Disorders of Muscular & Skeletal System | Biology for Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction
The human body is a well-oiled machine that has numerous components and functions that work in conjunction with each other to keep this machine in good operating condition. One of these parts is the muscular and skeletal system. In this informative piece, we will discuss Muscular and Skeletal Disorders.
The Musculoskeletal System Musculoskeletal System
Musculoskeletal System
This musculoskeletal system consists of muscles, ligaments, joints, tendons, connective tissue, bones, etc. The muscular system permits movement of the body, maintains posture, circulates blood and so on. Without the skeletal system or in the absence of bones the whole system would collapse and end up being a pile of tissues. Therefore, it can be understood that one cannot debate the importance of one component over the other.
Muscular and Skeletal Disorders
A disorder can be defined in layman terms as a deviation from an order or an abnormality. This disorder can afflict any machine or human body. The human body, like most machines, undergoes wear and tear over time, because of age or misuse. This wear and tear lead to disorders. The muscular and skeletal system is also subject to diseases and this affects the human body adversely. Below are mentioned a few Muscular and Skeletal Disorders. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
List of Disorders
- Myasthenia gravis: It is the abnormal weakening and rapid fatigue of certain muscles. It is due to a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles.
- Muscular Dystrophy: This is mostly hereditary. It causes progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscle, which controls movement.
- Tetany: It is caused due to low blood calcium and is characterized by rapid or wild spasms.
- Arthritis: Inflammation of one or more joints. Arthritis leads to the limited movement of joints and pain.
- Osteoporosis: The chances of contracting this disease increases with age, resulting in reduced bone mass and fragile bones, thus increasing chances of fracture. Low levels of estrogen are a common cause.
- Gout: This too is the inflammation of joints, but due to an accumulation of uric acid crystals.
A) Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic neuromuscular disease that leads to fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue. The disease is characterized by variable degrees of weakness of the skeletal muscles. The name myasthenia gravis is derived from a Latin word, meaning “grave muscle weakness.” The muscle weakness happens mainly due to the circulation of antibodies which block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. By blocking the ability of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to bind to these receptors in the muscle, these antibodies deter motor neurons from signalling the muscle to contract.
The muscle weakness happens mainly due to the circulation of antibodies which block nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction. By blocking the ability of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to bind to these receptors in the muscle, these antibodies deter motor neurons from signalling the muscle to contract.
Alternatively, in a much rarer form, muscle weakness is the result of a genetic defect in some portion of the neuromuscular junction that is inherited at birth as compared to the development through passive transmission from the mother’s immune system at birth or through autoimmunity later in life.
Myasthenia Gravis Symptoms
The major symptom of myasthenia gravis is in the form of weakness in the voluntary skeletal muscles, that are the muscles which control the area. The muscles fail to contract as they are unable to respond to nerve impulses. Without proper transmission of the impulse, the communication is blocked between nerves and muscles.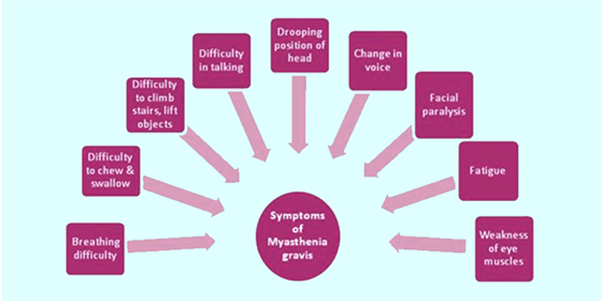 Myasthenia Gravis Symptoms
Myasthenia Gravis Symptoms
Symptoms of myasthenia gravis include:
- Hoarse voice.
- Double vision.
- Drooping of eyelids.
- Difficulty in talking.
- Difficulty in swallowing or chewing.
- Problems in lifting objects and walking upstairs.
- Difficulty in breathing due to muscular weakness.
Although myasthenia gravis could affect any of the muscles that you control voluntarily, certain muscle groups are more commonly affected than others, some of them are:
1. Eye Muscles
- Double vision.
- Drooping of one or both eyelids.
2. Face and Throat Muscles
- Altered speaking.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Problems in chewing.
- Limited facial expressions.
