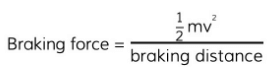Estimating Decelerating Forces & Factors Affect Thinking Distance, Reaction Time & Braking Distance | Physics for Grade 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Estimating Decelerating Forces |

|
| Factors Affecting Reaction Time |

|
| Factors Affecting Braking Distance |

|
| Braking & Friction |

|
| Braking Force & Speed |

|
Estimating Decelerating Forces
- The work done by the brakes when a vehicle slows to a halt is given by the following equation:
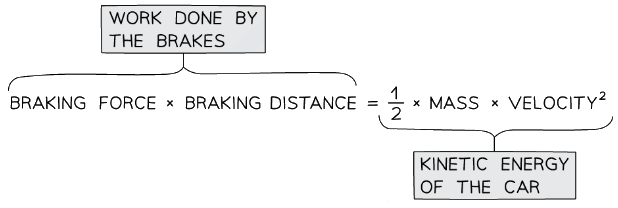 This equation shows the work done (energy transferred) by the brakes on the wheels of a car
This equation shows the work done (energy transferred) by the brakes on the wheels of a car - This equation shows that:
- The work done is the transfer of kinetic energy
- The braking distance is proportional to the speed squared (if the speed is doubled, the distance increases 4 times)
- We can use this equation to estimate the decelerating forces required for a typical vehicle moving at everyday speeds
Example: At 18 m/s (40 mph) the braking distance of a typical car of mass 1500 kg is about 24 m. Use this information to estimate the braking force for a typical car.
Step 1: List the known quantities
(i) Mass, m = 1500 kg
(ii) Braking distance, s= 24 m
(iii) Speed, v= 18 m/s
Step 2: State the relevant equation
Step 3: Rearrange for the braking force
Step 4: Substitute the values into the equation
Exam Tip: You should be able to deduce from the equation that the braking distance is proportional to the vehicle's speed2. Note, this actually doesn't apply at very high speeds because the brakes get hot and become less effective. This reduces the braking force, causing the braking distance to increase even further.
Factors Affecting Reaction Time
- The thinking distance is defined as:
The distance travelled by a car from when a driver realises they need to brake to when they apply the brakes - The reaction distance is equal to:
Reaction Distance = Speed of the car × Driver’s reaction time - The main factor that affects the thinking distance is the car’s speed, however additional factors can affect the thinking distance
- It is increased by:
- Tiredness
- Distractions (e.g. using a mobile phone)
- Intoxication (i.e. consumption of alcohol or drugs)
- Since these factors can affect the driver's reaction time, they directly affect the thinking distance
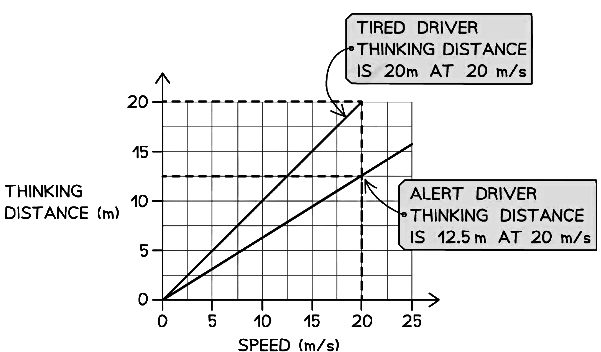
Example: The graph below shows how the thinking distance of a driver depends on the speed of the car.
(a) Describe the connection between thinking distance and speed.
(b) Some people drive when they are tired, despite warnings against doing so. Draw a new line on the graph to show how thinking distance varies with speed for a tired driver.
Part (a)
Step 1: Check if the line is straight and if it goes through the origin
(i) The graph shows a straight line through the origin
(ii) Therefore, the thinking distance is directly proportional to the speed of the carPart (b)
Step 1: Recall the factors which affect the thinking distance
Three additional factors affect the thinking distance, because they affect human reaction time:
(i) Tiredness
(ii) Distractions
(iii) Intoxication
Hence, a tired driver's reaction time is greater (i.e. it takes longer for them to react)
Step 2: Draw a line that shows greater thinking distance for the same speed
