Metallocenes & Ferrocene: Reactions & Properties | Inorganic Chemistry PDF Download
Metallocene
A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related catalyze olefin polymerization. Some metallocenes consist of metal plus two cyclooctatetraenide anions namely the lanthanocenes and the actinocenes (uranocene and others).
Metallocenes are a subset of a broader class of compounds called sandwich compounds.
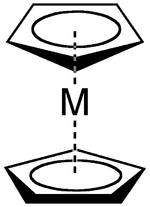
Ferrocene
IUPAC name: [Bis (cyclopentadienyl)iron(II)]
Synthesis
When metallic sodium reacts with a solution of Cyclopentadiene in THF to form sodium cyclopentadienide and liberate hydrogen.
The reaction of sodium cyclopentadienide with FeCl2 in THF gives ferrocene
Physical Properties:
1. Ferrocene is a diamagnetic cr ystalline solid.
2. Ferrocene is the most stable of the all the metallocenes.
3. It is insoluble in water but dissolves in most organic solvents.
4. It is unaffected by air. It is also stable towards hyd rolysis due to absence of ionic bonding.
5. It is readily oxidized by the oxidizing agent such as dil. HNO3, I2, Ag+, etc to give paramagnetic blue ferrocenium ion Cp2Fe+.
6. In solid state ferrocene exists in staggered form and in gas phase it exists in eclipsed form.
7. Ferrocene gives only one 1H-NMR signal because all hydrogens have same electronic environment.
8. Ferrocene behaves a Lewis base.
Reactions of Ferrocene :
The rings in ferrocene are aromatic in nature hence it undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution like benzene. Ferrocene undergoes EAS faster than benzene which shows that electrons of cyclopentadienyl are more easily available. Some EAS reactions are as follows.
Friedal – Craft Acylation
Friedal – Craft Alkylation
Sulphonation
Mannich Reaction:
Nitration and Halogenation:
The direct nitration and helogenation are not possible on ferrocene because ferrocene easily reduces to ferrocenium ion b y the conc. HNO3 and halogens
Some specific catalyst used in the special type of process
| Process | Catalyst |
| Alkene polymerization | Ziegler-Natta Catalyst (TiCl4 + AlR3) |
| Water Gas Shift Reaction | Heterogeneous catalyst: Fe—Cr or Zn—Cu oxides. Homogeneous catalyst: Fe(CO)5 or [Ru(bpy)2(CO)Cl]+ |
| Monsanto Acetic Acid Process | [Rh(CO)2I2]– |
| Wacker Process | [PdCl4]2– |
| Hydroformylation or Oxo process | Co catalyst |
| Hydrogenation of Alkenes | Wilkinson’s catalyst [RhCl(PPh3)3] |
|
50 videos|92 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Metallocenes & Ferrocene: Reactions & Properties - Inorganic Chemistry
| 1. What are metallocenes and how are they related to ferrocene? |  |
| 2. What are some common reactions of metallocenes and ferrocene? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of metallocenes and ferrocene? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of metallocenes and ferrocene? |  |
| 5. How can the knowledge of metallocenes and ferrocene be relevant to the field of materials science? |  |






















