Nervous System Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| What is the Nervous System? |

|
| The Brain |

|
| The Spinal Cord |

|
| Nerves |

|
| What are Sense Organs? |

|
What is the Nervous System?
- Imagine your body as a big machine.
- The nervous system is like the wires that connect all the parts of this machine.
- It consists of special cells called neurons that send messages between different parts of our body and our brain.
Parts of the Nervous System
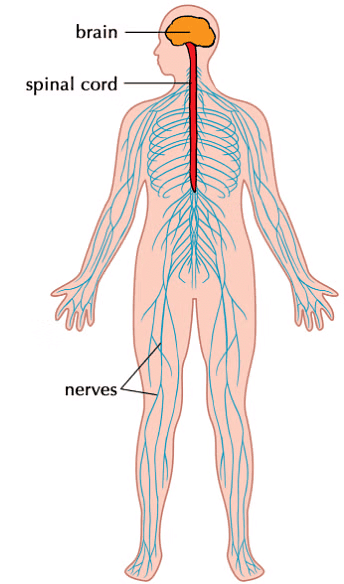
1. The Brain is the body's control centre, functioning like a computer.
2. The Spinal cord is a bundle of nerves that carries messages to and from the brain and the rest of the body.
3. Nerves connect all body parts to the brain, similar to telephone wires.
The Brain
- The brain is the primary organ of the nervous system.
- It is a soft organ that regulates all bodily functions.
- The brain is safeguarded by the skull, which is a bony enclosure.
- It sends and receives information from every part of the body.
Parts of the Brain
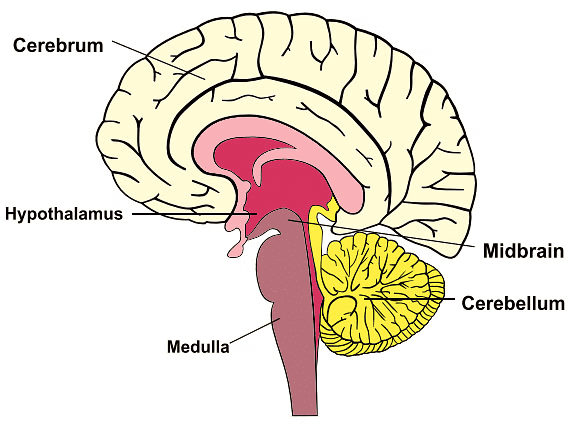
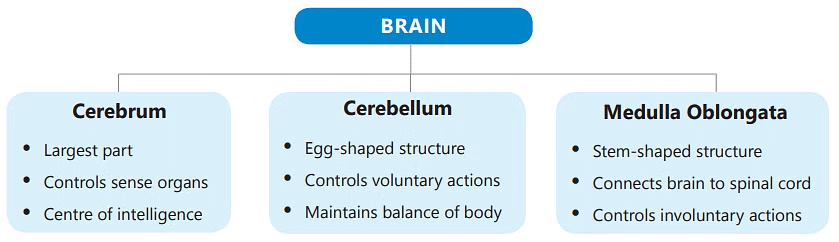
1. Cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest and most important part of the brain.
- It has bumps and folds, called ridges, on its surface that help it store information and control activities.
- The cerebrum manages our sense organs and is the centre of intelligence.
- It regulates our voice and helps us think, learn, remember, and recall memories. Additionally, it controls our emotions.
2. Cerebellum
- The cerebellum is an egg-shaped structure located below the cerebrum and is the second largest part of the brain.
- It manages and coordinates the actions of voluntary muscles for activities such as running, walking, dancing, and standing.
- Voluntary muscles are the muscles in your body that you can control when you want to move. For example, when you decide to lift your arm or walk, you are using your voluntary muscles.
- The cerebellum also helps maintain the balance of the body, keeping us in an upright posture.
3. Medulla Oblongata
- The medulla oblongata, also known as the brain stem, is a stem-shaped structure located below the cerebrum and in front of the cerebellum.
- It connects the brain to the spinal cord.
