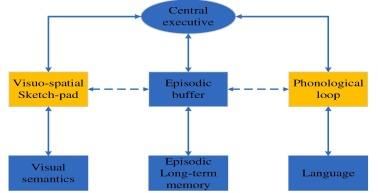
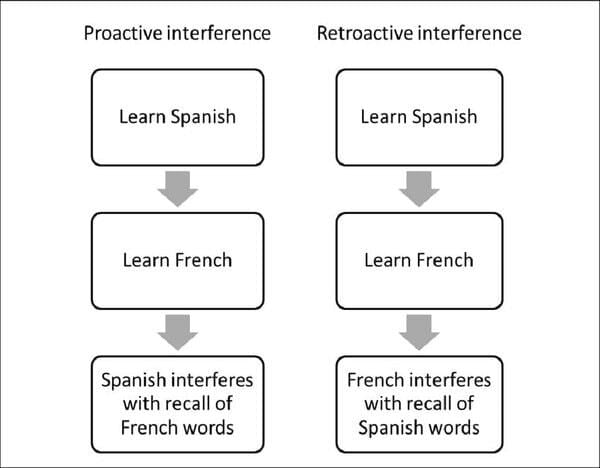
|
True or False: Short-term memory (STM) can retain information for an extended period without rehearsal. |
Card: 5 / 48 |
|
False. STM typically holds information for 30 seconds or less without rehearsal. 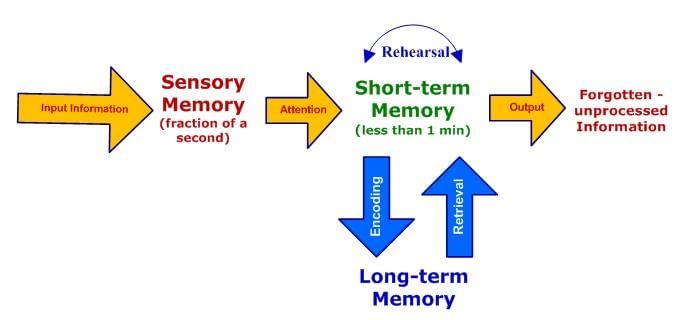 |
Card: 6 / 48 |
|
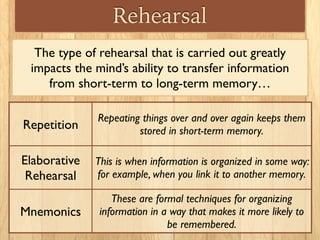
The process of transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory often involves ___ and ___ rehearsals. |
Card: 7 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Information in long-term memory (LTM) is primarily encoded ___ and can be challenging to retrieve. |
Card: 9 / 48 |
|
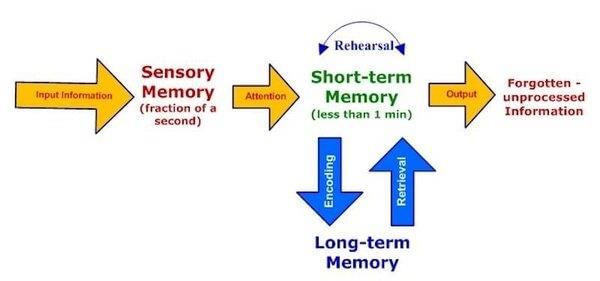
To register incoming information as an exact replica of the stimulus for a very brief period. 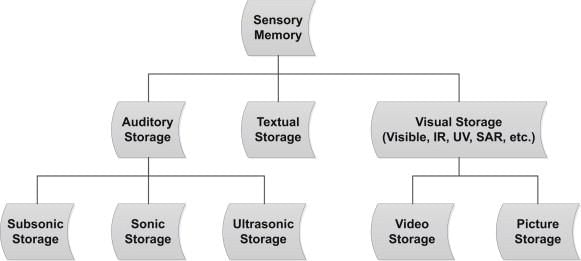 |
Card: 12 / 48 |
|
True or False: According to the Stage Model, all information in long-term memory is easily accessible. |
Card: 13 / 48 |
|
False. Information in long-term memory may be difficult to retrieve, leading to perceived forgetfulness. |
Card: 14 / 48 |
|
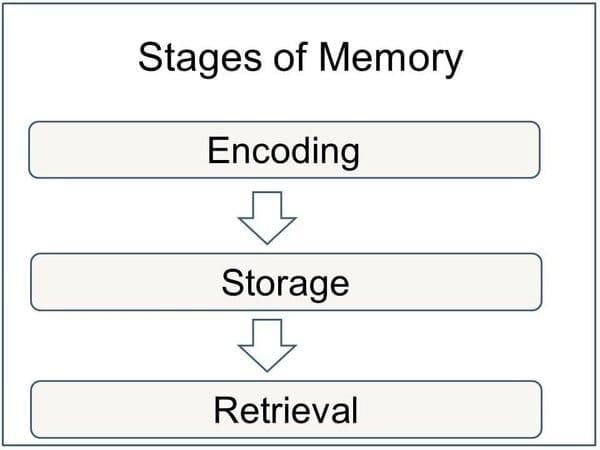
What distinguishes short-term memory from long-term memory in terms of capacity and duration? |
Card: 15 / 48 |
|
Short-term memory has a limited capacity and lasts for a short duration, typically 30 seconds or less, while long-term memory has a vast capacity and can store information indefinitely.  |
Card: 16 / 48 |
|
What does the levels of processing theory by Craik and Lockhart emphasize regarding information retention? |
Card: 17 / 48 |
|
The levels of processing theory emphasizes that the depth at which information is perceived, analyzed, and understood affects its retention; deeper semantic processing leads to better long-term memory. 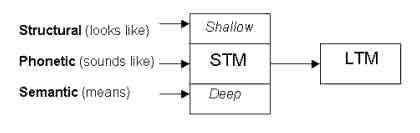 |
Card: 18 / 48 |
|
Fill in the blank: Memory produced at shallow and intermediate processing levels is likely to ____ quickly. |
Card: 19 / 48 |
|
