Distance and Direction | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Direction? |

|
| Finding Out Distance |

|
| Concepts for Understanding |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
What is Direction?
Direction is the information contained in the relative position of one point with respect to another point without the distance information. Directions may be either relative to some indicated reference or absolute according to some previously agreed upon frame of reference.
Cardinal directions: The four cardinal directions or cardinal points are:
- North
- East
- South
- West
Their initials commonly denote these directions: N, E, S, W.
East and West are at right angles to North and South, with east being in the clockwise direction of rotation from north and west being directly opposite east.
The intermediate directions of the four cardinal directions are:
- North – West
- North – East
- South – West
- South – East
Assumptions:
The direction of the top of the page is always considered as North unless specified in the question.
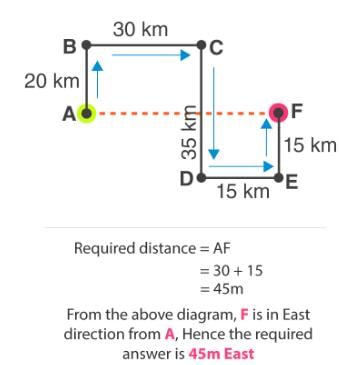
Finding Out Distance
- The student is generally expected to find out the distance between the starting point and the destination.
- And, we are expected to find out the shortest distance between the two points i.e. starting point and the destination Point.
- To find out this distance, one should draw the diagram, which shows actual path followed by the person, along with the distance traveled by him.
- Finally, the starting point and destination are joined by a straight line and distance is observed.
- For this we use Pythagoras Theorem which is as follows:-
Pythagoras Theorem
RULES FOR QUESTIONS REGARDING SHADOWS
- At the time of sunrise if a man stands facing the east, his shadow will be towards west.
- At the time of sunset the shadow of an object is always in the east.
- If a man stands facing the North, at the time of sunrise his shadow will be towards his left and at the time of sunset it will be towards his right.
- At 12:00 noon, the rays of the sun are vertically downward hence there will be no shadow.
Example: One morning after sunrise, Nandita and Ravi were sitting in a lawn with their backs towards each other. Nandita’s shadow fell exactly towards her left-hand side. Which direction was Ravi facing?
(a) East
(b) West
(c) North
(d) South
The correct answer is option (d)
Solution:
Since it was morning and Nandita’s shadow fell exactly to her left-hand side, Nandita was facing North and hence Ravi should be facing South.
Concepts for Understanding
- The right and left directional movement
- The directional reference point
- The directions of sun rays and shadow
- The correct map v/s wrong map
- Directions in Clocks
- Directions in Seating arrangement
Topic 1: The Right and Left directional movement
The right and left movement of a person is always with reference to the body moving in the scenario. It is not with respect to the person who is solving the questions.
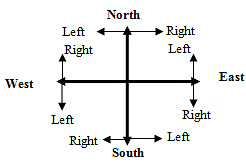
Example: A person is walking towards you, and after walking for a few meters, he takes a right turn. Which direction is he moving?
Sol: The direction we are facing is always assumed as North. Hence, if a person is walking towards us, he is walking facing (towards) South. After taking right turn, he is moving towards West.
Example: Mr Deepak Mohan walks 5 km towards the south and then turns to the right. After walking 3 km he turns to the left and walks 5 km. What direction is he facing right now?
(a) West
(b) South
(c) North-East
(d) South-West
Ans: (b)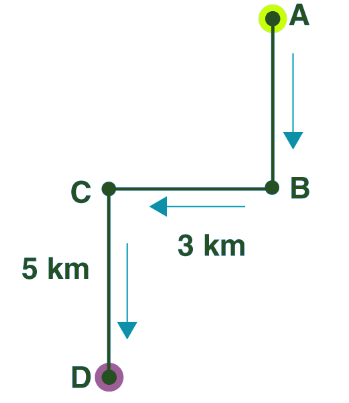 The right and left movements are with respect to Mr. Deepak Mohan. After walking 5 km towards the South, he takes a right turn and now will be facing West. After walking 3 more km he turns left and walks 5 more km. Now he is facing South.
