Earth and Its Natural Satellites (Part 1) Class 5 Notes Science
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| The Earth |

|
| Internal Structure of the Earth |

|
| The Sun |

|
| The Moon |

|
| Effect on Tides |

|
| Eclipses |

|
| Artificial Satellites |

|
| Space Travel |

|
Introduction
- Scientists think that about 5 billion years ago, our solar system was a swirling cloud of hot gas and dust.
- Most of the material in this cloud came together at the centre to create the Sun.
- In various other areas, the material also clumped together to form the planets.
- The Earth, the Sun, and the Moon are all part of our solar system.
- In addition to the Earth, there are seven other planets in our solar system.

The Earth
- The Earth is the third planet in our solar system.
- It consists of air, water, and land.
- The Earth is surrounded by a layer of air known as the atmosphere.
- The atmosphere serves to protect us from the harmful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun.
Internal Structure of the Earth
- Imagine the Earth as a big surprise-filled chocolate!
- Just like chocolate has different layers – the outside shell, a soft centre, and maybe a crunchy piece inside – the Earth also has various layers.
- These layers are hidden deep below the surface we walk on.
- The first layer is the crust, which is where we live.
- Below the crust is the mantle, which is hot and gooey.
- At the centre of the Earth is the core, which is extremely hot, like a furnace!
- Each layer has an important job in keeping our planet just the way it is.
- Let’s explore these layers and see what makes the Earth so amazing from the inside out!
1. Crust
- The outer layer of the Earth is called the crust, and it is made up of rocks.
- Its thickness varies depending on where you are: it can be about 5 kilometres thick beneath the ocean floor.
- Under the continents, the crust can be as thick as 70 kilometres.
- This layer is where all the continents and oceans are found.
2. Mantle
- It is located below the crust of the Earth and has a thickness of about 2900 km.
- The upper section of the mantle is made up of hard rocks, while the lower section consists of extremely hot, molten rocks.
- During a volcanic eruption, magma is released from this layer.
- This layer contains important elements like iron, magnesium, and aluminium.
The crust and the outer mantle together form the tectonic plates, which move very slowly. The place where these plates touch each other is called a fault. When the plates move, they bump against each other. This is how an earthquake occurs.
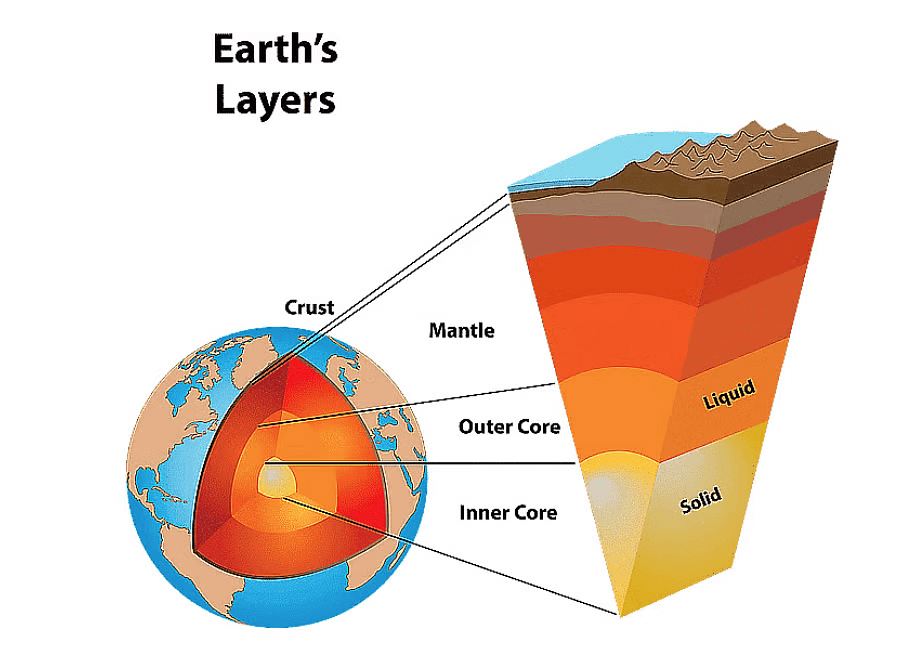
3. Core
- It is the innermost layer of the Earth.
- It has two sections: outer core and inner core.
- The outer core is approximately 2300 km thick and is made up of liquid iron and nickel.
- The inner core is around 1200 km thick and is a solid ball composed mainly of iron.
The Sun
- The sun is a massive sphere made of hot, burning gases.
- It is located at the centre of the solar system.
- There is a thin layer of air around the sun called the corona.
- The sun is the closest star to Earth, situated about 150 million kilometres away.
- The main elements that make up the sun are hydrogen and helium.
- At the very centre of the sun is the core.
- The core is the hottest part of the sun.
- In the core, hydrogen atoms are transformed into helium, which releases a significant amount of heat and light energy.
The Moon
The Moon is a big rock that travels around the Earth. It doesn’t have air or water and shines by bouncing sunlight. The Moon looks different each night, and these changes are called phases. It also makes the ocean tides go up and down. In this chapter, we will learn more about the Moon and its effects on Earth.

