Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Notes - People as Resource
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Economic Activities by Men and Women |

|
| Quality of Population |

|
| Unemployment |

|
| Difficult Words |

|
Introduction
Human resources are essential for economic and social development. This chapter, "People as a Resource," highlights how individuals' skills, knowledge, and health contribute to a nation’s progress.
Key Areas of Focus:
- Education and Skills: Enhancing productivity and employability through effective education and vocational training.
- Health: The impact of healthcare on workforce productivity and overall quality of life.
- Challenges: Addressing issues like unemployment and skill gaps to optimize human potential.
The chapter emphasizes that investing in human resources is crucial for achieving sustainable growth and improving societal well-being.
Human Capital Formation
- Educated and healthier individuals not only experience higher incomes but also contribute to society in indirect ways.
- The advantages of education and health spread to those who were not directly educated or provided healthcare.
- Human capital is emphasized as superior to other resources like land and physical capital because it can actively utilize these resources. Unlike land and capital, human resources can make themselves useful and contribute to economic growth.
- Education and health investments enhance the quality of labour, leading to increased productivity and contributing to economic growth.
Formation of human capital
- It increases the productivity of the workers.
- Educated, trained, and healthy people can use natural resources in a better way.
- It adds to the quality of labour.
- A country can earn foreign exchange by exporting services.
Examples: The Green Revolution and IT Revolution in India illustrate how knowledge input significantly enhances productivity, showcasing the pivotal role of human capital over material and machinery.
Sakal's Story
Sakal, a twelve-year-old from Semapur, faced financial challenges but had supportive parents who valued education.
Educational Journey: Sakal joined the village school and then completed higher secondary education. Pursued vocational training in computers with a loan. Secured a job in a private firm. Designed innovative software, boosting sales. Received recognition and promotion.
Impact of Education: Enhanced productivity and total economic growth. Higher income due to education and innovation.