The right and left movements are with respect to Mr. Deepak Mohan. After walking 5 km towards the South, he takes a right turn and now will be facing West. After walking 3 more km he turns left and walks 5 more km. Now he is facing South.
Hence, the answer is option (b).
Topic 2: The directional reference point
Observe the five cities on the map shown below. The five cities are New Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Chennai, and Kolkata.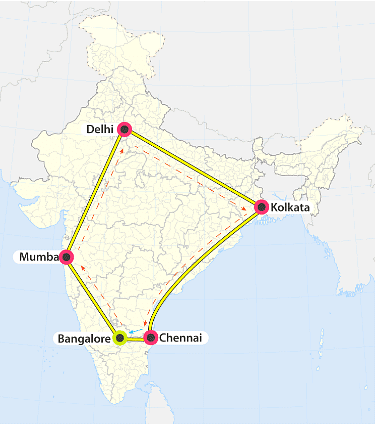
The city Bengaluru is exactly below New Delhi, Hence, Bengaluru is in the South direction with respect to New Delhi whereas it is in the West direction with respect to Chennai.
Mumbai is in North West direction with respect to Bengaluru whereas Bengaluru is in the South-East direction with respect to Mumbai. One should draw a cardinal direction at a reference city/place to find the direction of the other city.
Example: Mrs. Veena wants to go to the Krishna Rajendra market. She moved northwards and after covering some distance turned left and moved 4 km and reached a crossing. The road in front of her led to Jaynagar while the road on to her left led to Bangalore Medical College and the road on to her right led to the Krishna Rajendra market. In which direction the Krishna Rajendra market is located with reference to the starting point?
(a) West
(b) North-West
(c) South-West
(d) East
Ans: (b)
Option (b) is the correct answer.
Topic 3: The directions of sun rays and shadow
A boy is playing with a skipping rope in the playground and is facing North in the morning then, he observes that his shadow was towards his left as the Sun appeared in the East. The boy turned 180 degrees while playing, he is facing the South now. His own shadow will be towards his right as the Sun is in the east.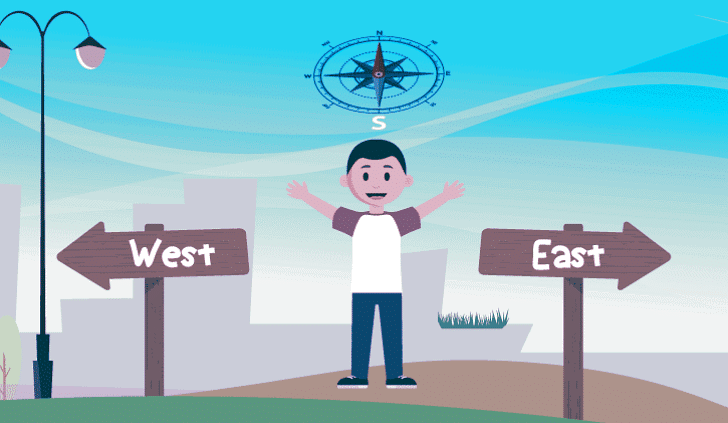 Sunrise/sunset and the shadow
Sunrise/sunset and the shadow
He does this every day once in the morning and evening. He plays facing south and observed that his shadow was towards his left and then turns and faces North he observed that his shadow was towards his right. The direction of one’s’ shadow depends on the direction and time she/he is facing.
The table below summarises the relation of shadow with respect to the direction and time: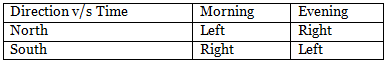
Example: One morning after sunrise, Nandita and Ravi were sitting in a lawn with their backs towards each other. Nandita’s shadow fell exactly towards her left-hand side. Which direction was Ravi facing?
