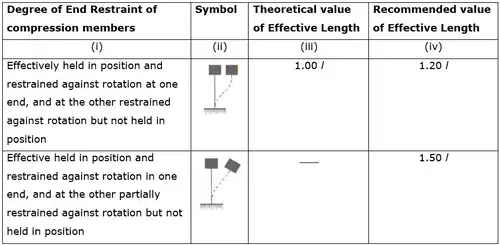
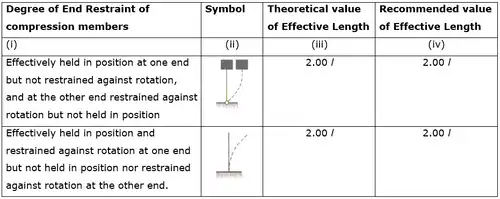
Column with helical reinforcement
Strength of the column is increased by 5%
P = 1.05(σscAsc + σccAc) for short column
P = 1.05Cr(σscAsc + σccAc) for long column
Longitudinal reinforcement
- Minimum area of steel = 0.8% of the gross area of the column
- Maximum area of steel
(i) When bars are not lapped Amax = 6% of the gross area of the column
(ii) When bars are lapped Amax = 4% of the gross area of the column
Minimum number of bars for reinforcement
For rectangular column 4
For circular column 6
Minimum diameter of bar = 12 mm
Maximum distance between longitudinal bar = 300 mm
Pedestal: It is a short length whose effective length is not more than 3 times of lest lateral dimension.
Transverse reinforcement (Ties)
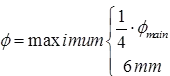
where ϕmin dia of the main longitudinal bar
φ = dia of the bar for transverse reinforcement
Pitch (p)
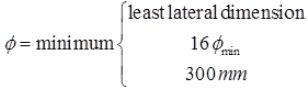
where, φmin = minimum dia of main longitudinal bar
Helical reinforcement
- Diameters of helical reinforcement is selected such that
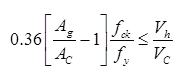
- Pitch of helical reinforcement: (p)
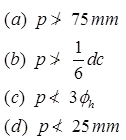
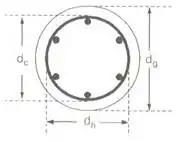
where, dC = Core diameter = dg – 2 × clear cover to helical reinforcement
AG = Gross area = π/4(dg)2
dg = Gross diameter
Vh = Volume of helical reinforcement in a unit length of the column
φh = Diameter of steel bar forming the helix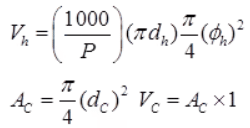
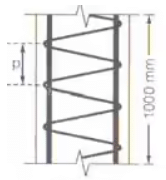 dh = centre to centre dia of the helix
dh = centre to centre dia of the helix
= dg – 2 clear cover - φh
φh = diameter of the steel bar forming the helix
Some others IS recommendations
- Slenderness limit
(i) Unsupported length between end restrains 60 times least lateral dimension.
(ii) If in any given plane one end of the column is unrestrained than its unsupported length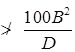
- All column should be designed for a minimum eccentricity of
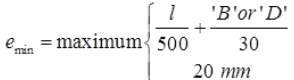
Limit state method
- Slenderness ratio (λ) if
 λ<12 Short column
λ<12 Short column
- Eccentricity
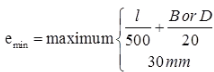
If emin ≤0.05D then it is a short axially loaded column.
where, Pu = axial load on the column. - Short axially loaded column with helical reinforcement
Pu = 0.4 fckAc + 0.67 fyAsc - Some others IS code Recommendations
Pu = 1.05(0.4 fckAc + 0.67 fyAsc)
(i) Slenderness limit
(a) Unsupported length between end restrains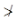 60 times least lateral dimension
60 times least lateral dimension
(b) If in any given plane one end of the column is unrestrained than its unsupported length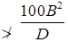
(ii) All column should be designed for a minimum eccentricity of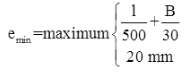
Concentrically Loaded Columns
Where e = 0, i.e., the column is truly axially loaded.
Pu = 0.45 fckAc + 0.75 fyAsc
This formula is also used for member subjected to combined axial load and bi-axial bending and also used when e > 0.05 D.
|
13 videos|42 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Design of Columns - RCC & Prestressed Concrete - Civil Engineering (CE)
| 1. What are the different types of columns used in civil engineering? |  |
| 2. How do you design a reinforced concrete column? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of column design in structural engineering? |  |
| 4. How do you calculate the load capacity of a column? |  |
| 5. What are the common failure modes in column design? |  |