Dual Mode of Operations | Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
An error in one program can adversely affect many processes, it might modify data of another program, or also can affect the operating system. For example, if a process stuck in the infinite loop then this infinite loop could affect the correct operation of other processes.
So to ensure the proper execution of the operating system, there are two modes of operation:
1. User mode
When the computer system is run by user applications like creating a text document or using any application program, then the system is in user mode. When the user application requests for a service from the operating system or an interrupt occurs or system call, then there will be a transition from user to kernel mode to fulfill the requests.
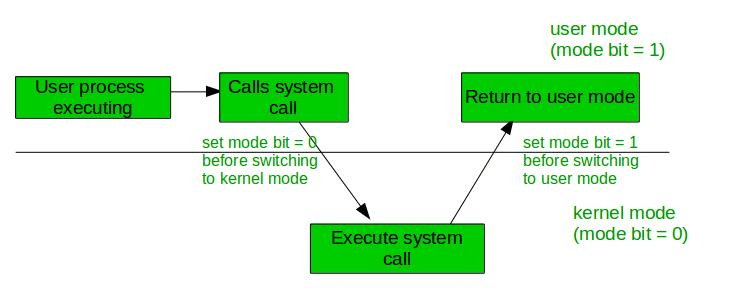
Note: To switch from kernel mode to user mode, the mode bit should be 1.
Given below image describes what happen when an interrupt occurs:
2. Kernel Mode
When the system boots, hardware starts in kernel mode and when the operating system is loaded, it starts user application in user mode. To provide protection to the hardware, we have privileged instructions which execute only in kernel mode. If the user attempts to run privileged instruction in user mode then it will treat instruction as illegal and traps to OS. Some of the privileged instructions are:
- Handling Interrupts
- To switch from user mode to kernel mode.
- Input-Output management.
Note: To switch from user mode to kernel mode bit should be 0.
Privileged and Non-Privileged Instructions in Operating System
In any Operating System, it is necessary to have a Dual Mode Operation to ensure the protection and security of the System from unauthorized or errant users. This Dual Mode separates the User Mode from the System Mode or Kernel Mode.
What are Privileged Instructions?
The Instructions that can run only in Kernel Mode are called Privileged Instructions.
Privileged Instructions possess the following characteristics:
- If any attempt is made to execute a Privileged Instruction in User Mode, then it will not be executed and treated as an illegal instruction. The Hardware traps it in the Operating System.
- Before transferring the control to any User Program, it is the responsibility of the Operating System to ensure that the Timer is set to interrupt. Thus, if the timer interrupts then the Operating System regains the control.
Thus, any instruction which can modify the contents of the Timer is Privileged Instruction. - Privileged Instructions are used by the Operating System in order to achieve correct operation.
- Various examples of Privileged Instructions include:
(i) I/O instructions and Halt instructions
(ii) Turn off all Interrupts
(iii) Set the Timer
(iv) Context Switching
(v) Clear the Memory or Remove a process from the Memory
(vi) Modify entries in the Device-status table
What are Non-Privileged Instructions?
The Instructions that can run only in User Mode are called Non-Privileged Instructions.
Various examples of Non-Privileged Instructions include:
- Reading the status of Processor
- Reading the System Time
- Generate any Trap Instruction
- Sending the final printout of Printer
Also, it is important to note that in order to change the mode from Privileged to Non-Privileged, we require a Non-privileged Instruction that does not generate any interrupt.
|
10 videos|99 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Dual Mode of Operations - Operating System - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is dual mode of operations? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of dual mode operations? |  |
| 3. How does dual mode operation work? |  |
| 4. What types of devices support dual mode operations? |  |
| 5. Are there any limitations or drawbacks to dual mode operations? |  |


















