Detailed Notes: Note Making | Business Correspondence and Reporting (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation PDF Download
What Do You Understand by Note Making?
Note making is an essential study skill. According to a dictionary definition, note making is the practice of recording information from another source. The source could be a book, an event, a meeting or a general oral discussion. Note making is useful as going through bulky documents (both hard copy and soft copy), listening to long lectures and attending day-long conferences trying to remember what was preached, can be very tedious.
What Are the Advantages of Note Making?
- One of the chief advantages is that the learner can make notes in a pattern that he / she is comfort able and familiar with.
- Notes are useful records of important points for future use. They aid in writing in a more organised and planned manner as you can see what information you have.
- Note making also helps in organisation as you can rearrange and remember notes in a different order.
- Making notes that are effective is about making sense of the material in a manner that is personal a nd individualized, thus ensuring a better understanding.
- Note making helps learners master the art of learning volumes of text quicker and aids in saving time while revising, particularly before exams.
What Are the Strategies for Effective Note Making?
- Frame a heading / title based on the main idea. It should be short. Avoid using long sentences as a title.
- Ignore information or points which are less important. Be as brief and specific possible. Leave out examples and other unnecessary details.
- Sys tematically dividing and sub-div iding the i mportant in formation, write the points in l ogical sequence.
- Though you write in phrases or points only, the information should be complete.
- Leave no space for ambiguity
- Avoid adding your own interpretation.
- Ensure that you DO NOT change the author’s intended meaning.
- Abbreviate often-repeated terms or lengthy words. Any abbreviation used should not hamper comprehension.
What Do You Mean by Note Making and Note Taking?
Often the two terms, note taking and note making, are used synonymously. But we must distinguish between the two as there are subtle differences between them. Note taking should be regarded as the first-stage of the process and should lead to note making.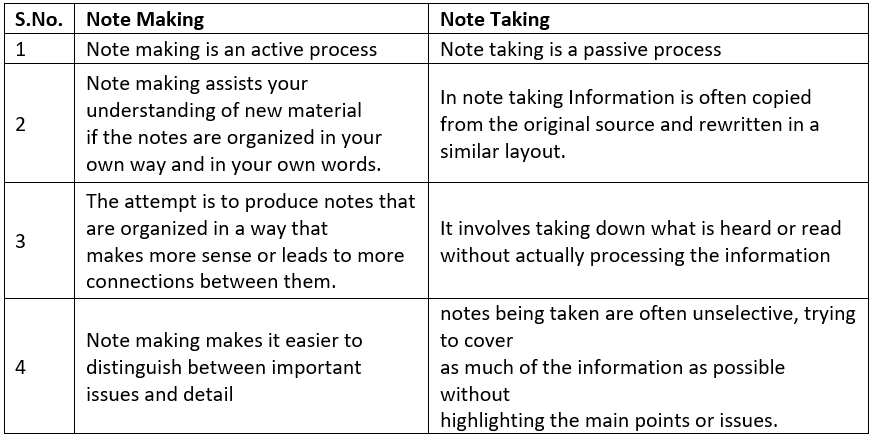
What Are the Various Styles of Note Making?
As mentioned earlier, note making allows one to skim and scan through available sources and make note of the desired knowledge in a form that is not only easy to write, easy to read but also less theoretical. Therefore, there are various ways in which one can present their notes.
Typically, there are two styles of note making: Linear and Non-linear.
(I) Linear Note Making
- Linear note making is the simplest, therefore, the most common style of note making used by people.
- In this form of note making, notes are written down the page, one line after the other in a structured manner.
- Such notes include headings for main ideas and concepts, sub-headings for main points within those ideas.
- Linear notes include use of key words, underlining, indentation, and use of abbreviations.
Example:
Note Making Tips
A. Reading
A.1 read twice
A.1.11st time – identify main idea
A.1.22nd time – identify important points
A.2 UL imp. words
B. Planning – division of content acc. to B.1 theme
B.2 importance
B.3 time
C. Writing
C.1 sub - headings
C.1.1 about 3 – 4
C.1.2use phrases
C.1.3 ignore unimportant info.
