Electromeric Effect | Additional Study Material for JEE PDF Download
Electromeric Effect
It involves the complete transfer of electrons of a multiple bond to one of the bonded atom in presence of an electron attacking reagent. It is called the E effect.

This effect is temporary and takes place only in the presence of a reagent. As soon as the reagent is removed, the molecule reverts back to its original position.
Electromeric effect is of two types:
+E effect: If the electrons of the π-bond are transferred to that atom of the double bond to which the reagent gets finally attached, the effect is called +E effect.
For Ex: Addition of acids to alkenes
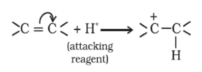
-E Effect : If the electrons of the double bond are transferred to an atom of the double bonds other than the one to which the reagent gets finally attached the effect is called -E Effect.
For Ex: Addition of Cyanide ion to the carbonyl group.
|
22 videos|163 docs|17 tests
|
FAQs on Electromeric Effect - Additional Study Material for JEE
| 1. What is the definition of the electromeric effect? |  |
| 2. How does the electromeric effect differ from the inductive effect? |  |
| 3. What are the factors that influence the magnitude of the electromeric effect? |  |
| 4. How does the electromeric effect affect the reactivity of a molecule? |  |
| 5. Can you provide an example of a reaction where the electromeric effect plays a crucial role? |  |





