- Economic Struggles: Single-parent household, earning meagre income from selling fish. Vilas developed arthritis; no access to healthcare.
- Lack of Educational Opportunities: Unable to attend school due to financial constraints. He continued low-skilled work like his mother.
- Contrasting Outcomes: Economic hardships and limited opportunities for Vilas. Lack of investment led to a cycle of low productivity.
- Comparison: Sakal's education and skills led to economic success where as Vilas faced economic challenges due to the absence of education and health care.
Virtuous and Vicious Cycles
A virtuous cycle is described, where educated parents invest heavily in their child's education and health, creating a positive impact.
- In contrast, disadvantaged parents may create a vicious cycle, perpetuating a similar disadvantaged state for their children.
- The example of countries like Japan highlights that investing in human resources, despite lacking natural resources, contributes to their development.
- These countries efficiently use other resources like land and capital, facilitated by the efficiency and technology evolved through investments in people.
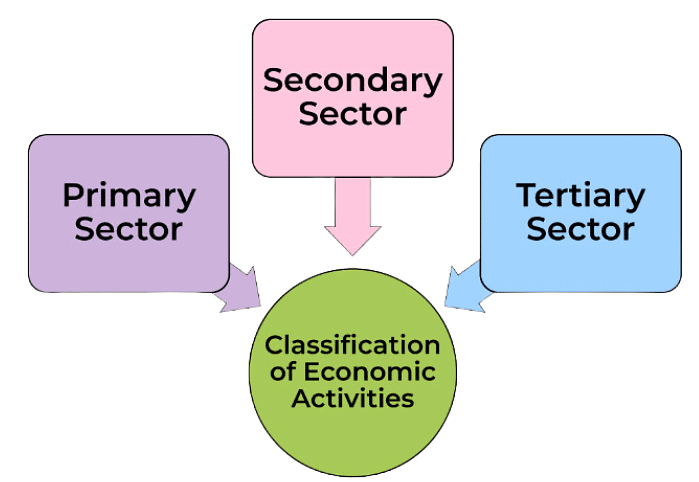
Economic Activities by Men and Women
People, like Vilas and Sakal, engage in various economic activities classified into three sectors: primary, secondary, and tertiary.Classification of Economic Activities
- Primary Sector: Involves agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing, poultry farming, mining, and quarrying.
- Secondary Sector: Includes manufacturing activities.
- Tertiary Sector: Includes trade, transport, communication, banking, education, health, tourism, services, insurance, etc. Contributes to the production of goods and services, adding value to national income.
Market and Non-Market Activities
- Market Activities: Involve salary for services performed, such as the production of goods or services.
- Non-Market Activities: Include production for self-consumption, like processing primary products or own account production of fixed assets.
Gender Roles and Economic Activities
Historical Division of Labour
- The traditional division between men and women in economic activities is due to historical and cultural reasons.
- Women are often responsible for domestic chores, while men engage in fieldwork.
Unpaid Contributions
- Women's domestic work is not recognized in the National Income.
- Example: Sakal's mother, Sheela, handles household duties without salary.
Market Entry
- Women are paid when they enter the labour market, with earnings determined by education and skills.
- Disparities exist; women with lower education often earn less and face job insecurity.
Challenges in Women's Employment:
- Employment sectors lack legal protection, maternity leave, childcare, and social security.
- High education and skill formation enable women to achieve pay parity with men, especially in fields like teaching and medicine.
Quality of Population
- The quality of the population depends on literacy rate, life expectancy, and skill formation.
- Literate and healthy populations are considered assets for a country.
 |
Download the notes
Detailed Chapter Notes - People as Resources
|
Download as PDF |
Education
Education enhances national income, cultural richness, and governance efficiency.
- Efforts include universal access, retention, and quality in elementary education, with special emphasis on girls.
- Establishment of pace-setting schools like Navodaya Vidyalaya in each district.
- Development of vocational streams for high school students.
Budgetary Allocations and Expenditure
- Plan outlay on education increased from Rs 151 crore in the first plan to Rs 99,300 crore in 2020–21.
- Expenditure on education as a percentage of GDP rose from 0.64% in 1951–52 to 3.1% in 2019–20 (B.E.).
- However, there is a decline to 2.8% in 2020–21 (B.E.), as per the Budget Documents of Union State Governments and the Reserve Bank of India.
 Trends in Literacy Rates In Post-Independent India
Trends in Literacy Rates In Post-Independent India
Literacy Rates and Disparities
- Over the years, literacy rates have shown a commendable upward trend, reaching 85% in 2018.
- Literacy is acknowledged not just as a fundamental right but also as a prerequisite for citizens to effectively fulfil their duties and enjoy their rights.
- However, gender and regional disparities persist, with males exhibiting a 16.1% higher literacy rate than females.
- Urban areas also show a 14.2% advantage over rural areas, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions to bridge these gaps.
Challenges in Primary Education
- While the expansion of the primary school system to over 7,78,842 lakh in 2019–20 reflects a positive stride, concerns arise over the dilution of educational quality and high dropout rates.
- The implementation of initiatives like Sarva Siksha Abhiyan, with elements such as bridge courses, back-to-school camps, and the mid-day meal scheme, aims to counter these challenges, striving for universal elementary education.
Higher Education Scenario
- In the realm of higher education, the Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) for the age group of 18 to 23 years reached 27% in 2019–20, aligning broadly with the world average.
- The strategic focus revolves around increasing access, ensuring quality, modifying curricula to suit state-specific needs, encouraging vocationalization, and embracing information technology.
- Noteworthy is the emphasis on distance education and the convergence of various education formats, encompassing formal, non-formal, distance, and IT education institutions.
Health
- In the pursuit of profit maximization, firms place a significant emphasis on workforce efficiency.
- The selection of employees with optimal health is crucial for ensuring productivity and achieving organizational goals.
- The premise is that individuals in good health are better positioned to contribute effectively to the overall growth and success of the organization.
Significance of Health
- Good health enables individuals to realize their potential and effectively contribute to organizational growth.
- Healthy individuals can maximize their output, positively impacting overall organizational performance.
Health Infrastructure in India
- National Policy Focus: The national policy emphasizes improving healthcare access and services, focusing on the underprivileged.
- Infrastructure Development: Over the last five decades, India has built extensive health infrastructure in the government and private sectors. Manpower development spans primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors.
Health Progress Indicators
- Life Expectancy: Increased life expectancy to over 67.2 years in 2021.
- Infant Mortality Rate (IMR): IMR reduced from 147 in 1951 to 28 in 2020.
- Crude Birth Rates: Dropped to 20.0 (2018).
- Death Rates: Reduced to 6 (2020).
Healthcare Disparities and Infrastructure Gaps
- Despite progress, healthcare disparities persist in various regions of India. Many areas lack even basic healthcare facilities.
- The availability of medical and dental colleges is unevenly distributed, with only 542 medical colleges and 313 dental colleges nationwide.
- States such as Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu host a concentration of medical colleges, revealing regional imbalances in healthcare infrastructure.
Unemployment
Unemployment is characterized by the inability of willing individuals to secure jobs at prevailing wages. It is crucial to differentiate between those not seeking employment and those facing challenges in finding suitable opportunities. In India, both rural and city areas face unemployment, but the reasons differ.