C.1.4 indent and number sub-headings and sub- points
C.2 abbreviation
C.2.1 abbreviate long words / often rpted words
C.2.2 use common symbols and acronyms
(II) Non- Linear Note -Making
- Non- linear notes have some distinctive patterns.
- They present and connect ideas in diagrammatical, non-linear forms.
- Non-linear styles of note making include mind maps, tables, flowcharts, and tree diagrams.
- This technique has a number of advantages. It enables you to see a large amount of information on one page and the connections between the key concepts can be shown easily.
 |
Download the notes
Detailed Notes: Note Making
|
Download as PDF |
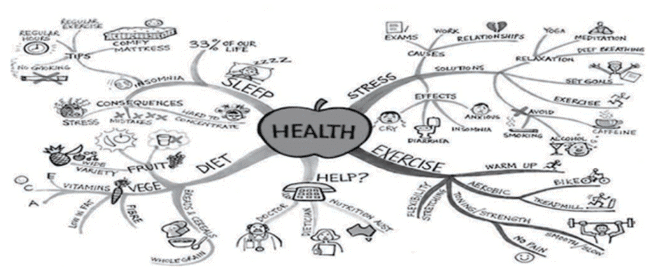
What Do You Mean by Mind Mapping?
Mind mapping is a more visual representation of information.
- Ideas are presented in a diagram form.
- The mind map starts with a main concept and branches out to other concepts related to the main idea.
- Each of these is comparable to the sub-heading and details in linear note making.
- Mind maps can include images, words, symbols and other visual representations of concepts. Moreover, additional information can be included easily and the open ended nature of the pattern means that new connections can be made easily.
A table is most commonly used to make comparisons. This form of note making is an extremely simple and effective way of presenting differences and similarities with clarity.
Example: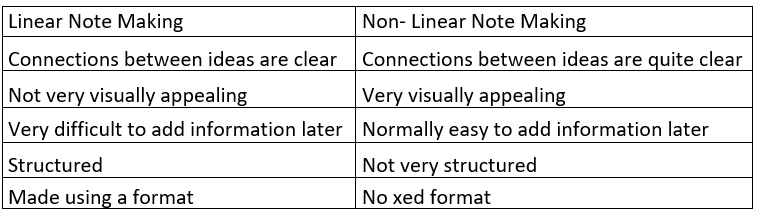
What is a Flow Chart?
A Flowchart is a useful form of notes. It is best used when a process or a change over time needs to be depicted. A flowchart usually has steps shown in boxes connected by arrows which give one an idea about the sequence of events or the process.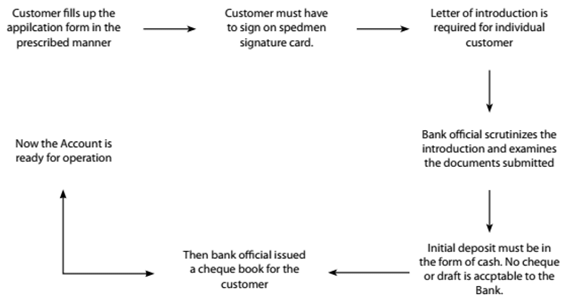
What is a Tree Diagram?
A tree diagram, if turned upside-down, resembles a tree. They are used to show classification.