(a) East
(b) West
(c) North
(d) South
Ans: (d)
Since it was morning and Nandita’s shadow fell exactly to her left-hand side, Nandita was facing North and hence Ravi should be facing South. Hence the answer is option (d).
Topic 4: Correct Map v/s Wrong Map
This section involves the comparison of two maps between which one is definitely wrong. One has to find the correct direction in the wrong map by applying logical analysis.
Example: At a crossing, there was a direction pole, which was showing all the four correct directions. But due to the wind, it turns in such a manner that now West pointer is showing South. Harish went in the wrong direction thinking that he was travelling East. In what direction he was actually travelling?
(a) South
(b) North
(c) West
(d) East
Ans: (b)
The correct answer is option (b), i.e., North.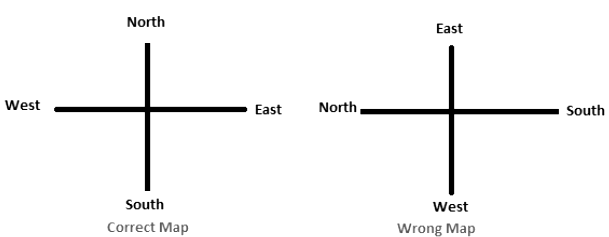
Topic 5: Directions in Clocks
All the pirates and travellers during the 16th and 17th Centuries used the compass as a navigation device which helped them in the discovery of the land that was unknown to mankind. The clocks were lacking directional information as the main task of the clock was just to tell the time.
Adding the directions to the clock paved the way to the invention of many ideas in the future. The direction in which the number ‘12’ exists was considered as the North for the reference. And all the remaining directions were marked accordingly. Hence, the numbers ‘3’, ‘6’ and ‘9’ were considered to be at East, South, and West, respectively.
Example: A clock is so placed that at 2:00 p.m. the minute hand points towards North-west. In which direction does the hour hand point at 6:00 p.m.?
(a) North-West
(b) West
(c) North-East
(d) South-East
Ans: (d)
If the Minute hand is at 12 which is North-West, then at 6.00 p.m. the hour hand will be pointing at the number 6. Since the numbers 12 and 6 are exactly the opposite. The opposite of North-West should be South-East. Hence, option (d) is the correct answer.
Topic 6: Directions in board games
In this section, the directional concepts are applied to popular board games like Chess and Carrom board or Snake and ladder to solve the questions.
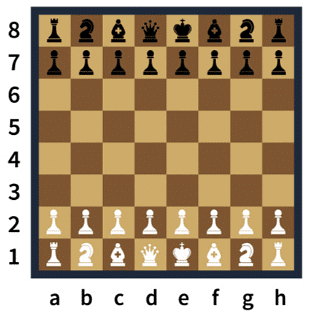
Example: A chess piece undergoes the following motion during the game. It starts from D-8, and reaches H-5, from there it reaches A-3, finally, it moves to the position H-8 and dies. In what direction the piece was when it died if the chess board is assumed to be placed in front of you?
Ans:
- Initial Position: Chess piece starts at D-8.
- Movements:
- D-8 → H-5 (Southeast)
- H-5 → A-3 (Southwest)
- A-3 → H-8 (Northeast)
- Final Position: H-8
- Direction at Death: The piece moved northeast to reach H-8.
Correct Answer: North-East
Example: P, Q, R, and S are playing a game of carrom. P, R, and S, Q are partners. S is to the right of R who is facing west. Then Q is facing?
(a) North
(b) South
(c) East
(d) West
Ans: (a)
Since R is facing West and P is the partner of R P is facing East. Also, S is to the right of R, so S will be facing South and Q is the partner of S. Therefore, Q will face North. Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Topic 7: Directions of Seating arrangement
This section involves the combination of directional logic with the seating arrangement.
