Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic Induction | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Induced EMF
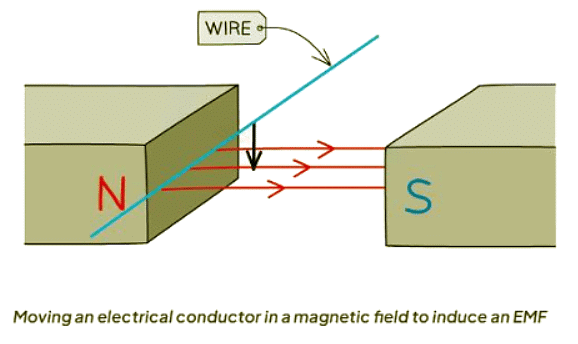
- An electromotive force (EMF) is produced in a conductor when there is relative motion between the conductor and a magnetic field.
- EMF can also be induced if the conductor remains stationary but is exposed to a changing magnetic field.
- When an electrical conductor moves within a fixed magnetic field, such as a wire cutting through magnetic field lines, it generates an EMF.
Process of Inducing an EMF
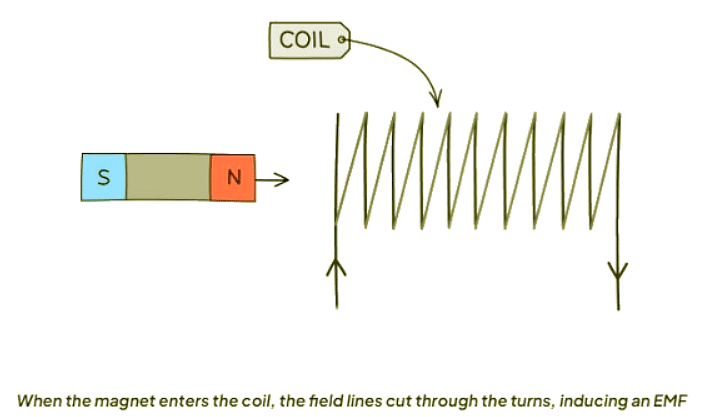
- As a magnet moves through a conductor (e.g., a coil), the magnetic field lines intersect with the turns of the conductor, inducing an EMF.
- When the magnetic field changes, an EMF is generated in the coil due to the cutting of field lines.
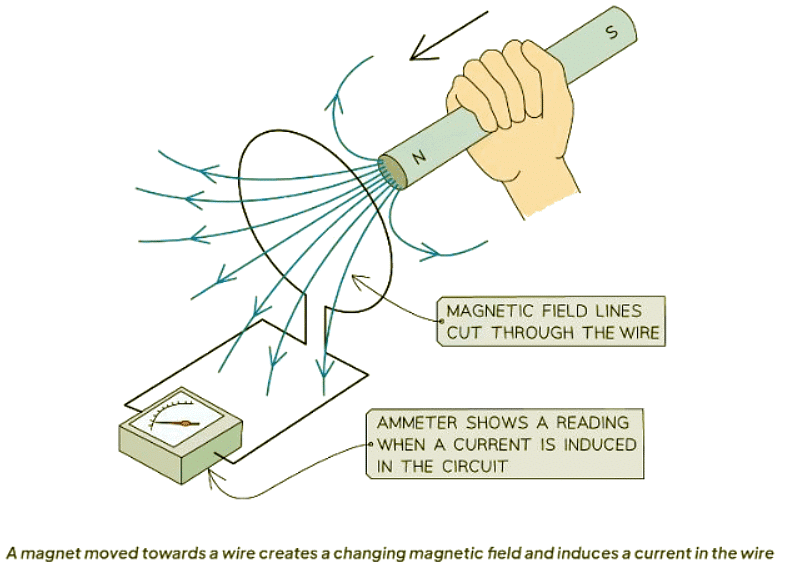
- A sensitive voltmeter is a crucial tool for measuring induced EMF
- When a conductor forms a complete circuit, it induces a current detectable by an ammeter
Lenz's Law
- The Principle of Lenz's Law: Lenz's Law is a fundamental concept in electromagnetism that describes the direction of an induced electromotive force (emf) in a circuit. It states that the induced emf always opposes the change in magnetic flux that produces it.
- Opposing Changes: This means that when there is a change in magnetic flux through a circuit, an induced current will flow in such a way as to create a magnetic field that opposes the change in flux.
- Application in Practice: For instance, if a magnet is pushed into a coil of wire, the induced current will create a magnetic field that opposes the motion of the magnet. This action is in accordance with Lenz's Law.
- Generator Effect: When a magnet is moved towards a coil, the changing magnetic field induces a current in the coil. This induced current generates a magnetic field that resists the motion of the magnet, as described by Lenz's Law.
Demonstrating Lenz's Law
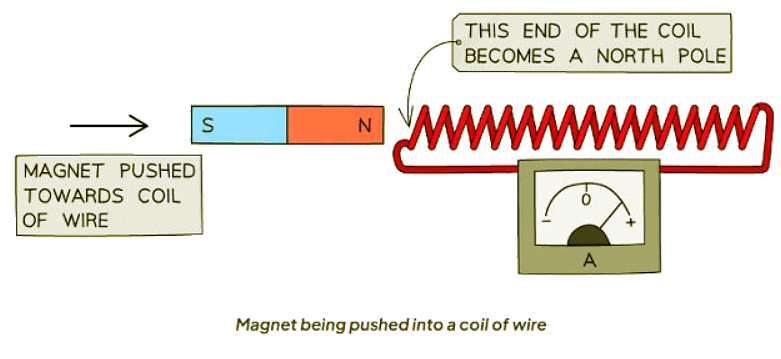
- When a magnet is pushed into a coil, a potential difference is induced in the coil due to the generator effect.