Example: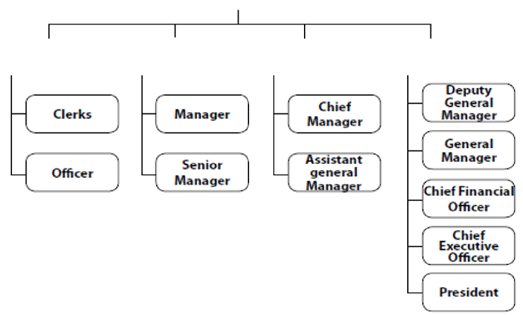
Mechanics of Linear Note Making
(i) Format
A typical note making format should look somewhat like this:
Heading
I. Sub Heading I a. sub point
I b. sub point
I c. sub point
I c (i). sub – sub point
I c (ii). sub - sub point
II. Sub Heading
II a. sub point
II a (i). sub – sub point
II a (ii). sub - sub point
II a (iii). sub – sub
point II b. sub point
IIc. sub point
III. Sub Heading
III a. sub point
III b. sub point
III c. sub point
III c (i). sub – sub point
Key:
Abbreviations used
Symbols used
(II) Heading/title
This basically refers to the topic in question. A suitable heading/title makes it easy to connect with the topic, or subject of discussion for which the notes have been made. You can choose a title for the notes by identifying the main idea or theme of the given passage or text. Keep the title as short as possible. Avoid using long sentences. Titles for notes have to be direct and to the point. They usually will answer the question ‘What is the article / text / report about?’
Example: Careers in Commerce; Healthy Living; Social Media: A Bane; Mutual Funds: Risks and Return
(III) Sub-heading
The sub heading, as the name suggests, is a subordinate division of the main topic. In other words, it is the heading given to the sub-section of an article, report, or any event. Under the sub-heading would follow details (sub – points and sub-sub points) of the sub-section/topic, which is part of the main topic. So if the sub-heading is numbered as Roman numeral I, details would follow as sub- point I a, and sub – sub points I a (i) and so on.
For Example Electronic Communication → Heading
1. Types of communication → Sub heading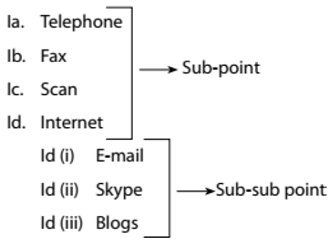
Note: Try to keep the notes (sub-headings, sub-points and sub-sub points) as brief as possible. Most texts or essays can be divided into the following sub- headings:
- Facts, causes, benefits, and suggestions (for positive content)
- Facts, causes, consequences, and solutions (for negative content)
- Facts, advantages and disadvantages
- Past, Present, and Future
(IV) Indentation
The act of proper alignment and spacing of written matter is called indentation. In linear note making indenting, i.e., shifting from the margin is used to clearly indicate subheadings, sub–points and sub-sub points. Similarly, sub-headings, though separated by points are placed below one another. Sub - points and sub-sub points too come below one another. Such use of indenting gives your notes a visual character. You can see the main idea and its various aspects at a glance. These days, with the extensive use of gadgets, such as computers for writing, indentation has become an easy task. User-friendly software like MS Word, MS Excel, etc., take care of headings, sub headings, bullets, pointers, styles and so on. A point that must be noted is that too many indents/pointers make the content complicated to understand.
Need for Indentation
- Offers a well defined structure.
- Makes it readable and comprehensible.
- Increases the objectivity of the content.
(V) Abbreviations / Acronyms / Symbols
Abbreviations, acronyms and symbols are used in order to save time and space Moreover their use can make your notes easier to read. Acronyms can be used both (whether you’re typing or writing by hand), The shortened form of a word is called its abbreviation. Example: contd.(continued). An acronym is a stand-in for a string of words. Unlike abbreviations, they are words consisting of the first letters of each word in the name of something.
Example: NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration)
Ways to abbreviate words
Almost any word can be shortened during note-making. Given below are some ideas about how to do this.
(A) Use the beginnings of words.
One way to shorten a word is to use only the first few letters of the word. Example:
- info - information
- max. – maximum
- stat. – statistics
- corp. – corporation
- pop. – popular
- int. – interest
- promo. – promotion
(B) Use the beginnings of words with the final letter.
Sometimes a word can be abbreviated by using the first few letters of the word and adding the final letter to it. An apostrophe (‘), may be added in the place of the omitted letters. For example:
- govt. or gov’t - government
- interl. or inter ’l- international
- dept. or dep’t – department
- prodn. or prod’n – production
- intl. or int’l – international
(C) Omit vowels
Abbreviations can also be formed by leaving out the vowels. It is still possible to understand the word. Example:
- prblm – problem
- schl - school
- bckgrnd – background
- yrs – years
- vr – avour
- bsns – business
(D) Use the first letter and the last letter of a word.