Myasthenia Gravis Causes
Myasthenia gravis is resulted by a defect in the transmission of nerve impulses to muscles. It occurs when normal communication between the nerve and muscle is interrupted at the neuromuscular junction—the place where nerve cells connect with the muscles they control.
This neuromuscular disease is caused by transmission defects in nerve impulses to muscles. The neuromuscular junction is apparently affected: acetylcholine, which produces muscle contraction under normal conditions no longer produces the contractions necessary to muscle movement.
Myasthenia Gravis Diagnosis
Myasthenia Gravis is a long-term and autoimmune condition, which results in muscle weakness. It is very difficult to diagnosis Myasthenia gravis as its symptoms tend to get worse with the severity of the weakness and varies from person to person.
Based on the symptoms, infectious diseases and other past medical histories, an individual is allowed to undergo certain physical examinations and several other tests to confirm the exact cause of the disease. These tests include – blood tests, electromyography, CT scan or MRI scan, few neurological tests, nerve stimulation, edrophonium tests, etc.
Myasthenia Gravis Treatment
Myasthenia gravis is believed to be caused by variations in certain genes. The disorder occurs when the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body’s tissues. There is no cure for myasthenia gravis. The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms and control the activity of your immune system through the below-mentioned ways:
- Medication.
- Plasma Exchange.
- Lifestyle Changes.
- Thymus Gland Removal.
- Intravenous Immune Globulin.
- Avoid stress and heat exposure.
- Rest to help minimize muscle weakness.
B) Tetany
Tetany refers to a condition in which the nerves innervating a particular muscle become overstimulated and cause involuntary contractions of muscles called as spasms. Tetany is also referred to as tetanic seizures.
Manifestations
- Includes spasms of the carpal (wrist) muscles, an extension in interphalangeal joints (joint present between bones of fingers of hands and toes of feet).
- Spasms in the larynx (laryngospasm).
- Convulsion episodes.
- Tingling sensation in distal extremities called paresthesias.
- Heart dysfunction, vomiting.
Causes of Tetany
Hypocalcemia: This condition refers to a below-normal level of calcium in plasma. Note- the normal concentration of calcium ions in a healthy adult is about 8-10.5 mg/dl in serum. Low free calcium levels in the plasma increase the depolarization of the neurons thereby increasing neuronal excitability.
What are the possible ways by which hypocalcemia can occur?
- Decreased levels of parathormone: Parathormone (PTH) is a hormone released by the parathyroid gland (Glands present behind thyroid gland). PTH functions as maintaining serum calcium levels by exercising its effect on bone, kidneys and intestine. Basically, its main function is to increase the calcium levels in the plasma. Now, this can be achieved by various methods.
Firstly, it takes out or mobilizes calcium from bone to plasma.
Secondly, it can increase absorption of calcium present in the food through the intestine to increase calcium in the plasma.
Lastly, it can increase the plasma calcium levels through increased resorption of calcium from renal tubules thereby increasing calcium levels in blood plasma and reducing it in the urine.
Accidental damage to the parathyroid gland, autoimmune disorders, congenital defects can also lead to decreased PTH secretion. - Low vitamin D levels can also cause hypocalcemia as vitamin D helps in absorbing calcium. Low Vitamin D levels can be caused by lack of exposure to sunlight, malnutrition etc.
- Other factors include loss of calcium due to kidney and gastrointestinal diseases.
(i) Low levels of magnesium: As magnesium is very vital to PTH synthesis.
(ii) Alkalosis: An increase in blood pH causes albumin, a blood protein, to bind with free calcium in the plasma. This causes decreased availability of free calcium ions. Severe alkalosis may lead to tetany. Alkalosis may be caused by continuous vomiting (loss of gastric acids), increased intake of alkaline foods etc.
(iii) Clostridium tetany toxin: An infection of clostridium tetany releases a neurotoxin which inhibits the release of neurotransmitters. This can lead to increased muscle tone and muscle spasm. The disease caused so is called tetanus (lockjaw disease)
(iv) Hypokalemia: This refers to decreased potassium (K+) concentration in the blood. As we know, potassium is essential for repolarization of nerve cells, a decrease in potassium levels can lead to the various manifestation of tetany.
Treatment of Tetany
- Intravenous or oral calcium supplemented with vitamin D.
- Magnesium administration to maintain optimum Mg2+ levels.
