UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Power Resources
Power Resources | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
The subject ‘Power’ appears in the concurrent list of the Constitution and as such responsibility of its development lies both with Central and State governments.
- The construction and operation of generation and transmission projects in the Central sector are entrusted to Central Sector Power Corporations.
- The National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC),
- The National Hydro Electric Power Corporation (NHPC).
- The North Eastern electric Power Corporation (NEEPCO).
- The Power Grid Corporation of India Limited (PGCIL).
- The Power Grid is responsible for all the existing and future transmission projects in theCentral sector and also for the formation of the National Power Grid.
- Two joint-venture Power Corporations namely, Nathpa Jhakri Power Corporation (NJPC) and Tehri Hydro Development Corporation (THDC), are responsible for the execution of the Nathpa Jhakri Power Project in Himachal Pradesh and Projects of the Tehri Hydro Power Complex in Uttar Pradesh respectively.
- Two statutory bodies, i.e., the Damodar Valley Corporation (DVC) and the Bhakra Beas Management Board (BBMB), are also under the administrative control of the Ministry of Power.
- Programmes of rural electrification are provided financial assistance by the Rural Electrification corporation (REC) under the Ministry of Power.
- The Power Finance Corporation (PFC) provides term-finance to projects in the power sector.
- Further, the autonomous bodies (societies),i.e., Central Power research Institute (CPRI), the National Power Training Institute (NPTI) and the Energy Management Centre (EMC), are also under the administrative control of the Ministry of Power.
Rural Electrification
- Rural Electrification involves supply of energy for two types of programmes:
- Production-oriented activities like minor irrigation, rural industries, etc., and Electrification of villages.
- Rural Electrification Programmes are formuated and executed by the SEBs/State government departments.
- Likewise, the use of hydroelectricity gained currency in the areas where running water and needed technology was readily available.
- After the World War II yet another sources of energy was added. It was the nuclear energy. It called for a very sophisticated level of technology.
- All these sources of energy are known as conventional sources of energy. Among them the coal still occupies a prominent position.
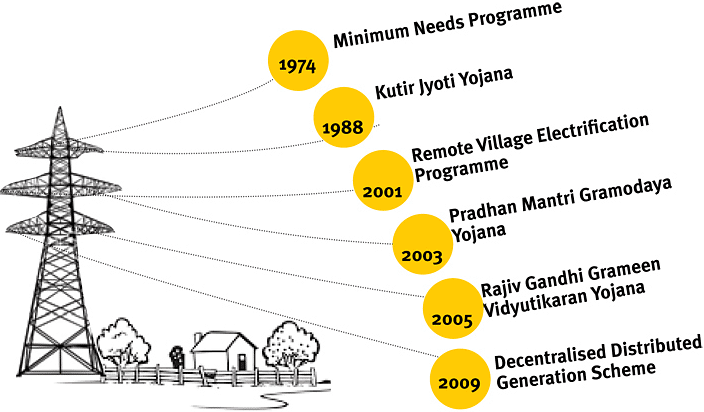 Rural Electrification
Rural Electrification
Coal
- Coal, besides being a prime source of industrial energy, is also a raw material. It is an indispensable input in steel and chemical industries. Coal, inclusive of lignite, even today accounts for 60 per cent of the country’s commercial power requirements.
- The coal deposits in India, to the tune of 98 percent belong to the Gondwana age.
- Nearly three-fourths of the coal deposits are located in the Damodar River Valley
- As on 1 January 1996, the coal resources of India (upto a depth of 1200 metre have been estimated by the Geological survey of India at 2,08,751.89 million tonnes. As on 1 January 2006 it is 2,53,300 million tonnes.
- Coal mining in India started at Raniganj in West Bengal in 1774.
- After independence the entire coal mining was taken over by the State from private hands to avoid exploitation of labour.
- The major coal fields after their regrouping are (1) Raniganj (2) Jharia (3) East Bokaro and West Bokaro (4) Panch-Kanhan, Tawa Valley (5) Singrauli (6) Talchar (7) Chandawardha and (8) Godavari Valley.