Some words, especially those words that have just one syllable, can be abbreviated by writing the first and last letter of the word.
Example:
- mt - mount
- qt - quart
- gl - girl
- Mr. – mister
(E) Shorten the suffix at the end of the word.
At times words can be abbreviated by shortening the suffix at the end of the word.
- productn - production
- consistn - consisting
- processg - processing
- implem n - implementation
- decrg - decreasing
- ckg - checking
Common Symbols and Acronyms
There are many common abbreviations, acronyms and symbols which can be used for note-making. You already are aware of many (especially the mathematical symbols). Try to start using them while making notes.
Examples of Symbols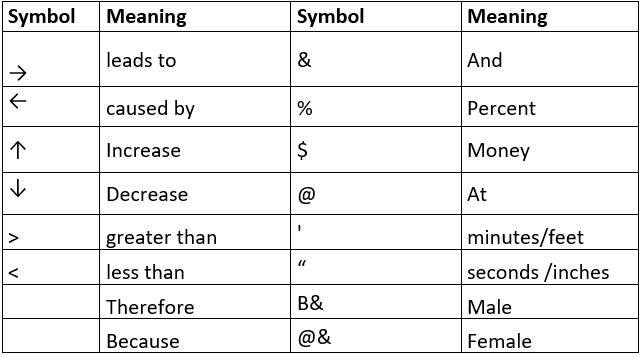
Examples of 5 Acronyms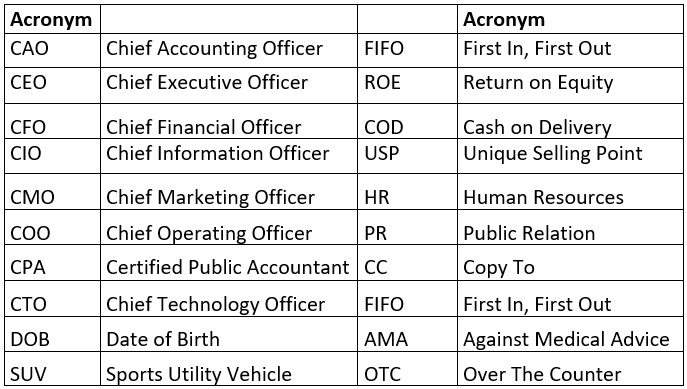
Q. what are some Suggested tips while using Abbreviations / Acronyms / Symbols?
- Judicial and controlled use of abbreviations should be made.
- While using self made abbreviations, adhere to a pattern so that while going through the notes, one can recall what the abbreviation meant.
- According to a general rule, headings should not be abbreviated. Sub headings may/may not have abbreviations.
- Avoid forming a sentence with only abbreviations and symbols. It would not be comprehensible for others.
- Include a key listing the abbreviations, symbols and acronyms used.
Useful tip: Students are advised to use standard acronyms while making notes. However, there can be more flexibility while using abbreviations. The list of abbreviations used should be listed down at the end of note making as ‘Key for reference’.
(VI) Summarizing the notes
A summary is a shortened or condensed version of a longer essay or reading. It is not a redraft of the original text and should not be long. Your purpose while writing the summary is to give a basic idea of the original text, what it was about and what the author wanted to communicate. A summary should not have a word limit exceeding 25 percent of the original text. Remember that a summary must include all the points from the notes. Abbreviations must not be used while summarizing notes. To write a summary, you must use your own words to express briefly the main idea and relevant details. Given below is a list of points to be kept in mind while summarizing notes:
- Use the information given in the notes.
- Do not add or subtract any piece of information.
- Do not make assumptions.
- Use short and crisp sentences as opposed to detailed and long ones of the original content.
- Avoid sounding repetitive; use new words to express the same information.
- Try to cover maximum points
- Reach a conclusion if required.