(i) At the same speed, a tired driver's thinking distance will be greater than a driver who is alert
(ii) This means a line should be drawn with a steeper gradient, as shown below:
Factors Affecting Braking Distance
- The braking distance is the distance travelled by a car under the braking force - i.e. whilst it is slowing down
- The main factor affecting the braking distance of a car is its speed
- There are additional factors which affect the braking distance, such as:
- Vehicle condition - e.g. worn tyres or poor brakes
- Road condition - wet or icy roads make it harder to decelerate
- Vehicle mass - a heavy vehicle, such as a lorry, takes longer to stop
Braking & Friction
- When a driver applies the brakes, there is a frictional force between the brakes and the wheels of the car
- This frictional force does work on the brakes - i.e. it transfers energy from the car to the brakes
- Therefore, the kinetic energy of the car decreases and the thermal energy of the brakes increases - i.e. the brakes heat up
- This means the car decelerates (slows down)
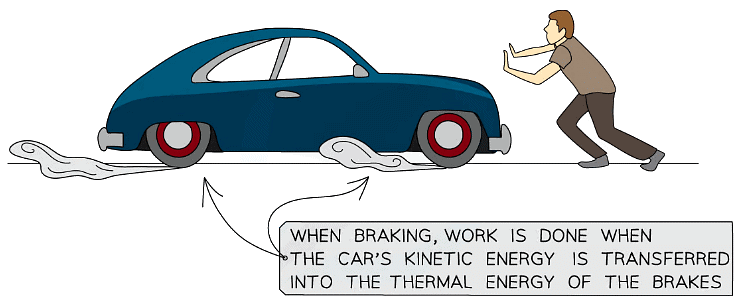 Work done by breaking transfers kinetic into thermal energy
Work done by breaking transfers kinetic into thermal energy
Braking Force & Speed
- The greater the speed of a vehicle, the greater the braking force required to bring the vehicle to a halt for a given distance
- Since the braking force would need to be larger, the deceleration of the vehicle will be large as well
- This is due to the link between resultant force and acceleration as stated in Newton's second law of motion
- Large decelerations could lead to the brakes overheating and / or loss of control of the vehicle
Example: A car is travelling at 15 m/s when the driver applies the brakes. The car decelerates uniformly and stops.The mass of the car and the driver is 1500 kg, and together they have a total kinetic energy of 168 750 J.
(a) How much work is done by the braking force to stop the car and the driver?
(b) The braking force used to stop the car and the driver was 6000 N. Calculate the braking distance of the car.
Part (a)
Step 1: Recall the process of applying brakes to a vehicle
(i) The work done is the energy transferred from the car and driver to the brakes
(ii) This energy transfer is from kinetic energy to thermal energy
(iii) In this case, the car is brought to a complete stop, so 168 750 J of energy is transferred from kinetic energy to heating up the brakes (assuming all energy is transferred to heat only!)Part (b)
Step 1: State the equation for work done
Work done = Force × distance travelled (or W = Fs)
In this case, the force doing the work (transferring energy) is the braking force
Step 2: Rearrange the equation and solve for distance travelled
Distance travelled = Work done ÷ Force
Step 3: Substitute the values for work and force
Distance = 168 750 ÷ 6000 = 28.1 m
Hence the braking distance (the distance travelled by the car under the braking force) is 28.1 m
Exam Tip: If you are asked to explain why the temperature of the brakes increases when a vehicle stops, remember, work is done by the frictional force between the brakes and the wheel.It's a common mistake to write about the friction between the wheels and the road. This does happen, but in this case, the wheels heat up the road! The brake temperature increases because there is a transfer of energy from the car's kinetic energy to the thermal energy of the brakes.
|
122 videos|150 docs|40 tests
|