Diagram Label Completion: Practice Test - 6 | Reading for Academic IELTS PDF Download
Directions: Answer the Diagram label completion questions from the passage as follows:
The platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus) is one of the most unusual, unlikely and evolutionary distinct animals alive. According to the BBC, the first time a platypus was brought from Australia to Britain, people believed that a hoodwinker had sewn two animals together and that they were the victims of a hoax. Platypuses are best described as a hotchpotch of more recognizable species such as the duck, beaver or otter. The physical structure, habitat and reproduction system of the platypus makes it an interesting and unique mammal.
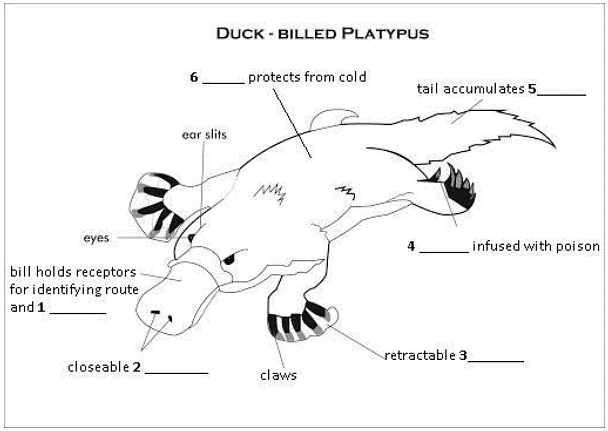
Weighing around three pounds, the platypus measures 15 inches (38 cm) from its head to lower back. The tail adds about 5 inches (13 cm). However, the creatures inhabiting colder regions are bigger. The physiology of the platypus is adapted for survival on land as well as in water. The shape of its bill gives it the name duck-billed platypus. This flexible body part is smooth like suede and has receptors for navigation and detection of movements of freely-swimming food, such as shrimp. The eyes and ears located in the grooves behind the bill are covered by folds of skin and a watertight seal that closes the nostrils when it is underwater. Platypuses have thick waterproof fur which allows them to stay warm underwater. Although most of its fur is dark brown, a patch near the eyes and on the underside is of a lighter shade. When on land, the webbing on their feet retracts, making their claws more pronounced and hence, these animals walk awkwardly on their knuckles to protect the web.
Yet another peculiar fact about these animals is that they are one of the very few mammals which are poisonous. Male platypuses have a horny spur on the ankles of their hind feet. It is connected to a venom gland in the upper leg. It releases a poison capable of causing excruciating pain to humans and is also capable of killing other small animals. Fat is stored in the tail.
These mammals inhabit only one small area of the world. Platypuses make their homes in freshwater bodies that flow throughout the eastern and south-eastern coasts of Australia and the island of Tasmania. Though these creatures exist only on one side of one continent, platypuses can be found in various climate extremes such as in lowlands, plateaus, cold mountains and tropical rainforests. Although platypuses spend a lot of time in the water, they waddle onto the riverbanks to claw through the mud using their nails and feet to make burrows which are tunnels with chambers or rooms. They can also reside under debris, rock ledges or roots.
Platypuses are nocturnal and hence are most actively hunting during the night which can last for about 10 to 12 hours. Hunting for food takes place under the water. As they swim, they try to detect food such as insects, larvae, worms or shellfish along the muddy bottom of the water body. They scoop the prey in their bills, store it in cheek pouches and swim to the surface. Because they do not have teeth but grinding plates, they use the gravel and dirt that they scooped up to fragment their food into digestible portions.
The platypus is listed as a species of ‘least concern’ by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). However, being a carnivore, its role as that of controlling the population of species in the lower level of the food chain cannot be ignored. The biggest threats include natural predators such as snakes, water rats and goannas, and some introduced animals such as foxes, dogs and cats. Human activities such as land clearing and dams are the biggest threat to the loss of habitat. However, platypuses have been able to evade most of the human intrusion of their natural environment.
Q. Label the diagram below. Choose NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers for 1–6 on your answer sheet.
Solution of 1:
"Food"
The shape of its bill gives it the name duck-billed platypus. This flexible body part is smooth like suede and has receptors for navigation and detection of movements of freely-swimming food, such as shrimp.
Solution of 2:
"Nostrils"
The eyes and ears located in the grooves behind the bill are covered by folds of skin and a watertight seal that closes the nostrils when it is underwater.
Solution of 3:
"Webbing"
When on land, the webbing on their feet retracts, making their claws more pronounced …
Solution of 4:
"Spur"
Male platypuses have a horny spur on the ankles of their hind feet. It is connected to a venom gland in the upper leg. It releases a poison …
Solution of 5:
"Fat"
Fat is stored in the tail.
Solution of 6:
"Fur"
Platypuses have thick waterproof fur which allows them to stay warm underwater.
|
27 videos|77 docs
|
FAQs on Diagram Label Completion: Practice Test - 6 - Reading for Academic IELTS
| 1. What is the diagram label completion task in the IELTS exam? |  |
| 2. How can I improve my performance in the diagram label completion task? |  |
| 3. Are there any specific strategies to approach the diagram label completion task effectively? |  |
| 4. Can I use my own words while labeling the diagram in the IELTS exam? |  |
| 5. How much time should I spend on the diagram label completion task during the IELTS exam? |  |
















