Energy Transfer | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
Energy exists in different forms (stores) and is transferred from one store to another.
Examples of energy stores:
- Light
- Sound
- Heat
- Chemical
- Electrical
- Kinetic (movement)
- Gravitational Potential (Stored by objects at a height)
- Elastic Potential (Stored by elastic materials)
Energy Transfer
Devices transfer energy from one store (form) into another.
- A light bulb converts electrical energy into light
- A loudspeaker converts electrical energy into sound
Sankey Diagrams
A Sankey diagram shows the energy transfers for a particular device.
- The energy supplied is shown at the start of the arrow
- The useful energy is shown by the arrow pointing straight ahead
- ‘Wasted’ energy is shown by the arrow curving away from the useful energy
The size of the arrows represents the amount of energy.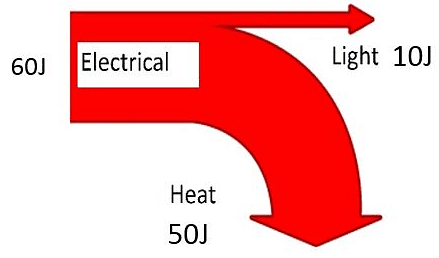
Example Sankey Diagrams:
TV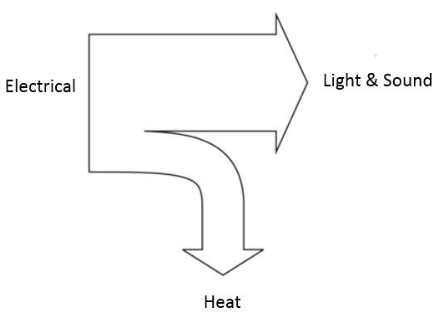
Battery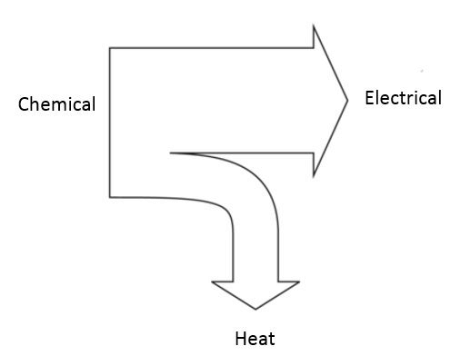 Car
Car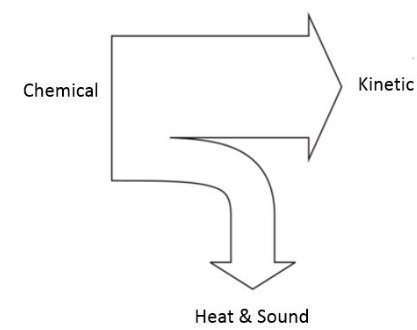
Elastic Potential Energy
Elastic Potential Energy (EPE) is stored in elastic materials when they are stretched or squashed. The EPE causes them to move back to their original shape when released.
For example:
- Energy is used to stretch a catapult
- EPE is stored in the the catapult while it is stretched
- EPE released (transformed into Kinetic Energy) when the catapult is released, causing the object to move forward
Elastic Potential Energy can be calculated using the following equation (you do NOT need to memorise this equation)
EPE = (ke2)÷2
__EPE __= Elastic Potential Energy (J)
K = spring constant (N/m)
e = extension (m)
Example 1: Calculate the EPE stored in a spring with spring constant 250N/m when it is stretched to extend by 0.2m
EPE=ke2÷2
EPE=250 x 0.22÷2
EPE= 5J
Example 2: If a spring with spring constant 300N/m has 20J of EPE, how much has it extended
e= √(2EPE÷ k)
e= √(2x20÷ 300)
e= 0.37m
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy possessed by a moving object. It depends on the velocity (speed) of the object and the mass of the object.
Kinetic Energy can be calculated using this equation: (you DO need to memorise this equation)
KE = (mv2)÷2
KE = Kinetic Energy (J)
m = mass (kg)
v = velocity (m/s)
Rearranging this equation to find velocity can be a bit tricky!
V = √(2KE ÷ m)
Example: Calculate the kinetic energy of a man of mass 80kg running at a speed of 7m/s.
KE = (mv2)÷2
KE = (80 x 72) ÷2
KE = 1960J
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational Potential energy is the energy stored by an object due to the gravitational field of the Earth (or other planet). As you lift an object higher above the Earth, it gains gravitational potential energy. If the object falls back down again, it loses gravitational potential energy.
Gravitational Potential Energy can be calculated using this equation: (you DO need to memorise this equation)
GPE = mgh
GPE = gravitational potential energy
m = mass (kg)
__g __= gravitational field strength (9.81 N/kg on the Earth)
h = height (m)
__OR __(because W=mg), this equation can be used:
GPE = Wh
W = weight (N)
Example: Calculate the gravitational potential energy gained by a pupil of mass 50kg who walks up 3 flights of stairs to a height of 15m. (gravitational field strength = 9.81 N/kg)
GPE = mgh
GPE = 50 x 9.81 x 15
GPE = 7358J
Dissipation of Energy
- Friction is a force exerted on an object sliding across another object
- Friction transfers energy as heat
- Heat energy is transferred to the surroundings which become slightly warmer
- As energy dissipates (spreads out) it gets less and less useful
- This dissipated energy is commonly referred to as ‘wasted’ energy
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|




















