Class 9 Civics Chapter 5 Extra Question Answers - Democratic Rights
Q1. What is Amnesty International?
Answer: It is an international human rights organisation which helps the people who suffer due to violation of human rights.

Q2. How are rulers of Saudi Arabia elected?
Answer: The country is ruled by a hereditary king and the people have no role in electing or changing their rulers.
Q3. How do citizens exercise their rights in Saudi Arabia?
Answer: Citizens cannot form political parties or any political organisation. There is no freedom of religion. Every citizen is required to be Muslim. Non-Muslim residents can follow their religion in private, but not in public.
Q4. What are rights?
Answer: Rights are claims of a person over other follow being over the society and over the government.
Q5. How can we claim our right?
Answer: A right is possible when we make a claim that is equally possible for others. We cannot have a right that harms or hurts others.
Q6. What are the three qualities of rights?
Answer:
- They are reasonable claims of persons.
- They are recognised by society.
- They are sanctioned by law.
Q7. Why are rights necessary for the very sustenance of a democracy?
Answer: In a democracy every citizen has to have the right to vote and the right to be elected to government. For democratic elections to take place it is necessary that citizens should have the right to express their opinion, form political parties and take part in political activities.
Q8. In what situation should a government project the citizen's rights?
Answer: Things may go wrong when some citizens may wish to take away the rights of others. This usually happens when those in majority want to dominate those in minority. The government should protect the citizen's rights in such a situation.
Q9. What are Fundamental Rights?
Answer: Some rights which are fundamental to our life are given a special status. They are called Fundamental Rights.
Q10. Name the six Fundamental Rights provided by the Indian Constitution to Indian citizens.
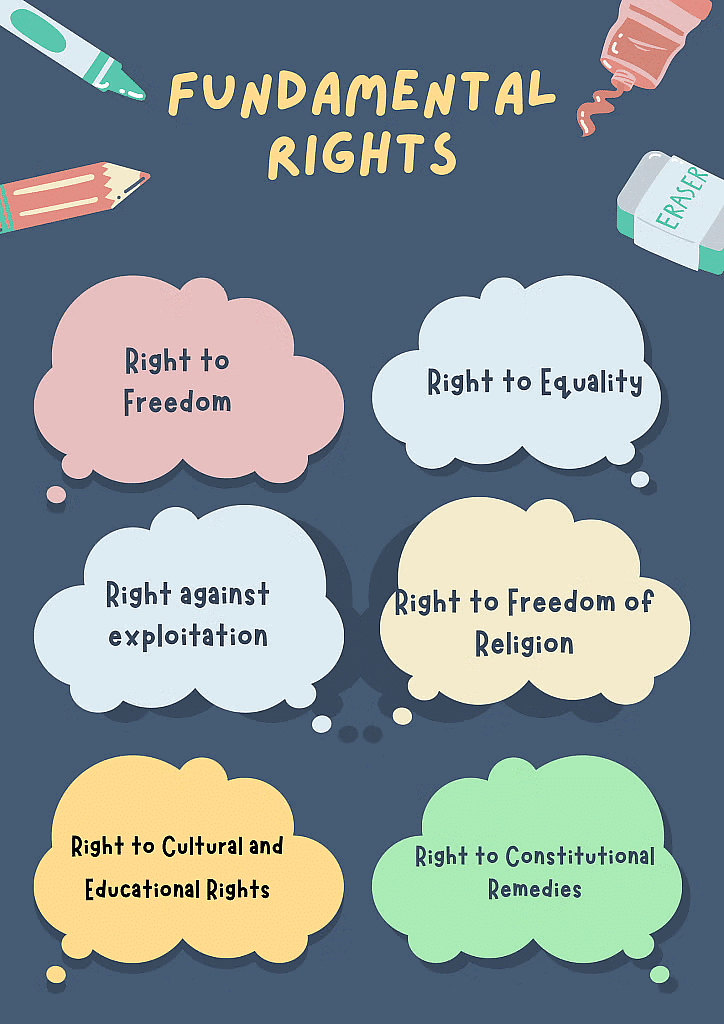 Answer:
Answer:
- Right to Equality
- Right to freedom of religion
- Right to freedom
- Cultural & Educational rights
- Right against exploitation
- Right to constitutional remedies.