- Administration of isotonic fluids, ammonium chloride in case of emergency (in case of alkalosis).
- Antibiotics and antitoxin in case of C.infection. For the prevention of tetanus, DPT (Diptheria, Pertussis, Tetanus) vaccination in childhood is advised.
Questions and Answers
Q.1. Do tetany and tetanus mean the same thing? What is the difference between tetany and tetanus?
Ans: One should not get confused between these two terms. Here are some differences between the two.
Q.2. Calcium ion concentration ion blood affects muscles contractions. Does it lead to tetany in certain cases? How will you correlate fluctuations in calcium levels with tetany? (NCERT)
Ans: Calcium ion concentration helps the muscle to contract in the following way:
- As an action potential reaches the muscle cells, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium in the sarcoplasm.
- The calcium so released goes and binds to the TpC subunit of troponin protein.
- The active site on actin is exposed as Ca2+ binds with troponin.
- The myosin head forms cross-bridge with actin and contraction takes place.
If the levels of calcium fall below normal, it increases the permeability of Na+ ions causing recurring depolarization and contractions. This condition is called tetany. Low calcium levels may be caused due to low parathormone levels.
C) Muscular Dystrophy
 Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy
What is Muscular Dystrophy?
Muscular dystrophy is a group of disorders that affect the voluntary muscles in the human body. People experience progressive weakening of skeletal muscle and loss of muscle mass suffering from this disease. The disease is caused due to the interference of abnormal genes in the formation of proteins required for muscle formation.
Muscular Dystrophy symptoms
The symptoms of muscular dystrophy generally manifest themselves in children, though certain forms of the disease do not surface till adulthood. The general symptoms include poor balance, inability to jump or run, waddling gait, deformation of the calf, trouble in getting up from lying or sitting positions, inability to learn from others.
Types of Muscular Dystrophy
As mentioned earlier, it is a group of diseases that affect different parts of the body. The major forms of the disease include:
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy: It is the most common form of the disease affecting 1 out of 3,500 male children worldwide. The symptoms of the disease generally occur between the age of 2 and 6. The muscles of the arms, legs, and spine are progressively deformed and in most cases, the patient is wheelchair-bound by the age of 12 and die in their late teens or early twenties.
- Becker muscular dystrophy: It is a less severe form of Duchenne which appears between the ages of 2 and 16. The progression of the disease is slow and people with Becker have a higher chance of survival than those with Duchenne.
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy: This form of the disease makes it onset in the teenage years. It begins with the weakening of the hips muscles and slowly moves up to arms, legs, and shoulders. People with this disease have difficulty in walking and are often bound to the wheelchair by the age of 20.
- Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: In this form, the disease affects the muscles of the face, shoulder blades and upper arms. The onset of the disease is generally in the early teenage years. A person suffering from this form of the disease might have trouble in chewing, closing their eyelids and moving their arms.
- Myotonic muscular dystrophy: It is the most common form of muscular dystrophy during adolescence. It is characterized by the inability to move muscles after a contraction. The muscles in the face and the neck are often the first to be affected.
 Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy
Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy Treatment
As of now, there is no precise treatment available in medical science. However, the course of the disease could be slowed down with the help of therapies, high protein diet, and medications. Exercise, yoga and respiratory care are often recommended for slowing down the rate of muscle weakening.
D) Arthritis
Arthritis is a very common disease found in almost all age groups and sexes. It is generally understood as different types of joint pains or joint disease. Arthritis is the most common cause of disability in the present world. More than 20 million individuals worldwide have Arthritis and make it very difficult for individuals to be physically active. The term Arthritis literally refers to the inflammation of joints.
What is Arthritis? Arthritis is a joint disorder featuring in the joint stiffness, joint damage or inflammation of one or more joints with the general symptoms of swelling, pain and burning sensation. There are different types of arthritis; around 200 conditions affect joints, the tissues surrounding the joint, and other connective tissue. It is a rheumatic condition, and another name for arthritis is wear and tear.
Arthritis is a joint disorder featuring in the joint stiffness, joint damage or inflammation of one or more joints with the general symptoms of swelling, pain and burning sensation. There are different types of arthritis; around 200 conditions affect joints, the tissues surrounding the joint, and other connective tissue. It is a rheumatic condition, and another name for arthritis is wear and tear.