Examples of Note-Making
Type 1-
Read the following passages and make suitable notes.
Most twins are fraternal, which means they developed from two separate eggs which were fertilized at the same time. Such twins are no more similar in physical characteristics than are any other brothers or sisters. About one third of twins are identical, which means they developed from a single fertilized egg, and usually share a common placenta. Unlike fraternal twins, their genetic makeup is identical, so they have very similar physical characteristics, and are always the same sex.
Twins
I. Fraternal twins
a) dvlp from 2 separate eggs
b) ferti’n of eggs happens at same time
c) not similar in phy. chrctrstcs
II. Identical twins
a) develop from 1 egg
b) share com. placenta
c) Simi lar in phy. chrctrstcs
Key:
1. dvlp – develop
2. ferti’n – fertilization
3. phy. – physical
4. chrctrstcs - characteristics
2. It may sound too fantastic to be true but if you are lucky enough to go to the Sahara Desert one day, then you too will be able to see thousands of engraved, decorated rocks! On these rocks, there are scenes of animals, of agriculture, of sheep-herding, and hunting; there are ceremonies and dances, and chariots drawn by galloping horses, all pictured on the rocks as if there were part of an illustrated book—a wonderful, stone book, which conjures up images and journeys of incredible journeys. And if we could make a voyage to the dawn time, we would nd that the Sahara was not then the desert we now know, but a green and fertile region instead. Mighty rivers owed down and the vegetation was Mediterranean style: Pine trees, Holm oaks, cedars, lime trees and ash trees.
Sahara Desert
I) What can you see?
a) engr ’d rocks
b) scenes of animals, hunting, agri.
c) pic. of dances, ceremonies and chariots with horses
II) What was Sahara like in initial days?
a) green and fertile
b) luxurious Mdtrn kind of veg.
c) rivers owing down
Key
1. engr ’d – engraved
2. agri. – agriculture
3. pic. – pictures
4. Mdtrn - Mediterranean
5. veg. – vegetation
Type 2
Read the following notes and summarize them using as few words as possible.
1) Functioning of the Ear
(i) Snd travels as waves
(ii) Ext. ear gathers the waves
(iii) Waves are led to ac
(iv) Ac inc. loudness and moves waves to erdrm
(A) parts of the erdrm: three tiny bones
(a) hammer
(b) anvil
(c) stirrup
(B) change weak sound waves into powerful ones
(v) Erdrm passes the waves to cochlea
(v) Waves reach the Corti
(vi) Hair like receptors convert sound waves to elec. impulses; pass to the brn
(vii) Brn allows us to hear the sound
Key
1. snd. –sound
2. ext. – external
3. inc. increases
4. elec. – electrical
5. ac – auditory canal
6. erdrm – eardrum
7. brn – brain
Summary
Sound travels in the form of waves which the external ears gather. Passing through the auditory canal which increases the loudness, these waves move to the eardrum. The dierent parts of the eardrums (hammer, anvil and stirrup) change the weak sound waves into powerful ones. Finally, the waves pass through the cochlea to the Corti, where they get converted to electrical impulses, and reach the brain which then allows us to hear the sound.
(2) The Importance of Strategic Planning
1. SP entails
1.1 plan of action
1.2 tool for large org. & nations
1.3 tool for ind.
2. Imp. of SP for people
2.1 helps bal. b/w passivity & trying to live acc.
