Elastic Potential Energy | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
When a spring is stretched (or compressed), work is done on the spring which results in a transfer of energy to the spring’s elastic store Elastic potential energy is defined as:
The energy stored in an elastic object when work is done on the object
This means that any object that can change shape by stretching, bending or compressing (eg. springs, rubber bands) can store elastic energy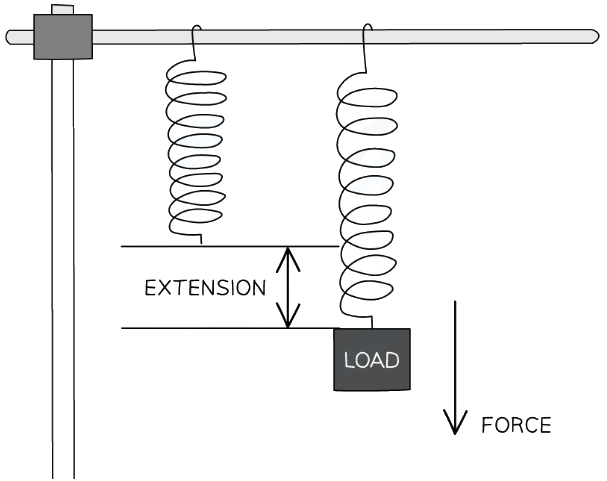 How to determine the extension, e, of a stretched spring
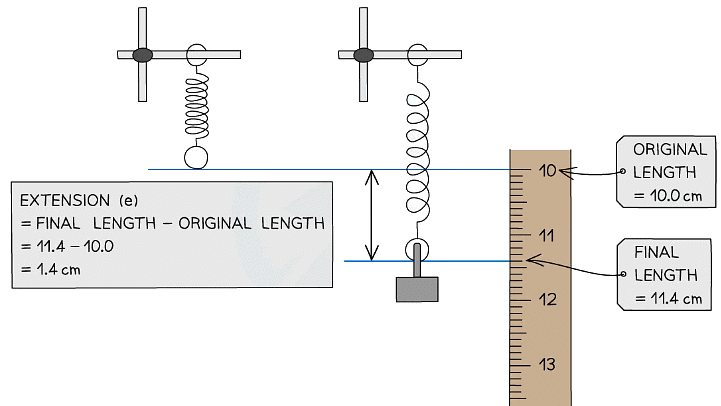
How to determine the extension, e, of a stretched spring
The amount of elastic potential energy stored in a stretched spring can be calculated using the equation:
Ee = ½ × k × e2
Where:
- Ee = elastic potential energy in Joules (J)
- k = spring constant in Newtons per metre (N/m)
- e = extension in metres (m)
The above equation assumes that the spring has not been stretched beyond its limit of proportionality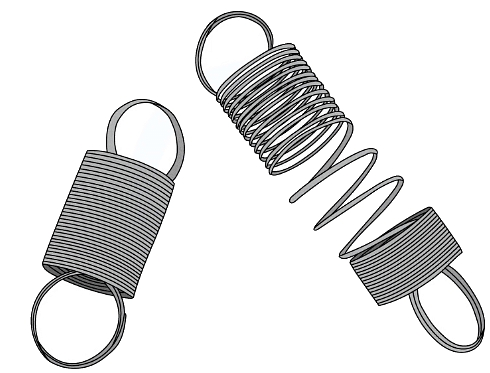 The spring on the right has been stretched beyond the limit of proportionality
The spring on the right has been stretched beyond the limit of proportionality
Example: A mass is attached to the bottom of a hanging spring with a spring constant of 250 N/m. It stretches from 10.0 cm to 11.4 cm. Calculate the elastic energy stored by the stretched spring.
Step 1: Determine the extension of the spring
Step 2: List the known quantities
Spring constant, k = 250 N/m
Extension, e = 1.4 cm = 0.014 m
Step 3: Write out the elastic potential energy equation
Ee = ½ ke2
Step 4: Calculate the elastic potential energy
Ee = ½ × 250 × (0.014)2 = 0.0245 J
Step 5: Round the answer to 2 significant figures
Ee = 0.025 J
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|