Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7 > Facts that Matter - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
Facts that Matter - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7 PDF Download
Facts that Matter
- Fabrics are made from fibres obtained from natural or artificial source.
- Jute, cotton, wool and silk are natural fibres, they are obtained from plants or animals. Nylon, rayon like fibres are synthetic or man-made fibres.
- Polymers: A polymer is an aggregated structure consisting of numerous small simple molecules of one or more kind, called monomers. Polymers are carbon compounds. Cellulose is a natural polymer occurring in the walls of plant cells. Its simple unit is glucose. Starch is also a natural polymer occurring in the walls of plant cells. Its simple unit is glucose. Starch is also a natural polymer occurring in grains, potatoes, etc. It is also made of glucose. Proteins of various kinds are also polymers, having amino acids as their monomers. Silk and wool are made of long chain proteins and so acquire special properties.
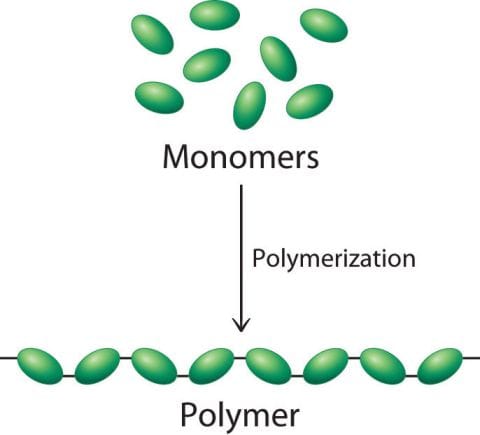 Polymers
Polymers
Man‑made common polymers are nylon, rayon, teflon, etc. They are all made by the action of heat and high pressure on the simple molecular units, forming a polymer made of many repeating units.
- Types of Synthetic Fibres
- Rayon or Artificial silk: It is made from pure cotton or wood pulp. The fibres of rayon are long, smooth and shiny. It sheds dirt easily. It is a good conductor of heat and cool to wear. The rayon fibres have properties similar to that of silk. It can be mixed with cotton to make bed sheets or mixed with wool to make carpets.
- Nylon: Nylon is a fully synthetic polymer developed simultaneously in New York and London. (Name is derived from the names of these two cities.) It was prepared from coal, water and air. Its fibres resemble the silk fibre. Chemically nylon is a polyamide like that of natural silk but these fibres are strong, tough, hard and water resistant. Nylon is used for making ropes for rocks climbing, fishing nets, combs, brushes, raincoats, parachutes, etc.
- Polyesters: Terrylene and Acrylic are synthetic fibres called polyesters. The fibres of polyester are long and smooth. These fibres do not absorb stains and easily wash. They are used for making clothes, curtains and dress material (a popular polyester). Terrylene when blended with cotton is called Terrycot while with wool it gives Terrywool. Clothes made of such polymers are convenient to use. They are crease-proof and may be used as wash and wear clothes. They are not suitable in summer as they do not absorb water and do not allow the air to pass through.
- Acrylic: These are the synthetic fibres which resemble to natural wool. They are durable and affordable. ä All the synthetic fibres are prepared by a number of processes using raw material of petroleum origin, called petrochemicals.
- Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
- Advantages:
(a) They dry up quickly, and are durable, less expensive, readily available and easy to maintain.
(b) Synthetic fibres melt on heating. - Disadvantages: If synthetic fibre clothes catch fire, they can melt and stick to the body of the person wearing it.
- Advantages:
- Plastics: P lastic is also a polymer like the synthetic fibre. All plastics do not have the same type of arrangement of units.
- Some plastic polymers have linear arrangement of units, whereas in others it is cross-linked arrangement.


Plastic is easily mouldable, recycled, reused, coloured, melted, rolled into sheets or made into wires.
Polythene ( poly + ethene) is a plastic which is used for making commonly used polythene bags.