- The moon is the natural satellite of the earth.
- It is a lifeless place. It has no air or water.
- It does not have its own light. It shines because it reflects the sunlight that falls on it.
- No sound can be heard on the moon due to the absence of air.
- Its surface is covered with rocks and dust.
- There are tall mountains and plains on the moon.
- There are also large round holes called craters.
- If you look at the moon on a full moon night, you can see the light and dark areas. The dark areas are plains, and the light ones are mountains.
- Craters of the moon can be easily seen with a telescope.Apollo 11 was the first spacecraft to land on the moon on 21st July, 1969. It carried three American astronauts – Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin and Michael Collins.
Chandrayaan–1 was India's first space craft that went to the Moon. It was launched on October 22, 2008, from Sriharikota by ISRO. The goal was to study the Moon's surface. The mission ended on August 30, 2009, after it achieved most of its goals.
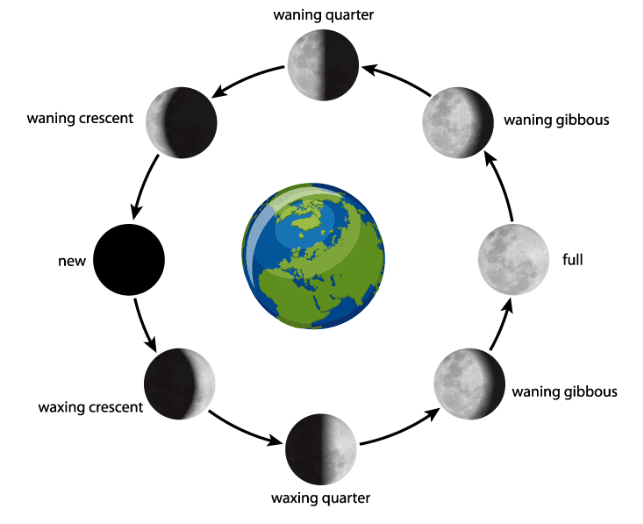
Phases of Moon
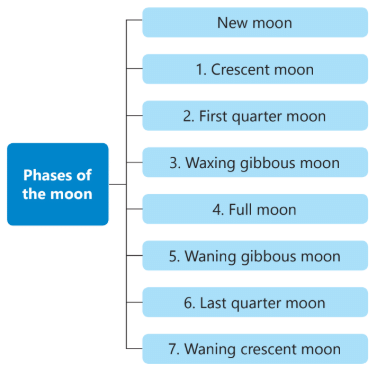
- The moon takes about one month to go around the Earth.
- It rotates slowly while revolving, so we always see the same side of the moon.
- The moon appears to change shape every day; these shapes are called phases.
- On New Moon Day, we can't see the moon because the side facing us gets no sunlight.
- A few days later, we see a crescent moon, which is a small part lit by the sun.
- In about a week, we see the first quarter moon (half of the moon is lit).
- After that, we see three-quarters of the moon, called the waxing gibbous moon.
- On the fourteenth day, we see the Full Moon, where the entire side is lit.
- After the Full Moon, the moon starts to get smaller again, going through the waning gibbous moon, last quarter moon, and waning crescent moon, until it returns to New Moon.
 Phases of Moon
Phases of Moon
[Question: 1799333]
Effect on Tides
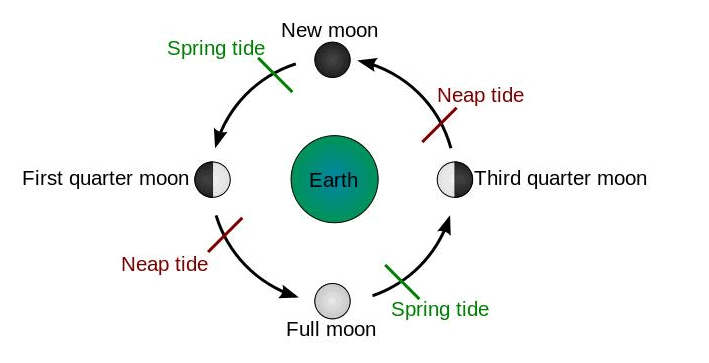
- Tides are the rise and fall of ocean water levels.
