Difference Between Sunnii & Shi'a Core Beliefs | Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| How the Six Articles of Faith Shape a Sunni Muslim’s Life |

|
| The Five Roots of Usul ad-Din in Shi’a Islam |

|
| Similarities and Differences Between Sunni and Shi’a Beliefs |

|
Introduction
The core beliefs of Sunni and Shi’a Islam are encapsulated in the Six Articles of Faith for Sunni Muslims and the Five Roots of Usul ad-Din for Shi’a Muslims. These foundational principles summarize the essential beliefs that guide the actions and words of Muslims, steering them toward the righteous path.
A verse from the Qur’an states: “O you who have faith, believe in Allah, His Messenger, the Book revealed to His Messenger, and the Scriptures sent down previously. Whoever denies Allah, His angels, His books, His messengers, or the Last Day has strayed far from the truth” (Surah 4:136).
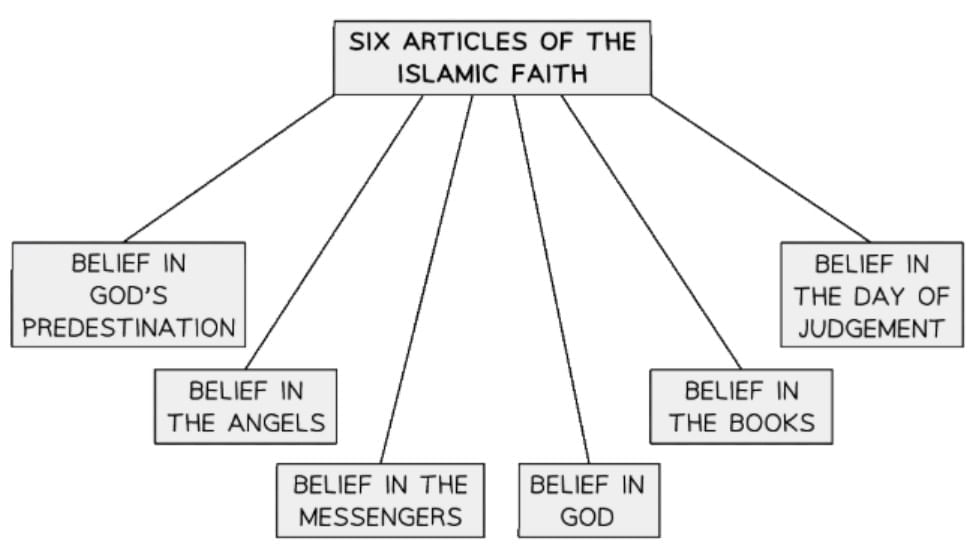
The Six Articles of Faith in Sunni Islam
The Six Articles of Faith in Sunni Islam are Tawhid, Malaikah, Kutub, Nubuwwah, Akhirah, and Al-Qadr. These principles shape the beliefs and practices of Sunni Muslims.
Tawhid (Belief in One God)
- The Qur’an (Surah 112:1-4) declares: “He is Allah, the One, Eternal, and Absolute. He is neither born nor gives birth, and there is none comparable to Him.”
- This affirms that Allah is the sole creator and sustainer of all existence, transcending human limitations such as birth, death, or aging.
Malaikah (Angels)
- Angels serve as Allah’s messengers, delivering divine revelations to prophets to guide humanity according to Allah’s will.
- They also record every individual’s deeds and words, compiling a record for accountability in the afterlife.
- Additionally, angels collect souls at the time of death. Unlike humans, angels lack free will and follow Allah’s commands without deviation.
Kutub (Holy Books)
- Muslims recognize five authoritative scriptures: the Torah of Moses, the Psalms of David, the Gospels, the Scrolls of Abraham, and the Qur’an.
- Sunni Muslims believe the first four have been altered over time, losing their original divine form. The Qur’an, however, remains unchanged, regarded as the direct word of Allah, revealed through the angel Jibril.
Nubuwwah (Prophethood)
- Prophets, chosen by Allah, convey His guidance to humanity. Sunni Muslims believe that Allah has sent prophets throughout history, with Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) being the final and most significant, as stated in the Qur’an (33:40): “Muhammad is not the father of any of your men, but the Messenger of Allah and the Seal of the Prophets.”
- The Qur’an, revealed to Muhammad, is considered the ultimate guidance, eliminating the need for further prophets.
Akhirah (The Afterlife)
- The Day of Judgment is when Allah will judge all individuals based on their earthly actions, determining their eternal destination—paradise or hell.
- Each person will stand alone before Allah, accountable for their thoughts and deeds. Life on earth is seen as a test for the eternal life to come.
Al-Qadr (Predestination)
- Sunni Muslims believe in Al-Qadr, meaning Allah has predetermined all events, as stated in Surah 13:42: “In all things, the master-planning is God’s.”
- While humans possess free will to make choices, Allah, with His infinite knowledge of the past, present, and future, already knows their decisions, though individuals remain unaware of their predetermined outcomes.
How the Six Articles of Faith Shape a Sunni Muslim’s Life
- Sunni Muslims dedicate their lives to serving Allah and adhering to His commandments. They follow the teachings of the Qur’an and the example set by the Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him).
- Knowing that angels record their every thought and action, they remain mindful of their behavior and interactions with others. The belief in the Day of Judgment motivates them to live righteously, anticipating accountability before Allah, which will determine their entry into paradise or hell.