Types of Arthritis
There are more than 100 types of identified arthritis. Among these, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout are the most common types of arthritis.
Following are the major types of arthritis:
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthritis, caused by the wear-and-tear or damages to the joint’s cartilage surrounding the bone, which results in the reduced friction among the bones. It causes severe pain and a burning sensation at the joints. It can be prevented by taking a balanced diet, maintaining the healthy weight, staying active and by avoiding injuries and repetitive actions. This type of arthritis is seen in older women and other individuals with prior joint trauma, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is the long-lasting autoimmune disorder which affects the chronic inflammation of joints and other body parts. It is caused when the immune system of individuals attacks their own cartilage and joint lining capsule – a tough membrane that encloses all the joint parts. Rheumatoid arthritis results in the erosion of two opposing bones usually affect the joints of wrists, knees and elbows and are more often seen in the teenagers or people aged 20 and above.
- Infectious arthritis: Infectious arthritis is another severe form of arthritis, caused by microbial infections, hence named as Infectious arthritis. The condition is caused by the invading of pathogens into the joints. This may lead to inflammation, swelling, and pain. The microbes that infect the joints are salmonella, shigella, Chlamydia, and gonorrhoea. Suitable treatment using antibiotics can cure the joint infection in many cases, but in rare cases, it may become critical to treat this Infectious arthritis.
Symptoms of Arthritis
Pain and burning sensation are common symptoms observed in all types of arthritis. Other symptoms include:
- Limping
- Poor sleep
- Deformity of joints
- Malaise and fatigue
- Tenderness of joints
- Muscle aches and pains
- Difficult in moving the joint
- Pain or ache around the joints
- Swelling and stiffness of joints
- Redness and warmth of the joints
In few cases, arthritis can also affect different types of joints and other organs in the body, leading to a variety of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, weight loss, swelling of glands, loss of flexibility, decreased aerobic fitness, weakness of the muscles.
Causes of Arthritis
There are many factors behind the cause of arthritis, and it depends on the type of arthritis. Women are more likely to experience osteoarthritis than men. Anything that damages the cartilage can result in Arthritis.
Few causes include:
- Old age
- Poor nutrition
- Improper Diet
- Immune attacks
- Family hereditary
- General wear and tear
- Metabolic abnormalities
- Infection attacks to the joints
Treatment of Arthritis
There is no proper or complete cure for this disorder. However, there are several other treatments available for treating the inflammation of joints, and it varies with the different types of arthritis. Overall, the goal of treatment is to reduce pain and prevent further joint damage. The most commonly used treatments are:
- Medicines
- Physical Therapy
- Joint Replacement Surgery
- Massaging and Acupressure
- Non-pharmacologic therapies
Prevention of Arthritis
There are many things that can be done to prevent arthritis. By adopting and following healthy habits, there are chances of preventing these painful diseases. Some healthy habits are:
- Regular physical activities like walking, running, swimming.
- Having a well – balanced diet food
- Including foods rich in vitamin D.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Avoid injuries and repetitive joint actions.
- Do regular exercise that has an impact on the joints.
E) Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that degrades the bones, causing it to turn brittle as a result of a loss of bone tissue and a low bone mass. Consequently, the person turns exceedingly susceptible to fractures. Such fractures are known as fragility fractures. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Causes of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis can be caused due to a variety of reasons such as:
- Low peak bone mass
- Low levels of testosterone and estrogen in men and women
- Imbalanced hormones
- Hyperthyroidism and other thyroid problems
- Kidney diseases, anorexia
- Surgical treatment on ovaries for its removal Low calcium diet
- Lack of Vitamin D
Symptoms of Osteoporosis
In the initial phases, people inflicted with osteoporosis show no visible signs or symptoms, but over time, the symptoms listed below begin to appear:
- Height loss: Loss in height in normal circumstances is a part of growth. With ageing, the discs in the spinal cord contract and shrink, leading to a loss of height. But a person suffering from this disease can experience height loss all of a sudden.
- Fractures: Fractures are the most grievous facets of this disease. It can cause debilitating, chronic and acute pain. It can be challenging associating fractures to this disease as it is asymptomatic. Fractures of the long bones in some cases, impair the mobility acutely and might require surgery.