2.2 antithesis to simply drifting
2.3 smartness to embrace opportunities
3. Imp. of SP in business
3.1 provides knwldg about employees
3.2 max. short/long term investments
4. Fundamental steps in SP
4.1 creating a plan
4.2 keeping track of rslts
4.3 altering course based on rslts
5. How can we plan for complexities in life?
5.1 pick area of life which is most challenged
5.2 start planning for it
5.3 when that area is stabilized, dev. plan for another aspect
5.4 learn to dev. skills in making trade-o s b/w various aspects of life
Key
1. b/w - between
2. ind. - individual
3. acc - according
4. dev. - develop
5. inv. – investment
6. rslts - results
7. SP – strategic planning
8. max. – maximize
9. org. – organizations
Summary
Strategic planning refers to a plan of action. It is an important tool used by large organizations, industries, nations and individual. It is important because it provides a balance between passivity and living according to Plan. Strategic planning leads to smartness in embracing opportunities. Planning is important in business because you need to know the individual and you need to maximize short-term and long-term investments. The fundamental activities in planning include creating a plan, keeping track of results and altering course based on results. One can plan for a complicated life by picking up an area of life that is most challenged and starting to plan for speci c areas. When one area is stabilized, start on the other.
Type 3
Read the following passages carefully and make notes on it, using headings, sub-headings, etc. Use recognizable abbreviations wherever necessary. Use a format you consider suitable. Supply an appropriate title to it. Also write a summary.
- If you are looking for ways to improve your writing skills there is one sure re way to accomplish this. Every time we sit down to write an article the intention should be to try and keep things short and sweet. Good articles are short articles that get a point across with the minimal amount of words used. All too often however we nd ourselves going o on tangents thereby increasing the length of the article. E ective writing skills include the ability to write less and say more but without repetition this skill can be hard to develop. Here are ways which can make you a better writer.
- Why say something in 100 words that can be said in just 50? Your readers will greatly appreciate this. It is always a good idea when writing to nish your composition and then let it sit for a while. With a little thought and a fresh perspective you can always edit out words, phrases, and even paragraphs that are not needed. Getting your point across using as few words as possible will give those words you do use more impact. Your ability to stick to the subject and get to the point is something every reader will appreciate. A common tendency for most writers is to sometimes deviate from the main point of their articles. In fact meandering away from your intended subject can irritate readers to the point where they don’t even nish reading what you wrote.
- The additional content does not necessarily add any value to the article itself and therefore can and should be left out when possible. Learn to write so everybody understands you and don’t try to impress them with your vocabulary. The need for a dictionary is not what your readers are looking for since this takes additional time and is inconvenient. Always write to and for the general audience and never assume that they have an appreciation for a verbose vocabulary. This only makes their reading all the more di cult and less enjoyable. The best way to improve your writing skills is through repetition. One of the most e ective writing talents a person can develop is the ability to write less and say more. This is particularly true when you write an article since you want to capture the readers’ attention without boring them. As a rule of thumb good articles are short articles.
Improve Your Writing Skills
I) Cnsldt your thoughts.
a) use few words
b) give the topic some thought
c) edit unwanted words, phrases, and even paras
II) Stick to the subj.
a) get rt. to the pt.
b) do not dvt. from the main pt.
c) addn content doesn’t necsrly add any val.
d ) dvting from the topic irritates readers
III) Write plainly
a) write for the general public
b) ensure everybody undrstnds you
c) use easy vocab
Key
1. cnsldt - consolidate
2. paras - paragraphs
3. rt. - right
4. pt. – point
5. sub. – subject
6. val. – value
7. addn – additional
8. vocab. – vocabulary
Summary
If you are looking for ways to improve your writing skills, then there are a few things you must keep in mind. The rst step is to stick to the subject. Do not divert from the topic. Getting your point across using as few words as possible will give those words you do use more impact. Additional content does not necessarily add value to the article and may irritate the readers. Remember to write for the general public. Use easy vocabulary to ensure that everybody understands you. The final step of writing your article is to let it sit for a while. Give it a little thought and edit out words, phrases, and even paragraphs that aren’t needed.
Class Work
Q.1. Read the following passages carefully and make notes on it, using headings, sub-headings, etc. Provide a key for the abbreviations used. Use a format you consider suitable. Supply an appropriate title to it.