Q11. What does 'Rule of law' mean?
Answer: The constitution says that the government shall not deny to any person in India equality before the law or the equal protection of the laws. It means that the laws apply in the same manner to all, regardless of a person's status. This is called the 'Rule of Law'.
Q12. How is Rule of Law considered the foundation of any democracy?
Answer: It means that no person is above the law. These cannot be any distinction between a political leaders, government official and an ordinary citizen.
Q13. Is it true that every citizen from the Prime Minister to a small farmer, is subjected to the same laws?
Answer: A few years ago a Prime Minister of the country faced a court case on charges of cheating. The court finally declared that he was not guilty. But as long as the case continued, he had to go to the court give evidences and file papers, just like any other citizen.
Q14. How is right to equality exercised?
Answer: The government shall not discriminate against any citizen on the grounds of religion, caste, ethnicity, sex or place of birth. Every citizen shall have access to public places like shops, restaurants, hotels and cinema halls. All citizens have equality in the matters relating to employment also.
Q15. What does 'untouchability' mean?
Answer: Untouchability does not only mean refusal to touch people belonging to certain castes. It refers to any belief of social practice which looks down upon people on account of their birth with certain caste labels.
Q16. What does 'Freedom' mean?
Answer: Freedom means absence of constraints. In practical life it means absence of interference in our affairs by others be it other individuals or the government.
Q17. What is meant by 'freedom of speech and expression'?
Answer: Our ideas and personality develop only when we are able to freely communicate with others. Even if a hundred people think in one way, we should have the freedom to think differently and express our views accordingly. Government in a democracy should give this freedom to its citizens.
Q18. How do citizens of India exercise freedom to travel to any part of the country?
Answer: Citizens of India enjoy single citizenship and are free to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India. This right allows lakhs of citizens to migrate from villages to towns and from poorer regions of the country to prosperous regions and big cities.
Q19. What is meant by 'traffic in human beings'?
Answer: Traffic here means selling and buying of human being, usually women for immoral purposes.
Q2O. What is 'Begar'?
Answer: 'Begar' is a practice where the worker is forced to render service to the 'master' free of charge or at a nominal remuneration. When this practice takes place on a lifelong basis, it is called the practice of bonded labour.
Q21. In what way is child labour prohibited by the Indian constitution?
Answer: The constitution prohibits child labour. No one can employ a child below the age of fourteen to work in any factory or mine or in any other hazardous work, such as railways and posts.
Q22. What is 'Secularism'?
Answer: Secularism is based on the idea that the state is concerned only with relations among human beings, and not with the relation between human beings and the God. Indian Secularism practices an attitude of a principled and equal distance from all religions.
Q23. What is a 'Secular State'?
Answer: A Secular state is one that does not establish any one religion as official religion. The state has to be neutral and impartial in dealing with all religions.
Q24. Why do we need Cultural and Educational rights?
Answer: It is language, culture and religion of minorities that needs special protection. Otherwise they may get neglected or undermined under the impact of the language, religion and culture of the majority. That is why, the constitution specifies the cultural and educational rights of the minorities.
Q25. What does Right to Constitutional Remedies imply?
Answer: It is possible that sometimes our rights may be violated by fellow citizens, private bodies or by the government. When any of our rights are violated we can seek remedy through courts. If it is Fundamental Right we can directly approach the supreme court or the High court of a state.
Q26. What are writs?
Answer: A formal document containing an order of the court to the government issued only by High Court or the Supreme Court.
Q27. What does 'Right to freedom of Religion' mean?
Answer: Every person has a right to choose, practise and propagate any religion he or she believes in. Every religious group or sect is free to manage its religious affairs.
Q28. What is PIL?