- Thermoplastics: Plastics which get deformed easily on heating and can be bent easily are known as Thermoplastics. Polythene and PVC are some examples of thermoplastics. These are used for manufacturing toys, combs and various types of containers.
- Thermosetting Plastics: Plastics which when moulded once, cannot be softened by heating are called Thermosetting plastics. Bakelite and Melamine are the examples of Thermosetting plastics.
Bakelite is a poor conductor of heat and light. Melamine is resistant to fire and can tolerate heat better than other plastics.
- Plastics as Materials of Choice
Due to various qualities, plastics are used in our everyday life.
- Plastics are non-reactive. They do not react with water, air and do not corrode easily. So, they are used to store various materials, including many chemicals.
- Plastics are light, strong and durable. They are generally cheaper than metal. So, they are widely used in industry and household articles.
- Plastics are poor conductors of heat and electricity:
— handles of screw drivers and handles of frying pans.
— special plastic cookware is used in microwave ovens for cooking food. Because in microwave ovens, the heat cooks the food but does not affect the plastic vessel.
— Teflon is a special plastic on which water and oil do not stick. It is used for non-sticking coating on cookwares.
— Melamine Plastic coating on uniforms of firemen make them flame resistant. - Plastics and the environment:
- Biodegradable: The materials which gets decomposed through natural processes, such as action by bacteria and other microbes like fungi are known as biodegradable materials.
- Non-biodegradable: The materials which are not easily decomposed by natural processes are known as non-biodegradable materials.
- Plastics take several years to decompose, thus cause environmental pollution. Burning o f synthetic materials releases lots of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere causing air pollution.
So, plastics and synthetic fibres are not environmental-friendly.
- How can we reduce abuse of plastics?
- Avoid the use of plastics as far as possible.
- Recycle plastic waste, especially thermoplastics which can be recycled.
- Collect biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes separately. The carelessly thrown polythene wrappers of food and bags may cause clogging of drains and choking respiratory system of animals like cows resulting in their death.
- The best way is to follow 4R principle, namely, Reduce, Reuse, Recycle and Recover.
The document Facts that Matter - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7 is a part of the Class 7 Course Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Facts that Matter - Synthetic Fibres and Plastics - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 7
| 1. What are synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres are man-made fibres that are created through chemical processes using petrochemicals or other raw materials. Plastics, on the other hand, are synthetic materials made from polymers that can be shaped and molded into various forms. They are widely used in everyday products like clothing, packaging, and household items.
| 2. What are the advantages of synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres and plastics have several advantages. They are durable, lightweight, and resistant to wear and tear. They can be easily molded into different shapes and sizes, making them versatile for various applications. Additionally, they are often cheaper to produce compared to natural materials, making them more affordable for consumers.
| 3. What are the environmental concerns associated with synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres and plastics pose environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradable nature. They can persist in the environment for hundreds of years, contributing to pollution and litter. Microplastics, which are tiny plastic particles, are also a concern as they can be ingested by marine life and enter the food chain. Furthermore, the production of synthetic fibres and plastics often relies on fossil fuels, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
| 4. How can we reduce the impact of synthetic fibres and plastics on the environment? |  |
Ans. To reduce the environmental impact of synthetic fibres and plastics, several measures can be taken. Recycling is an important step, as it helps to reduce the amount of waste generated and conserve resources. Using eco-friendly alternatives such as bio-based plastics or natural fibres can also help. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of reducing single-use plastics and promoting sustainable consumption habits can contribute to minimizing the impact.
| 5. What are some common applications of synthetic fibres and plastics? |  |
Ans. Synthetic fibres are commonly used in the textile industry to make clothing, including polyester, nylon, and acrylic fabrics. Plastics find applications in various sectors, such as packaging (e.g., bottles, containers), construction (e.g., pipes, insulation), automotive (e.g., dashboards, bumpers), and electronics (e.g., computer casings, cables). They are also used in the medical field for items like syringes and implants.
|
18 videos|34 docs|19 tests
|
Download as PDF

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches


















