Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Features of Waves
Features of Waves | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Waves - Basic
- Waves serve as carriers of both energy and information.
- Waves are characterized as oscillations or vibrations around a fixed point.
- For instance, ripples induce particles of water to oscillate vertically.
- Sound waves cause particles of air to oscillate horizontally.
- In all instances, waves transmit energy without transferring material.
- In the case of water waves, it is the wave itself, not the water, that travels.
- Similarly, for sound waves, it is the wave itself, not the air molecules, that moves.
- The behavior of floating objects on water offers evidence that waves solely transmit energy, not matter.
Wave Motion
- Wave vibrations can be demonstrated using ropes (transverse) and springs (longitudinal).
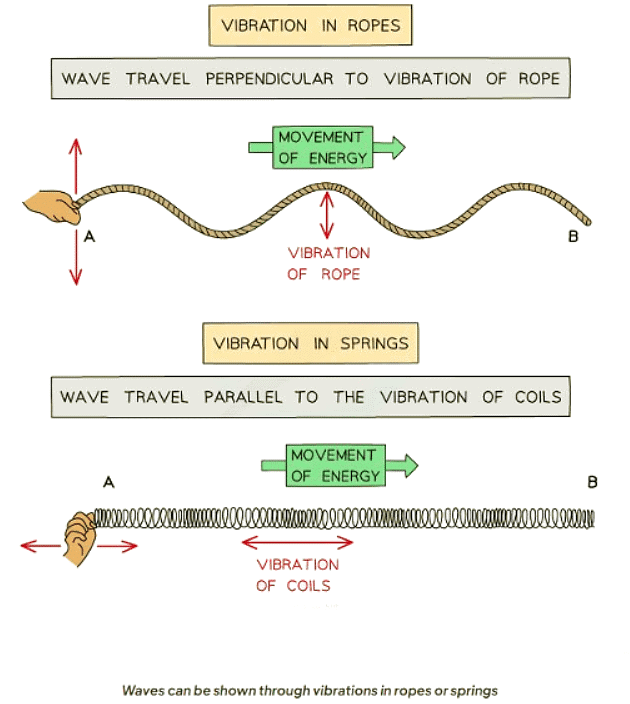
Demonstrating Wave Motion
- Characteristics of waves, like frequency, wavelength, and speed, can be studied using water waves in a ripple tank.
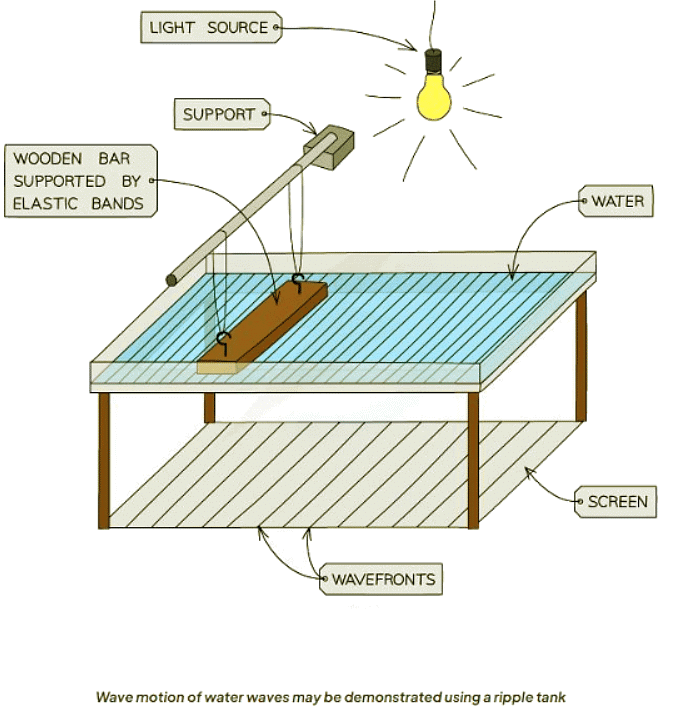
- Determining the wavelength of waves involves:
- Utilizing a ruler to measure the screen's length.
- Dividing this measured distance by the number of wavefronts.
- Calculating the frequency entails:
- Timing the passage of a specific number of waves past a designated point.
- Dividing the count of wavefronts by the recorded time.
- Finally, determining the wave speed is achieved by:
- Applying the formula: wave speed = frequency × wavelength.
Question for Features of WavesTry yourself: Which of the following statements is true about waves?View Solution
Features of a Wave
In explaining wave motion, it's crucial to understand various terms, including:
- Crest (Peak)
- Trough
- Amplitude
- Wavelength
- Frequency
- Wave speed
- Wavefront
Crest (Peak)
- A crest, or a peak, is the highest point on a wave above the equilibrium, or rest, position.
- For example, the topmost point of a water wave before it crashes onto the shore represents the crest.
Trough
- A trough is the lowest point on a wave below the equilibrium, or rest, position.
- Imagine the lowest point between two waves in an ocean; that is where the trough can be found.