- This part of the brain controls involuntary actions, such as the movement of the lungs during breathing and the heartbeat.
- Involuntary actions are the movements your body makes without you having to think about them. These actions happen automatically, like when your stomach digests food. You don’t have to tell your body to do these things; it just knows how!
The Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord is a thick, long bundle of nerves that runs from the medulla to the lower end of the backbone, which protects it.
- Nerves branch out from the spinal cord and reach all body parts.
- The spinal cord carries messages between the brain and the body and also controls actions that don’t involve the brain, known as reflex actions.
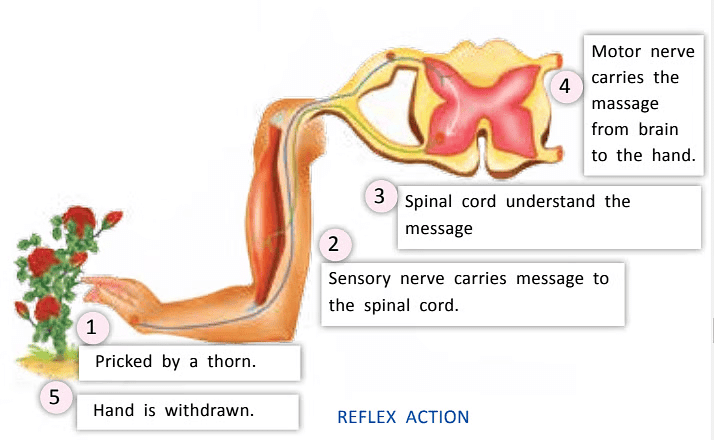
Reflex Actions
- When you touch a hot object or get pricked by a thorn, you quickly pull your hand away.
- This happens automatically, without thinking.
- Such automatic actions in response to an event are called reflex actions.
- The spinal cord controls reflex actions.
- An example of a reflex action is when your mouth waters at the sight of food.
Nerves
- Nerves are thread-like structures stretching from the brain and spinal cord to every body part.
- Each nerve consists of bundles of fibres called neurons, which carry impulses between the brain and other parts.
- Impulses are signals that travel through your nerves, telling your body what to do. These signals are very fast and help your body communicate and respond to different situations.
- These impulses are transmitted through electrical and chemical signals. This network of nerve cells runs throughout the body.
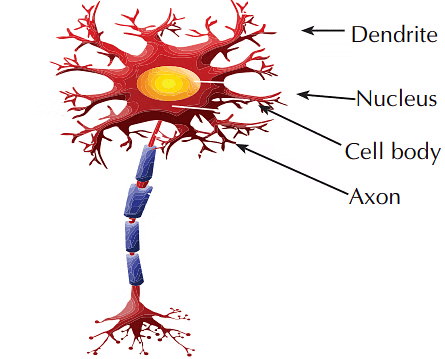
Types of Nerves
Nerves are of three types: sensory, motor and mixed nerves.1. Sensory Nerves
- A sensory nerve is a cord-like structure that carries impulses from receptor cells to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- It sends messages from sense organs to the brain and spinal cord.
2. Motor Nerves
- Motor nerves carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to different parts of the body like muscles, glands, or other organs.
- These nerves help make the muscles move by sending signals from the central nervous system.
3. Mixed Nerves
- A mixed nerve is made up of both sensory and motor nerves.
- It carries messages to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and also brings orders from the brain to different parts of the body.