- Broken wrists: One of the first symptoms suggesting osteoporosis is a broken wrist. After menopause, women are more susceptible to wrist fractures. Typically, one shoots their arm to the front as part of a reflex action to stop its fall. Bones in a healthy state must be able to oppose a simple fall, however, a fracture indicates osteoporosis.
- Broken hip: When a hip fractures, the top of the thigh-bone is usually the site where the break can potentially happen. Furthermore, people in their late 70s or 80s are at a higher risk for this type of injury. It is observed more in a fall-related injury.
A broken hip can give excruciating pain. In most cases, it calls for an operation. Complications arising due to old age also affect recovery.
Types of Bone Tissues
Bones provide the body with support, protection and structure for internal organs. It consists of calcium and other minerals rendering rigidity and strength. They also comprise the bone marrow, which is the site for synthesis of new blood cells.
Every bone comprises 2 types of bone tissues:
- Cortical Bone: A thick outer shell or cover rendering a solid and smooth appearance to the bones.
- Trabecular Bone: A strong mesh found within the shell.
These types of bone tissues are usually assisted by the blood supply and nerve. Bone marrow and fat fills up all the spaces in between. There are a few bones towards the end of the long bones, those in the arms and legs. These have a great proportion of trabecular bone.
Osteopenia
This condition can be thought of as a precursor to Osteoporosis. Here, the bones are not as delicate as observed in the condition of osteoporosis, but they are frailer than the normal bones. It is distinguished by the body’s inability to build new tissues as rapidly as the old bone tissues are reabsorbed making the bones weaker, which may potentially lead to osteoporosis.
It is typically observed in people above the age of 50. It can also be inherited among family members. Women are also prone to this ailment.
F) Gout
Gout is painful arthritis formed on the joints of the big toe. It is usually caused by the presence of high level of uric acid in the blood, which crystallizes and settles in the body. The uric acid in the body is formed due to the breakdown of the waste products in the bloodstream, mainly those containing the purines or alkalis. Purines are the organic compound which is produced naturally by the body. Also, they can be ingested from high-alkaline foods such as meat or by being over-weighted. Purines are the organic compounds produced naturally within the body.
When the body is affected by these uric acid crystals, it causes an inflammation and a kind of redness, swelling in the joint tissues of the big toe, which is the result of gout. This condition is commonly found in men under the age of 30 and rarely seen in women.
Symptoms of Gout
The severe or painful symptoms of gout usually resolve within a week, later they altogether disappear for months or over years of time. Some of the symptoms of this disease are given below:
- The joints such as the knees, heels, and sometimes wrist are also infected.
- More often the joint of the big toe is inflamed, which is seen in the form of reddish swollen like.
- Gout also causes severe bursitis: An inflammation caused by the fluid-filled sac of the joints.
- There is also a risk of kidney related diseases like kidney stones which are developed from the Gout.
- The occurrence of fatigue and also a high fever from this arthritis.
Pseudogout
Pseudogout, a kind of inflammatory gouty arthritis that causes stiffness, pain, redness, and swelling in the joints of the body. It can affect one or several joints at once. The knee is the part of the body that is majorly affected. Some of the other parts include the hips, elbows, shoulders, joints of the fingers, toes, and ankles.
Treatments and Prevention of Gout
The precautionary measures and remedies given below can help to prevent the gout attack:
- Add some of the nutritional supplements in your diets such as vitamin that improves and maintains health benefits.
- Focus on maintaining the normal uric acid levels, repairing tissue damages, and also promoting the healing of tissues.
- Several shreds of evidence show that regular application of ice cubes for about 20 minutes a day reduces swelling and the pain.
- Intake of protein supplements should be limited to under a 0.8g/kg of body weight per day.
- During a severe attack, a proper diagnosis and medication should be followed and a continuous focus on relieving inflammation and the pain.
|
219 videos|306 docs|270 tests
|
FAQs on Disorders of Muscular & Skeletal System - Biology for Grade 11
| 1. What are some common disorders of the muscular system? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis? |  |
| 3. What are some risk factors for developing musculoskeletal disorders? |  |
| 4. What are some common treatment options for musculoskeletal disorders? |  |
| 5. Can musculoskeletal disorders be prevented? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Grade 11 exam
|

|

