Answer: PIL is called as Public Interest litigation. Under PIL any citizen or group of citizens can approach the Supreme Court or a High Court for the protection of public interest against a particular law or action of the government.
Q29. What does 'Right to Education' mean?
Answer: Now school education has become a right for Indian citizens. The governments are responsible for providing free and compulsory education to all children up to the age of 14 years under this right.
Q30. What is RTI?
 Answer: RTI is Right to Information. Parliament has enacted a law giving the right to information to the citizens. This Act was made under the Fundamental Right to freedom of thought and expression. We have a right to seek information from government offices.
Answer: RTI is Right to Information. Parliament has enacted a law giving the right to information to the citizens. This Act was made under the Fundamental Right to freedom of thought and expression. We have a right to seek information from government offices.
Q31. What are Human Rights?
Answer: Human Rights are universal moral claims that may or may not have been recognised by law. But then rights give you a right to be treated as equal by law. Every human being who is born anywhere has the right to live and enjoy his life and should not be tortured by any means.
Q32. How were prisoners tortured by the US army in Guantanamo Bay prison?
 Answer:
Answer:
- The prisoners were being tortured in ways that violated the US laws.
- They were being denied the treatment that even prisoners of war must get as per the international treaties.
- Prisoners were not released even after they were officially declared 'not guilty'.
Q33. What was the background in which the ethnic massacre took place in Kosovo?
Answer:
- Kosovo was a province of Yugoslavia before it split. In this province, the Serbs were in minority and Albanians were in majority, while it was the other way round in the rest of the country.
- A narrow-minded Serb nationalist Milosevic had won the elections. His government was hostile to the Kosovo Albanians.
- He wanted the Serbs to dominate the country. Many Serb leaders thought that ethnic minorities like the Albanians should either leave the country or accept the dominance of the Serbs.
Q34. How does society affect the implementation of rights?
Answer: Every society makes certain rules to regulate one's conduct. They tell us what is right and what is wrong. What is recognised by the society as rightful becomes the basis of rights.
- The notion of 'right' changes from time to time and society to society.
- When the socially recognised claims are written into law, they acquire real force. Otherwise, they remain merely as natural or moral rights.
- When law recognises some claims, they become enforceable. We can then demand their application. When fellow citizens or the government do not respect these rights, we call it violation of our rights.
Q35. Which three qualities are required for calling any claim, a right?
Answer:
- Rights are reasonable claims of persons.
- Rights are recognised by the society.
- Rights are sanctioned by law.
Q36. How or why is the 'Right to Freedom' called a cluster of several rights?
Answer: Under the Indian Constitution, all citizens exercise a number of freedoms which are all covered in the right to freedom. So every citizen has the right to all of the following freedoms:
- Freedom of speech and expression
- Freedom of assembly in a peaceful manner
- Freedom to form associations and unions
- Freedom to move freely throughout the country
- Freedom to reside in any part of the country
- Freedom to practise any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business.
Q37. How can you say that 'Freedom of Speech and Expression' is one of the essential features of any democracy?
 Answer:
Answer:
- Our ideas and personality develop only when we are able to freely communicate with others. Even if hundred people think in one way, you should have the freedom to think differently and express your views accordingly.
- You may disagree with a policy of the government or activities of an association. You are free to criticise the government in your conversation with parents, friends and relatives.
- You may publicise your views through a pamphlet, magazine or newspaper. You can do the same through paintings, poetry or songs.
Q38. How can citizens exercise their freedom to hold rallies and demonstrations?
Answer:
- Citizens have the freedom to hold rallies and demonstrations in our country guaranteed by the constitution.
- But such meetings have to be peaceful.
- They should not lead to public disorder or breach of peace in society.
- Those who participate in these activities and meetings should not carry weapons with them.
- Citizens can also form associations like workers in a factory can form a workers' union to promote their interests.
Q39. Can an Indian citizen enjoy the freedom to travel in any part of the country?
Answer:
- Citizens are free to reside and settle in any part of India.
- This right allows lakhs of people to migrate from villages to towns and from poorer regions of the country to prosperous regions and big cities.