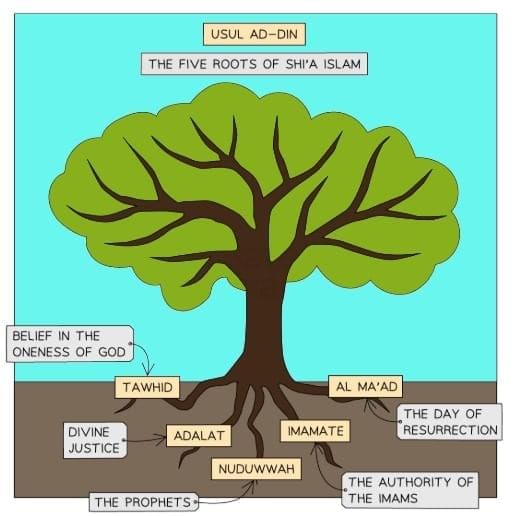
The Five Roots of Usul ad-Din in Shi’a Islam
Shi’a Islam is grounded in the Five Roots of Usul ad-Din: Tawhid, Adalat, Nubuwwah, Imamate, and Al-Ma’ad. These principles, meaning “foundations of the faith,” guide every aspect of a Shi’a Muslim’s life and support the Ten Obligatory Acts.
Tawhid (Belief in One God)
- As stated in Surah 112:1-4: “He is Allah, the One, Eternal, and Absolute.
- He is neither born nor gives birth, and there is none comparable to Him.” This emphasizes that Allah is the creator and sustainer of all, unbound by human limitations like birth or death.
Adalat (Divine Justice of Allah)
- Shi’a Muslims believe in Allah’s divine justice, meaning He is inherently just, wise, and incapable of wrongdoing. Humans are accountable for their actions, as Allah commands justice (Surah 16:19: “Indeed, Allah commands them to do justice”).
- Shi’a Muslims recognize the presence of good and evil and strive to follow Allah’s command to do good. While Allah’s purpose may sometimes be beyond human understanding, believers are encouraged to seek comprehension of His justice.
Nubuwwah (Prophethood)
- Allah selects prophets to deliver His guidance, with Prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him) being the final and most significant prophet.
- Shi’a Muslims believe prophets guide humanity toward a peaceful life in complete submission to Allah. The imam preserves these teachings to prevent the faith from being forgotten or corrupted in the absence of prophets.
Imamate (Authority of the Imams)
- Shi’a Muslims believe in the divine authority of the twelve Imams, who are infallible leaders descended from the Prophet’s family (Ahl al-Bayt).
- These Imams safeguard the truth of Islam, ensuring its teachings remain pure and guiding the community to stay on the right path.
Al-Ma’ad (Day of Judgment)
- Shi’a Muslims believe in a Day of Judgment when all individuals, Muslim and non-Muslim, will be resurrected and judged by Allah based on their words and actions during their earthly lives.
- The Qur’an and Hadith describe the events of this day, emphasizing accountability.
How the Five Roots of Usul ad-Din Influence a Shi’a Muslim’s Life
- Belief in Allah’s oneness inspires Shi’a Muslims to follow His path by doing what is right. Prophethood assures them that divine guidance is available through history and the Qur’an.
- The Imamate provides leadership to keep Muslims aligned with the faith in the modern world. The belief in the Day of Judgment reminds them of their accountability to Allah, encouraging good intentions and actions.
- Faith in divine justice fosters trust in Allah’s wise and purposeful actions, even when His plans are not fully understood.
Similarities and Differences Between Sunni and Shi’a Beliefs
Sunni and Shi’a Muslims share many core beliefs, but there are also notable differences.
Both Sunni and Shi’a Muslims uphold:
- Tawhid: Allah is the one true God, and worshipping others (shirk) is a grave sin.
- Angels: Angels carry out Allah’s commands without free will, with Jibril delivering revelations to prophets.
- Prophethood: Allah sent the same message of Islam through various prophets, starting with Adam.
- Holy Books: Both recognize the same revealed scriptures, but only the Qur’an remains unaltered as Allah’s true word.
- Day of Judgment: Both believe in resurrection, judgment, and the existence of heaven and hell.
Differences

|
172 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between Sunnii & Shi'a Core Beliefs - Religion, Philosophy & Ethics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What are the primary differences in core beliefs between Sunni and Shi'a Muslims? |  |
| 2. What are the Five Roots of Usul ad-Din in Shi’a Islam? |  |
| 3. How did the historical split between Sunni and Shi'a Islam occur? |  |
| 4. What role do the Imams play in Shi'a Islam? |  |
| 5. Why is the concept of justice (Adalah) significant in Shi’a Islam? |  |