- Potential Difference: The induced potential difference always acts in a way that opposes the change causing it.
- Opposition: The coil exerts a force to resist the magnet being pushed into it.
- Pole Formation: The end of the coil nearest to the magnet becomes a north pole, resulting in repulsion of the magnet's north pole.
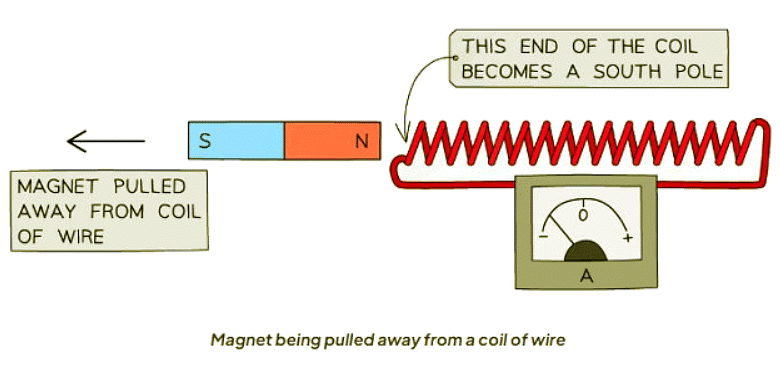
- If a magnet is pulled away from the coil, the end of the coil nearest to the magnet will become a south pole.
- South Pole Formation: The induced potential difference in the coil opposes the change and causes the end of the coil to act as a south pole, attracting the north pole of the magnet.
- Explanation:
- When a coil is moved near a magnet, a potential difference is induced in the coil.
- This induced potential difference always acts against the change that caused it.
- The coil exerts a force to resist the motion of the magnet away from the coil.
- As a result, the end of the coil closest to the magnet becomes a south pole.
- This south pole end of the coil will attract the north pole of the magnet.
Question for Electromagnetic InductionTry yourself: When does an electromotive force (EMF) get induced in a conductor?View Solution
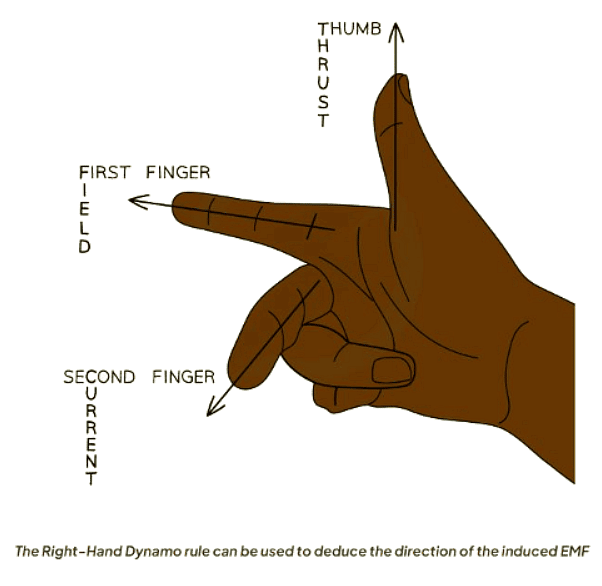
Right-Hand Dynamo Rule
- When a wire moves through a magnetic field, the Right-Hand Dynamo Rule helps determine the direction of the induced EMF.
Steps to Use the Rule:
- First Finger = Field:
- Begin by pointing the first finger (on the right hand) in the direction of the field.
- Thumb = Motion:
- Next, point the thumb in the direction that the wire is moving.
The Right-Hand Dynamo Rule simplifies the process of determining the direction of induced EMF when a wire moves through a magnetic field.
The document Electromagnetic Induction | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|182 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Electromagnetic Induction - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is electromagnetic induction? |  |
Ans. Electromagnetic induction is the process by which a changing magnetic field induces an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor, resulting in the production of an electric current.
| 2. What is Lenz's Law and how does it relate to electromagnetic induction? |  |
Ans. Lenz's Law states that the direction of the induced EMF in a conductor is always such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. This law is essential in understanding the direction of the induced current in electromagnetic induction.
| 3. How does the Right-Hand Dynamo Rule help in determining the direction of the induced current in a conductor? |  |
Ans. The Right-Hand Dynamo Rule states that if you point your thumb in the direction of the motion of the conductor, and your fingers in the direction of the magnetic field, then the direction in which your palm faces will give you the direction of the induced current.
| 4. What factors affect the magnitude of the induced EMF in electromagnetic induction? |  |
Ans. The magnitude of the induced EMF is influenced by the rate of change of the magnetic field, the number of turns in the conductor, and the area of the conductor loop.
| 5. How is induced EMF used in practical applications, such as in generators and transformers? |  |
Ans. Induced EMF is utilized in generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, and in transformers to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction.
Related Searches