- The coal produc-tion in India was just 35 million tonnes in 1951.
- The per capita consumption of coal has increased from 135 kg to nearly 225 kg.
Lignite
- It is also called brown coal.
- It is generally a low quality coal.
- But the Indian lignite has less ash content than coal, and is consistent in quality.
- Lignite reserves in the country have been estimated at around 36,009 million tonnes as on January 1, 2004.
- Neyveli area of Tamil Nadu contains about 4150 m.t. out of which 2360 m.t. fall in the proven category.
Oil and Natural Gas
- India has a very large proportion of tertiary rocks and alluvial deposits particularly in extra-peninsular India.
- These sedimentary rocks which were once under the shallow seas hold the possibility of harbouring oil and gas deposits.
- Such potential oil bearing area in India is estimated to be over a million square kilometres, a third of the total area.
- It covers the Northern Plains in Ganga-Brahmaputra Valley, the coastal strips together with their off-shore continental shelf, the Plains of Gujarat, the Thar desert and the area around Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Till independence Assam was the only state where mineral oil was drilled and refined in the refinery at Digboi.
- After independence Gujarat Plains and the Cambay off-shore area showed evidence of hydro-carbon deposits.
- The major reserves were unexpectedly found off the Bombay coast, 115 km from the shore. So far this has been richest oil field of India. This oil field is known as Bombay High.
- Sagar Samrat, bought from Japan, was the first mobile off-shore drilling platform.
- Now India manufactures oil drills and mobile platforms for drilling in deep coastal waters.
- The latest oil deposit discoveries have also come from off-shore areas off the deltaic coasts of Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri and Mahanadi. New resources have been located in Assam.
- ONGC was set up in 1956. Indian Oil Corporation was found in 1964.
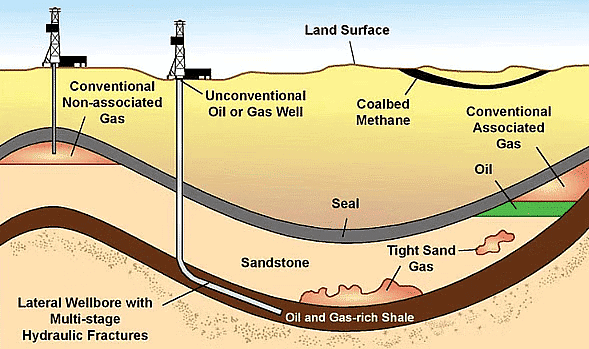 Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering
Petroleum and Natural Gas Engineering
- With acquisition of shares of Burmah Oil Company by Government in 1981, Oil India Limited became the second public sector undertaking engaged in oil exploration and production in the country.
- The gas reserves are generally found in association with oil fields. But exclu-sive natural gas reserves have been located in Tripura, Rajasthan and almost in all the off-shore oil fields of Gujarat, Maha-rashtra, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Orissa.
- Gross production of Natural Gas incre-ased from 2.36 billion Cubic Metre in 1980-81 to 16.99 billion Cubic Metre in 1989-90.
- Productin of natural gas in 1998-99 was 27.427 billion cubic metres (BCM) as compared to 26.401 BCM in 1997-98. The supply of natural gas in 1998-99 was 22.163 BCM as compared to 21.043 BCM in 1997-98. The balance recoverable reserves as on 1 April 1999 were 692 BCM. In the year 2005-06 it was 32.202 BCM.
- Hazira-Bijapur-Jagadishpur (HBJ) gas pipeline is 1730 km long and carries 18 million cubic metres of gas every day.
- Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL) was incorporated in August, 1984, with an immediate objective of construction of the cross-country HBJ Gas Pipeline.
Thermal Power
- Thermal power plants use coal, petroleum and natural gas to produce thermal electricity. These sources are of mineral origin. They are also called fossil fuels.
- Their greatest demerit is that they are exhaustible resources and can not be replenished by man. Moreover, they are not pollution-free as hydro-electricity is.