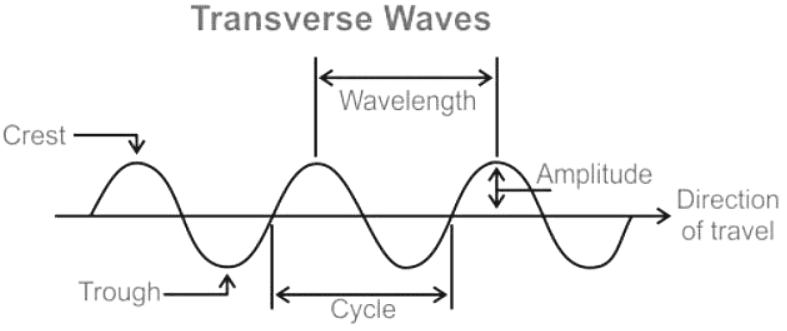
Amplitude
- Amplitude is defined as:
- The distance between the wave's undisturbed position and its peak or trough.
- Denoted by the symbol A and typically measured in meters (m).
- It represents the maximum or minimum displacement from the undisturbed position.
Wavelength
- Wavelength is defined as:
- The distance between a point on a wave to the corresponding point on the subsequent wave.
- In a transverse wave, it can be measured from one peak to the next peak.
- In a longitudinal wave, it can be measured from the center of one compression to the center of the next.
- Represented by the symbol λ (lambda) and typically measured in meters (m).
- The distance along a wave is usually depicted on the x-axis of a wave diagram.
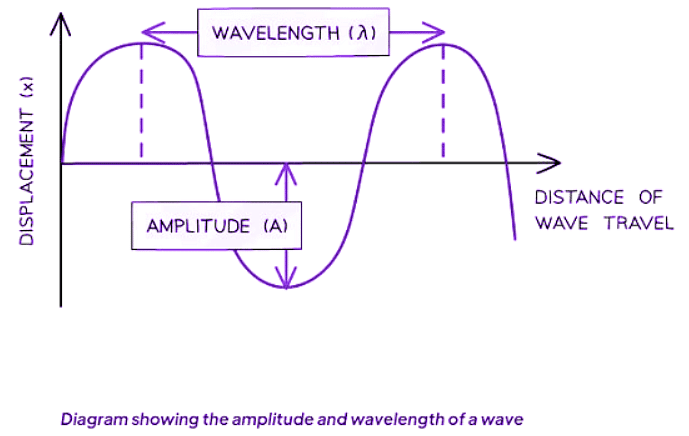
Frequency
- Frequency is the number of waves that pass a point in one second.
- It is represented by the symbol 'f' and is measured in Hertz (Hz).
Wave Speed
- Wave speed is the rate at which energy is transmitted through a medium.
- It is defined as the distance traveled by a wave per second.
- The symbol for wave speed is 'ν' and is measured in meters per second (m/s).
- Wave speed can be calculated using the formula: wave speed = frequency × wavelength.
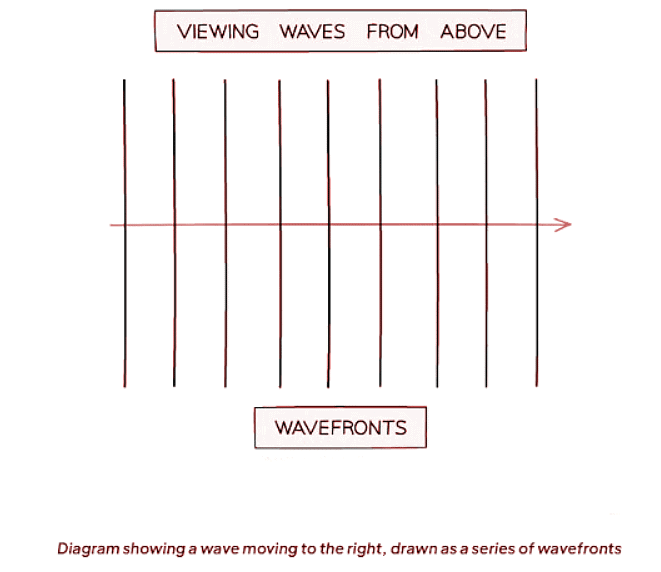
Wavefronts
- Wavefronts provide a helpful way to visualize waves from above, with each wavefront representing a single wave.
- The illustration below demonstrates how wavefronts are depicted, with the arrow indicating the wave's direction, also known as a ray.
- The spacing between wavefronts corresponds to the wavelength: closer wavefronts indicate a shorter wavelength, while distant wavefronts signify a longer wavelength.
The document Features of Waves | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
126 videos|194 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Features of Waves - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are the basic features of waves? |  |
Ans. Waves have properties such as amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. They can be transverse or longitudinal in nature.
| 2. How can we identify different types of waves? |  |
Ans. Different types of waves can be identified based on their motion - whether they move in a straight line or in a circular or oscillating motion.
| 3. How can we describe the motion of a toy duck in relation to waves? |  |
Ans. The motion of a toy duck floating on water can be affected by waves, causing it to move up and down or rock back and forth.
| 4. Can waves transfer matter from one place to another? |  |
Ans. Waves do not transfer matter from one place to another. They only transfer energy from one point to another.
| 5. How can we measure the characteristics of waves? |  |
Ans. The characteristics of waves, such as amplitude and frequency, can be measured using instruments like rulers, oscilloscopes, and frequency counters.
Related Searches