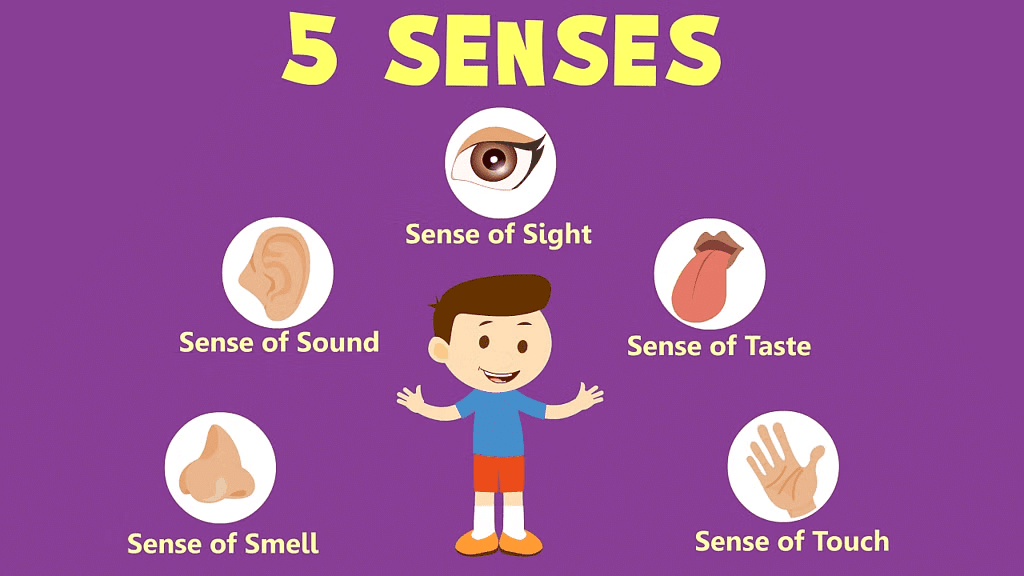
What are Sense Organs?
- Sense organs are parts of our body that help us understand and interact with the world around us.
- They collect information from our surroundings, such as sights, sounds, smells, tastes, and touches, and send that information to our brains.
- The main sense organs in our body are the eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Each of these organs helps us experience the world in a different way.
1. Eyes - Sense of Sight (Vision)
It is the most important sense organ, which works like a camera that takes pictures of the world around us. The different parts of the eyes are:
- Eyelid: It covers our eyes when we sleep or blink our eyes.
- Eyelashes: They protect our eyes from dust.
- Pupil: It is the black circle that lets light into our eyes.
- Iris: It is the coloured part around the pupil.
- Cornea: The circular and transparent front portion of the eye protects the pupil and iris.
- Retina: It is the back of the eye where images are formed.
- Optic nerve: It is the nerve that connects the eyes to the brain. The optic nerve carries the image to the brain.
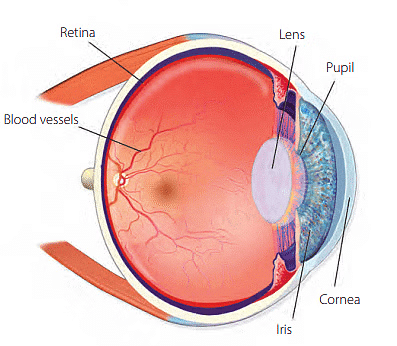 Structure of an Eye
Structure of an Eye
Care of the eyes
- Wash your eyes often with clean water.
- Do not work in low light or very bright light.
- Maintain a distance of at least six feet from the television.
- Avoid watching television for extended periods.
- Limit the time spent on computer games or video games.
- When reading, hold your book about 12 inches away from your eyes.
- Always sit upright while you read.
- Do not read while in a moving vehicle.
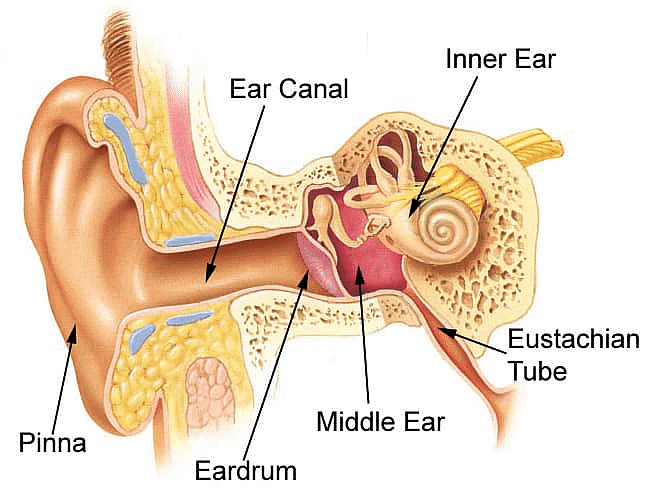
2. Ears - Sense of Hearing (Auditory)
Ears help us to hear the sounds around us. They also help us to maintain balance. The auditory nerve connects the ear to the brain. The structure of the ear is divided into three parts:
- The outer ear- The visible part of the ear collects sound waves and passes them into the middle ear.