- High tide is when the water level goes up; low tide is when it goes down.
- The moon’s gravity pulls water towards it, causing high tides.
- The sun also affects tides.
- When the sun and moon line up (during a full moon or new moon), we get spring tides, which are very high and low.
- When the sun and moon are at a right angle (during the waxing or waning moon), we have neap tides, which are lower than usual.
 Effect of Tides
Effect of Tides
[Question: 1799352]
Eclipses
- The sun is a source of light and the Earth and moon are opaque objects.
- When any opaque object comes in the path of light, it blocks light and casts its shadow.
- Sometimes, the sun, the Earth, and the moon happen to come in a straight line. At times, the Earth comes between the sun and moon or the moon comes between the sun and Earth.
- In such a situation, the object in the middle casts its shadow on the other. This is called an eclipse.
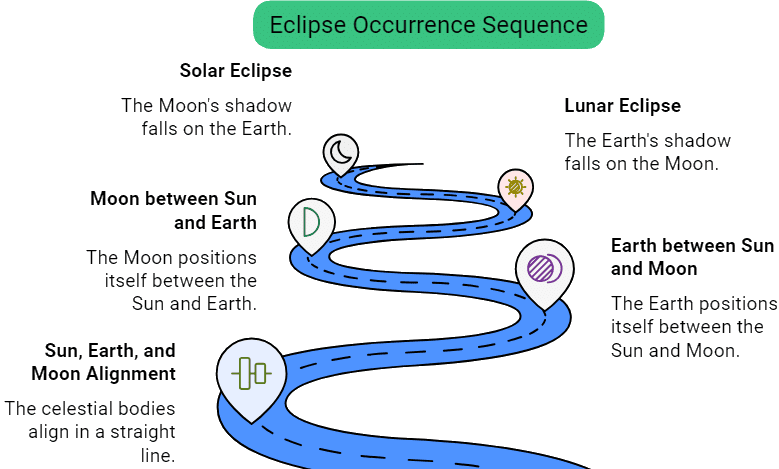
Types of Eclipse
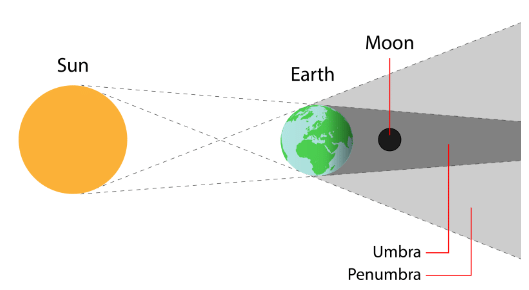
1. Lunar Eclipse
- A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth is between the sun and the moon, casting a shadow on the moon.
- If the moon is completely in the Earth's shadow, it is called a total lunar eclipse.
- If only part of the moon is in the Earth's shadow, it is called a partial lunar eclipse.
- The dark part of the shadow that blocks all the light is called the umbra.
- The lighter part of the shadow that only blocks some light is called the penumbra.
 Lunar Eclipse
Lunar Eclipse
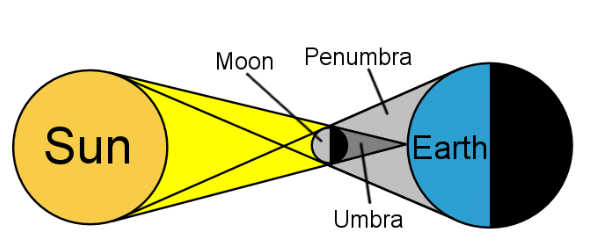
2. Solar Eclipse
- A solar eclipse occurs when the moon comes between the sun and the Earth, blocking sunlight from reaching the Earth.
- If the sun is completely blocked and cannot be seen, it is called a total solar eclipse.
- If only part of the sun is visible, it is called a partial solar eclipse.
- Solar eclipses last for a short time, usually just a few minutes..
 Solar Eclipse
Solar Eclipse
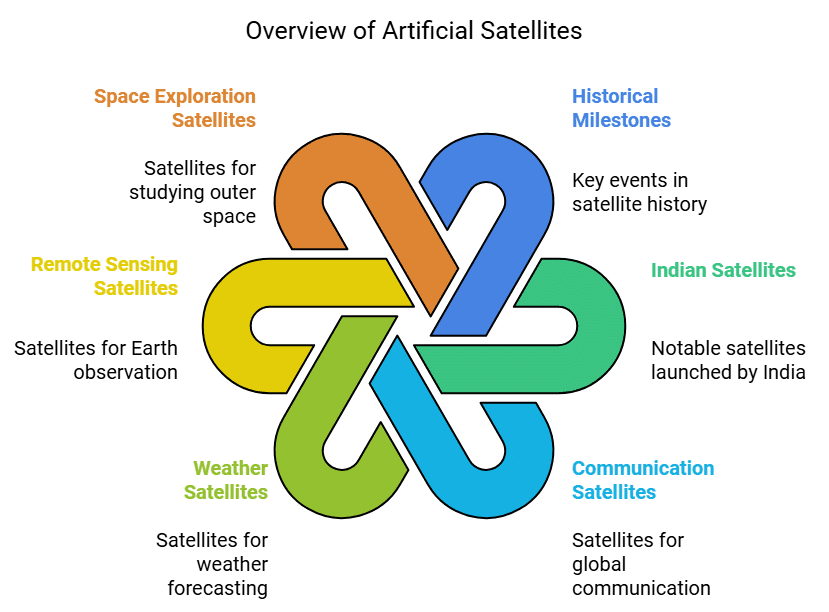
Artificial Satellites