- Anything printed and bound in book size can be called a book, but the quality or mind distinguishes the value of it. What is a book? This is how Anatole France describes it: “A series of little printed signs essentially only that. It is for the reader to supply himself the forms and colors and sentiments to which these signs correspond. It will depend on him whether the book be dull or brilliant, hot with passion or cold as ice. Or if you prefer to put it otherwise, each word in a book is a magic nger that sets a bre of our brain vibrating like a harp string and so evokes a note from the sounding board of our soul. No matter how skilful, how inspired the artist’s hand, the sound it makes depends on the quality of the strings within ourselves.” Until recently books were the preserve of a small section-the urban upper classes. Some, even today, make it a point to call themselves intellectuals. It would be a pity if books were meant only for intellectuals and not for housewives, farmers, factory workers, artisans and, so on.
- In India there are rst-generation learners, whose parents might have been illiterate. This poses special challenges to our authors and to those who are entrusted with the task of disseminating knowledge. We need much more research in the use of language and the development of techniques by which knowledge can be transferred to these people without transmission loss. Publishers should initiate campaigns to persuade people that a good book makes a beautiful present and that reading a good book can be the most relaxing as well as absorbing of pastimes. We should aim at books of quality no less than at quantitative expansion in production and sale. Unless one is constantly exposed to the best, one cannot develop a taste for the good. Smokers will often say that they are not addicted to cigarettes.
- These people think of smoking as a habit which they can control and would be able to stop at any time. While, it is true that some people can stop smoking at will (almost most cannot), it must be recognized that smoking is in fact an addiction, much like an addiction to alcohol, heroin or cocaine. Furthermore, smoking is addictive because nicotine, a substance that when given to monkeys, rats, dogs and even squirrels will precipitate chemical dependency in them.
- Cigarette addiction is the result of a complex interaction between the smoker (host), nicotine and the environment. For the host, factors such as personality, educational level and social setting are important. Smokers tend to associate certain situations or moods with smoking. These associations become cues that reinforce patterns of smoking. Having a cigarette with co ee, after dinner or while stressing out over a job are a common habit among smokers and these become associations that provoke craving for cigarettes.
Q.2. Read the following notes and summarize appropriately.
1. Headache and their Treatments
A. Classi n
(i) tnsn h'ach
(ii) mgrne h'ach
B. Symptoms
(i) tnsn h’ach
(a) feeling tight band around head
(b) pain in neck and shoulders (ii) mgrne h’ach
(a) pain on one side of the head
(b) vomiting and irritability
(c) bright sport of ashes of light
C. Causes:-
(i) tnsn h’ach
(a) long stretches of driving
(b) long hrs. of typing or sitting on the desk (ii) mgrne h’ach.
(c) chocolate, co ee, smoking.
(d) MSU is certain food items
D. Treatment:-
(i) self –care techniques for shorter pd.
(ii) doctor advice for permanent treatments.
2. Effects of Global Warming
A. What is GW?
(i) causes of GW
(a) human in u.
(b) carbon poln
(c) burning of forests
(ii) e ects of GW
(a) rise in temp.
(b) severe disasters like heat wave, oods and droughts
(c) epidemics and advent of various diseases
(d) higher death rate: ora and fauna both
(e) acidic oceans
B. How to prevent GW
(i) at the personal lvl
(a) reduce, reuse, recycle
(b) use less of ac
(c) use energy ecient products
(d) plant more trees
(e) use CNG vehicles
(ii) at the industry level
(a) recycle industrial waste
(b) install taller chimneys in industries
(c) campaigns against deforestation at the govt. level
(d) digitization of bills, accounts, writings: avoid use of paper
(e) stop forest res
Q.3. Read the following passages carefully and make notes on it, using headings, sub -headings, etc. Use abbreviations wherever necessary. Use a format you consider suitable. Supply an appropriate title to it. Also write a summary.
- The co ee plant, an evergreen shrub or small tree of African origin, begins to produce fruit 3 or 4 years after being planted. The fruit is hand-gathered when it is fully ripe and a reddish purple in colour. The ripened fruits of the co ee shrubs are processed where they are produced to separate the co ee seeds from their covering and from the pulp. Two di erent techniques are in use: a wet process and a dry process.