Impact of Unemployment
- Wastage of Manpower Resource: Converts potential assets into liabilities for the economy. Creates a feeling of hopelessness and despair among the youth.
- Economic Overload: Increases dependence on the working population. Adversely affects the quality of life for individuals and society.
- Social Consequences: Decline in health status, withdrawal from the school system, and general despair.
- Indicator of a Depressed Economy: An increase in unemployment signals economic challenges.
Types of Unemployment
- Seasonal Unemployment: In rural areas, seasonal unemployment is prevalent, particularly among those dependent on agriculture. Certain months witness reduced agricultural activities, leading to temporary job scarcity for these individuals.
- Disguised Unemployment: Disguised unemployment, common in family-based agricultural settings, gives the appearance of employment. However, surplus workers engage in activities that do not significantly contribute to productivity, highlighting the inefficiencies in resource utilization.
- Educated Unemployment (Urban): Urban areas witness a paradoxical situation where educated individuals, even with matriculation, graduation, or post-graduate degrees, struggle to find suitable employment. This creates a coexistence of surplus manpower in certain categories and a shortage in others.
Statistical Perspective
- While official statistics may indicate low unemployment rates, many individuals with low income and productivity are considered employed.
- Forced work for subsistence rather than by choice is prevalent, contributing to the statistical landscape.
Disguised Unemployment in Agriculture
- The agriculture sector in India experiences disguised unemployment, with self-employment characterized by surplus labour.
- Despite shared work and produce among family members, surplus labour eventually migrates from villages in search of alternative job opportunities.
Sectoral Employment Trends
- Agriculture: Most labor-absorbing; recent decline due to migration to secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Secondary Sector: Small-scale manufacturing as labor-absorbing.
- Tertiary Sector: Growth in new services like biotechnology and IT.
Story of a Village
- Self-Sufficient Village: Families produced food, made clothes, and taught children independently.
Education & Innovation: One family sent their son to agriculture college. The son became an agro-engineer, designed an improved plough, increasing wheat yield. New job of agro-engineer was created. - Economic Growth: Family sold surplus wheat in a neighboring village, earned profit. Success inspired other families to seek better futures for their children.
- Establishment of School: Families requested the panchayat to open a school. A teacher was recruited; all village children began attending school.
- Creation of Tailoring Job: A daughter trained in tailoring, started stitching clothes for villagers. New job of tailor was created, saving farmers' time and increasing farm yield.
- Village Prosperity: Farmers sold surplus produce in village markets. Village, initially with no job opportunities, now had multiple jobs (teacher, tailor, agro-engineer). Rising human capital led to complex and modern economic activities.
Difficult Words
- Human Capital: A measure of the economic value of an employee's skill set. This concept emphasizes that not all labor is equal and that the quality of employees can be improved by investing in them.
Vocational Training: Education or training that prepares individuals for specific crafts, trades, or careers at various levels from a trade, a craft, technician, or a professional position in engineering, accountancy, nursing, medicine, architecture, pharmacy, law etc.
Green Revolution: Refers to a series of research, development, and technology transfer initiatives, occurring between the 1940s and the late 1960s, that increased agriculture production worldwide, particularly in the developing world.
IT Revolution: Refers to the rapid advancements and widespread adoption of information technology that began in the late 20th century and continues to affect the global economy, communication, and efficiency.
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Sectors: These terms classify the different types of economic activities. The primary sector deals with the extraction and harvesting of natural products, the secondary sector involves manufacturing, and the tertiary sector refers to services.
Market Activities: Economic activities that involve transactions of goods and services for money, contributing directly to the economy.
Non-Market Activities: Economic activities that do not involve monetary transactions but satisfy personal and family needs, such as subsistence farming or household work.
Disguised Unemployment: Occurs when more people are engaged in a job than are actually needed to perform the job; these extra people do not increase productivity.
Educated Unemployment: A situation where individuals with academic and training qualifications cannot find employment at an appropriate level or wage.
Virtuous and Vicious Cycles: In economics, a virtuous cycle has favorable results while a vicious cycle has detrimental effects. For instance, investment in education can lead to higher incomes, which can lead to more investments in education (virtuous cycle), whereas lack of education can lead to low income and thus less investment in education (vicious cycle).
Gross Enrollment Ratio (GER): The number of students enrolled in a given level of education, regardless of age, expressed as a percentage of the official school-age population corresponding to the same level of education.
Navodaya Vidyalaya: A system of central schools for talented students predominantly from rural India. They are run by Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti, New Delhi, an autonomous organization under the Department of School Education and Literacy, Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India.
Sarva Siksha Abhiyan (SSA): A government of India program aimed at the universalization of elementary education in a time-bound manner, as mandated by the 86th amendment to the Constitution of India making free and compulsory education to children aged 6–14 a fundamental right.
Mid-Day Meal Scheme: A school meal program in India designed to improve the nutritional status of school-age children nationwide.
|
56 videos|439 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Notes - People as Resource
| 1. What are the main economic activities performed by men and women? |  |
| 2. How does the quality of the population affect economic development? |  |
| 3. What is the current status of unemployment among men and women? |  |
| 4. What are some common challenges faced by women in the workforce? |  |
| 5. How can improving the quality of the population help reduce unemployment? |  |




