Example: J,K,L,M,N,O,P and R are eight huts. L is 2 km east of K. J is 1 km north of K and Q is 2 km south of J. P is 1 km west of Q while M is 3 km east of P and O is 2 km north of P. R is situated right in the middle of K and L while N is just in the middle of Q and M.
(i) Distance between K and P is
(a) 1.0 km
(b) 1.23 km
(c) 1.41 km
(d) 1.5 km
Ans: (c)
Given Information:
- L is 2 km east of K.
- J is 1 km north of K.
- Q is 2 km southof J. This means:
- J is 1 km north of K.
- Q is 2 km south of J, so Q is 1 km south of K.
- P is 1 km west of Q.
Finding the Distance Between K and P:
- Horizontal distance from K to P = 1 km (since P is west of Q).
- Vertical distance from K to P = 1 km (since Q is 1 km south of K).
Since K, P, and Q form a right-angled triangle, we use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate the shortest distance:
Distance (KP) = Square root of (1² + 1²)
= Square root of (1 + 1)
= Square root of 2
= 1.41 km
Correct Answer: Option (c) 1.41 km
(ii) Distance between K and R is:
(a) 1.41 km
(b) 3 km
(c) 2 km
(d) 1 km
Ans: (d)
Given Information:
- L is 2 km east of K.
- R is in the middle of K and L.
Since R is exactly in the middle, the distance from K to R is half of 2 km:
Distance (K to R) = 2 ÷ 2 = 1 km
Correct Answer: Option (d) 1 km
Solved Examples
Type 1:
Q: Siva starting from his house, goes 5 km in the East, then he turns to his left and goes 4 km. Finally he turns to his left and goes 5 km. Now how far is he from his house and in what direction?
Solution:
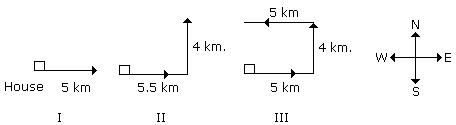
From third position it is clear he is 4 km from his house and is in North direction.
Type 2:
Q: Suresh starting from his house, goes 4 km in the East, then he turns to his right and goes 3 km. What minimum distance will be covered by him to come back to his house?
Solution:
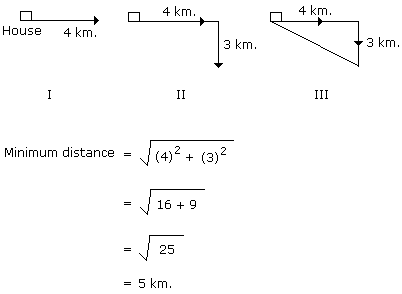
Type 3:
One morning after sunrise Juhi while going to school met Lalli at Boring road crossing. Lalli's shadow was exactly to the right of Juhi. If they were face to face, which direction was Juhi facing?
Solution: In the morning sunrises in the east.
So in morning, the shadow falls towards the west.
Now Lalli's shadow falls to the right of the Juhi. Hence Juhi is facing South.
Type 4:
Q: Hema starting from her house walked 5 km to reach the crossing of Palace. In which direction she was going, a road opposite to this direction goes to Hospital. The road to the right goes to station. If the road which goes to station is just opposite to the road which IT-Park, then in which direction to Hema is the road which goes to IT-Park?
Solution:
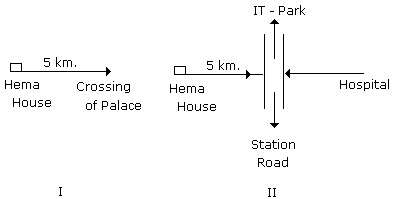
From II it is clear that the road which goes to IT-Park is left to Hema.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
FAQs on Distance and Direction - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the concept of direction in finding out distance? |  |
| 2. How can understanding direction help in determining distance? |  |
| 3. How are concepts related to distance and direction useful in bank exams? |  |
| 4. What are some common types of questions related to distance and direction in bank exams? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare effectively for distance and direction questions in bank exams? |  |