- First the fresh fruit is pulped by a pulping machine. Some pulp still clings to the co ee, however, and this residue is removed by fermentation in tanks. The few remaining traces of pulp are then removed by washing. The co ee seeds are then dried to a moisture content of about 12 percent either by exposure to the sun or by hot-air driers. If dried in the sun, they must be turned by hand several times a day for even drying. In the dry process the fruits are immediately placed to dry either in the sun or in hot-air driers. Considerably more time and equipment is needed for drying than in the wet process. When the fruits have been dried to a water content of about 12 per cent the seeds are mechanically freed from their coverings. The characteristic aroma and taste of co ee only appear later and are developed by the high temperatures to which they are subjected during the course of the process known as roasting. Temperatures are raised progressively to about 220-230°C.
- This releases steam, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and other volatiles from the beans, resulting in a loss of weight of between 14 and 23 per cent. Internal pressure of gas expands the volume of the co ee seeds from 30 to 100 per cent. The seeds become rich brown in colour; their texture becomes porous and crumbly under pressure. But the most important phenomenon of roasting is the appearance of the characteristic aroma of co ee, which arises from very complex chemical transformations within the beans.
- The co ee, on leaving the industrial roasters, is rapidly cooled in a vat where it is stirred and subjected to cold air propelled by a blower. Good quality co ees are then sorted by electronic sorters to eliminate the seeds that roasted badly. The presence of seeds which are either too light or too dark depreciates the quality.
- Swimming pools were once considered a luxury limited only to the rich. Today, thanks to plastics and plenty, they number in the millions. Few, of course are of Olympic size where a swimmer can quickly do his laps and stay in shape. Most are above-ground, round mini-pools, line for a cool-o and a’ frolic. But, health experts have come to realize that exercises created especially for such swimming pools can tone the muscles, strengthen the heart and pacify the spirit of people of all ages and conditions. And these exercises aren’t restricted to small pools alone. Any type of pool, including a crowded municipal one, will do.
- Designer of the principal popular exercises is C. Carson Conrad, executive director of the California Bureau of Health. Physicians approve of Conrad’s exercises for three reasons.
- First, since water pressure, even on a nonmoving body, stimulates the heart to pump blood throughout the body, exercise in the water promotes thorough circulation still more e ectively. Second, water exercise is rhythmic. And continuous, rhythmic exercises, authorities agree, are one of the best defenses against circulatory ailments which might cause athersclerosis, often the precursor of coronary attacks and strokes. Third, water exercise can be enjoyed with bene t by both young and old, healthy and in rm, swimmers, and in shallow water, non swimmers. Dr. Ira H. Wilson and Fred W.
- Kasch, a physicianand-physiologist team, assert that even persons with paraplegia, rheumatic heart, asthma, emphysema, victims of polio or strokes, or amputation can exercise in water and enjoy weightless movement. Arthritics move easily under water. Some physicians use hydrocalisthenics for their cardiac patients. At the University of Illinois Prof. Richard H. Pohndori studied the e ect of water exercise on a “typical” couple. He chose as subjects a man-and-wife team of physicians, 43 and 41 years old respectively, who had been sedentary for years. His program was simple: “Swim from one end of the pool to the other until you can swim 1000 yards a day. Swim every day for ten weeks.”
- Before they started, the couple took 151 physical tests. At the end of ten weeks, they were tested again: their pulse rate had dropped, their rate of breathing had dropped, their blood pressure had come down to normal, the cholesterol level in their blood had dropped 20 percent. Further, more than half of the broken blood vessels dis guring the woman’s thighs had vanished, her husband had improved in all his physical- tness tests; he reduced the size of his heart, making it more e cient. Both felt younger, more vigorous.
|
27 videos|44 docs
|
FAQs on Detailed Notes: Note Making - Business Correspondence and Reporting (Old Scheme) - CA Foundation
| 1. What do you understand by note making? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of note making? |  |
| 3. What are the strategies for effective note making? |  |
| 4. What do you mean by note making and note taking? |  |
| 5. What are the various styles of note making? |  |