- Artificial satellites are man-made objects that orbit around the Earth.
- They are used for various purposes, like forecasting the weather and transmitting signals for mobile phones and TV programs.
- The first artificial satellite was Sputnik 1, launched by Russia on October 4, 1957.
- Many countries, including India, have launched hundreds of satellites.
- Aryabhata was India’s first satellite, launched in 1975.
- Cartosat-2 is a remote-sensing satellite launched by India on January 12, 2018.
- India also launched the world’s first educational satellite called EDUSAT in September 2004.
- Other Indian satellites include Bhaskara, Rohini, INSAT-2A, and CARTOSAT.Uses of Artificial Satellites
- Communication satellites (like GSAT-15, launched on November 11, 2015) are used to send telephone calls and TV programs worldwide.
- Weather satellites help forecast the weather and provide early warnings for storms and cyclones.
- Remote sensing satellites take pictures of the Earth to study its surface and features.
- Some satellites are designed to study outer space, helping us learn more about planets and stars.
Space Travel

- Space is a lonely and difficult place.
- Who go to space are exposed to high levels of radiation.
- Vigorous training is needed to prepare for space missions.
- Rakesh Sharma, late Kalpana Chawla and Sunita Williams are astronauts of Indian origin who have travelled in space.

Space Travel
In short, the moon is a big rock that orbits Earth and affects the tides. It changes shape, which we call phases, and can block the sun or Earth during an eclipse. Man-made satellites help us talk to each other and predict the weather, while space travel lets us explore beyond Earth, but it's very hard to do.
|
45 videos|202 docs|45 tests
|
FAQs on Earth and Its Natural Satellites (Part 1) Class 5 Notes Science
| 1. What are the main layers of the Earth's internal structure? |  |
| 2. How does the Sun affect life on Earth? |  |
| 3. What causes tides on Earth? |  |
| 4. What are solar and lunar eclipses? |  |
| 5. What is the purpose of artificial satellites? |  |