- For example, a person who belongs to Assam wants to start a business in Hyderabad. He may not have any connections with that place or people there, he may have not seen it ever. Yet as a citizen of India, he has the right to set up base there.
Q40. What procedure should a citizen follow to get proper legal justification, if he or she is arrested?
Answer:
- A person who is arrested and detained in custody will have to be informed of the reasons for such arrest and detention.
- A person who is arrested and detained shall be produced before the nearest magistrate within a period of 24 hours of arrest.
- Such a person has the right to consult a lawyer or engage a lawyer for his defence.
Q41. Which three evils are tackled by right against exploitation?
Answer:
The Constitution mentions three specific evils and declares them illegal.
- Traffic in human beings: Traffic here means selling and buying of human beings, usually women, for immoral purposes.
- Begar: Our constitution also prohibits forced labour or begar in any form. It is a practice where the worker is forced to render service to the 'master', free of charge or at a nominal salary. When this practice takes place on a lifelong basis, it is called 'bonded labour'.
- Child labour: The Constitution also prohibits child labour. No one can employ a child below the age of 14 years to work in any factory or mine or in any other hazardous work such as in the railways and at ports. Many laws have been made to prohibit children from working in industries such as beedi making, firecrackers and matchbox, printing and dyeing
Q42. How does a person exercise his right to freedom of religion?
 Answer:
Answer:
- Every person has a right to profess, practise and propagate the religion he or she believes in.
- Every religious group or sect is free to manage its religious affairs.
- A right to propagate one's religion, however, does not mean that a person has the right to compel another person to convert into his religion by means of force, fraud, inducement or allurement.
Q43. What are the provisions of cultural and educational rights?
Answer:
- The Constitution specifies the cultural and educational rights of the minorities. (i) Any section of citizens with a distinct language or culture have a right to conserve it.
- Admission to any educational institution maintained by the government or receiving government aid cannot be denied to any citizen on the grounds of religion or language.
- All minorities have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice. Here, minority does not mean only religious minority at the national level.
Q44. Mention any one exception to the Right to Equality as a Fundamental Right. Give reasons also.
Answer.
- The state has the authority to implement special provisions aimed at benefiting women and children.
- Special treatments are necessary to ensure equal opportunities for all members of society, particularly those from disadvantaged or vulnerable sections.
- These measures aim to address historical and societal inequalities faced by women and children.
- Special provisions may include targeted policies, programs, and initiatives to uplift and empower women and ensure the well-being of children.
- Such provisions are crucial for achieving true equality and social justice within a diverse society.
Q45. Mention any two limitations of freedom of speech and expression.
Answer.
Defamation and Libel: Freedom of speech does not protect statements that harm the reputation of others. Defamatory statements that are false and maliciously intended can lead to legal consequences.
Incitement to Violence: Speech that directly encourages or incites violence or illegal activities is not protected under freedom of speech. This includes speech that poses a clear and present danger to public safety or order.
Q46. “Right to Constitutional Remedies is a very special right”. What is so special about this right?
- Safeguarding Fundamental Rights: This right acts as a guardian for all other fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution.
- Access to Courts: Citizens have the right to approach the Supreme Court, High Courts, or other authorized courts if their fundamental rights are infringed upon by the State, individuals, or groups.
- Ensuring Justice: Provides a legal avenue for individuals to seek justice and redressal when their rights are unlawfully encroached upon.
- Upholding Constitutional Values: Reinforces the principle of rule of law and ensures adherence to constitutional provisions and values.
- Role in Democracy: Strengthens democratic principles by maintaining a balance between individual rights and state authority.
|
55 videos|635 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Civics Chapter 5 Extra Question Answers - Democratic Rights
| 1. What are democratic rights and why are they important? |  |
| 2. How do democratic rights protect citizens in a democracy? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the right to vote in a democracy? |  |
| 4. How can citizens protect their democratic rights? |  |
| 5. What are the consequences of violating democratic rights? |  |






