- The middle ear- This is the part of the ear that is between the external and internal ear. It helps to amplify the sound received and carries it to the inner ear.
- The inner ear- It is the innermost part of the ear. The sound is carried by the auditory nerve to the brain.
Care of the ears
- Do not prick sharp objects in your ears. It may injure the eardrum.
- Use an earbud to clean your ears.
- Avoid listening to loud music with plugged earphones.
- Do not let water enter your ears. Use a dry towel to clean them.
3. Nose - Sense of Smell (Olfaction)
The nose helps us to smell and breathe.
- There are many nerve endings from the olfactory nerves located in the upper part of the nose.
- These nerve endings are important because they help us detect different smells.
- When we have a cold, these nerve endings can become blocked, making it hard for us to smell.
- Inside the nose, there are tiny hairs that act like a filter for dust particles.
- These tiny hairs prevent dust from entering the nose when we breathe in.
Care of the Nose
- Blow your nose to keep your nostrils clean.
- Avoid inserting objects into your nose.
- Always use your nose for breathing.
4. Tongue - Sense of Taste (Gustation)
- The tongue helps us to taste.
- It also helps in speaking.
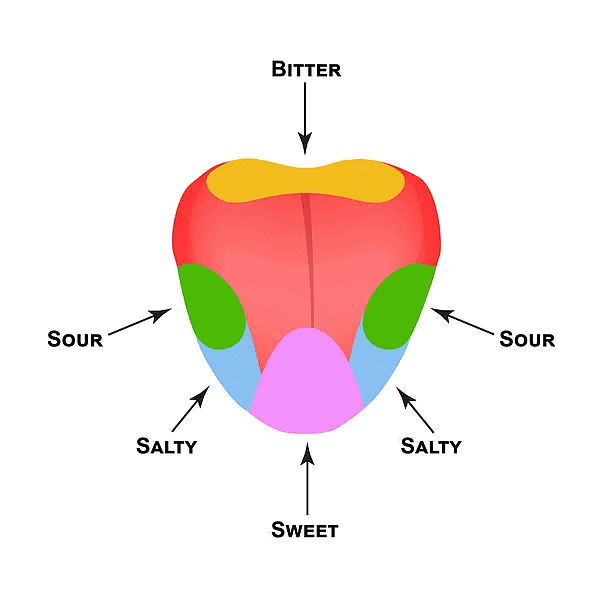
- There are tiny sensory structures on the tongue called taste buds which help us to distinguish different tastes.
- Taste buds have nerve endings that carry messages to the brain.
- The tongue can detect four tastes: sweet, sour, salty, and bitter.
Care of The Tongue
Clean your tongue with a tongue cleaner when you brush your teeth.
5. Skin - Sense of Touch (Tactile)
The outermost covering and the largest organ of our body is the skin.
- The skin contains millions of nerve endings that allow us to sense temperature, pain, pressure, and touch.
- Tiny pores on the surface of the skin help the body release waste through sweat.
- The skin acts as a protective barrier for our internal organs.

Care of The Skin
- Take a bath often using soap and clean water to wash away dirt from your body.
- Wear clean clothes every day.
- If you have a cut or scratch on your skin, use an antiseptic cream to help prevent infection.
|
114 videos|387 docs|97 tests
|
FAQs on Nervous System Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What is the main function of the nervous system? |  |
| 2. What are the three main parts of the nervous system? |  |
| 3. How do sense organs help us? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the spinal cord in the nervous system? |  |
| 5. Why are nerves important in the nervous system? |  |





