- However, electricity, whether thermal, nuclear or hydro, is the most convenient and versatile from of energy.
- The power generating plants in India work at only 53 per cent plant load factor.
Nuclear Power
- India being deficient in quality coal and natural oil, nuclear power is expected to play a complementary role.
- Uranium mines are located in Singhb-hum in Bihar and parts of Rajasthan.
- More abundant source is monazite sands on the shores of Kerala. Thorium is derived from these sands.
- Placer deposits of Bihar have further enlarged our nuclear mineral reserves.
- Cheralite and Zircomium are among the world’s largest reserves. Likewise graphite is also known to exist in the Eastern Hills.
- India’s atomic power plants are at Tarapur on Maharashtra-Gujarat border on the Arabian Sea Coast, at Rawatbhat near Kota in Rajasthan, Kalpakkam in Tamil Nadu and Narora on the banks of Ganga in Western U.P. Together they have an installed capacity of nearly 1.5 million kw.
Wind Energy
- The total potential for wind energy in the country is estimated to be 20,000 mw.
- It can be used for pumping water, a prime need in irrigating farms in the countryside.
- The States of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra and Orissa are better placed in regard to this energy.
- As of the last fiscal, Tamil Nadu accounts for the hightes share at 56.7 per cent of the cumulative capacity followed by Maharastra which accounts for 12.7%.
Tidal Energy
- The Gulf of Kachchh and Cambay are ideally suited to develop electricity from the energy produced by high tides entering into narrow creeks.
Geo-Thermal Energy
- India is not rich in this source. However, efforts are on to utilize natural energy of the hot springs at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh. Energy so produced can be used for running cold storage plants.
Energy Plantation
- Waste and denuded lands are being used for plantation and trees with high calorific value.
- They in turn provide fuel wood, charcoal, fodder, power and also scope for rural employment.
- Gasifier and Stirling Engine Systems are being developed indigenously.
- A 100 kw Gasifier System has been established at Port Blair.
Energy from Urban Waste
- A pilot plant for demonstration purposes has already been set up in Delhi to treat solid municipal waste for conversion into energy.
- It produces nearly 4 mw energy every year. Sewage in cities is used for generating gas and electricity.
Bagasse Based Power Plants
- Bagasse bassed co-generation new programme, launched in January 1994, envisages creation of 300 mw power generation capacity during the Eighth Plan.
- It is estimated that sugar mills in India can generate 2,000 mw surplus electricity during crushing season.
- Out of 10 mw energy produced by a mill, 4 mw would meet own power requirements and the rest of 6 mw energy can be utilized in irrigating fields by feeding it into the local grid.
- Like bagasse several other farm wastes like rice husk are also being used to produce electricity.
Solar Energy
- It is a universal source and has huge potential. A notable achievement has been the solar cookers.
- There are about 6 lakh soalr cookers used in the country.
- The successful applications of the solar energy so far have been for cooking, water heating, water desalination, space heating, crop drying.
- It is going to be the energy of future when fossil fuels, namely coal and oil, are totally exhausted.
The document Power Resources | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|624 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Power Resources - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are some common types of power resources? |  |
Ans. Some common types of power resources include fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, and natural gas), renewable energy sources (such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power), and nuclear power.
| 2. How is power generated from fossil fuels? |  |
Ans. Power is generated from fossil fuels by burning them to produce heat, which is then used to create steam. The steam turns a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity.
| 3. What are the advantages of using renewable energy sources for power generation? |  |
Ans. The advantages of using renewable energy sources include lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced dependence on fossil fuels, and the potential for long-term cost savings.
| 4. How does hydroelectric power work? |  |
Ans. Hydroelectric power is generated by harnessing the energy of flowing water. Water is stored in a reservoir behind a dam, and when released, it flows through turbines to generate electricity.
| 5. What are some challenges associated with using nuclear power as a power resource? |  |
Ans. Some challenges associated with using nuclear power include the risk of accidents, the long-term storage of radioactive waste, and the high initial costs of building nuclear power plants.
Related Searches

