True or False: Rote memorization is more effective than deep processing for long-term memory retention. |
Card: 21 / 48 |
|
False. Deep processing is more effective for long-term memory retention than rote memorization. 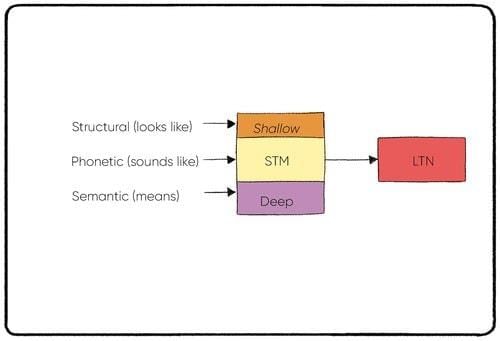 |
Card: 22 / 48 |
|
Thinking of a cat as an animal with fur, four legs, a tail, and connecting that image to personal experiences. |
Card: 24 / 48 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
Multiple choice: Which of the following best describes deep processing? A) Memorizing facts without understanding B) Analyzing the meaning of information C) Focusing on the physical appearance of information D) Recognizing words without understanding their meanings |
Card: 29 / 48 |
|
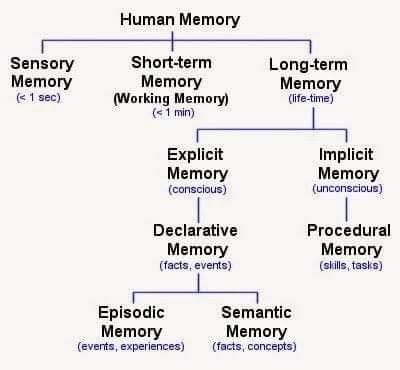
Episodic memory, which pertains to personal experiences and specific events, and semantic memory, which relates to general knowledge and facts. 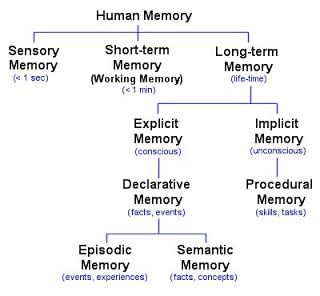 |
Card: 32 / 48 |
|
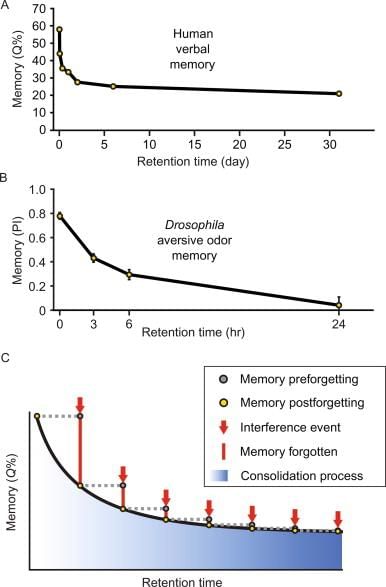
True or False: The rate of forgetting is constant over time according to Ebbinghaus's Forgetting Curve. |
Card: 35 / 48 |
|
False. The rate of forgetting is highest in the first nine hours, especially within the first hour, and then it slows down. |
Card: 36 / 48 |
|
It suggests that memories form physical changes in the brain called memory traces, which decay and become inaccessible when not used over time. |
Card: 38 / 48 |
|
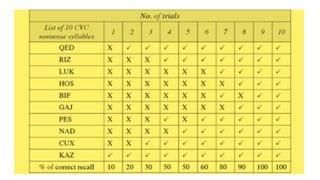
Fill in the blank: Ebbinghaus's experiments focused on memorizing lists of ___ syllables. |
Card: 39 / 48 |
|
What is the primary criticism of the Trace Decay Theory based on Ebbinghaus's findings? |
Card: 41 / 48 |
|
Experiments showed that people who remain awake after learning forget more than those who sleep, contradicting the idea that decay is the sole reason for forgetting. 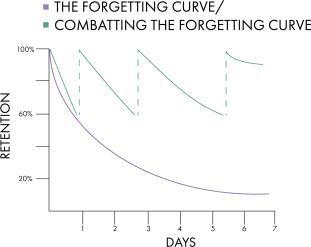 |
Card: 42 / 48 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which type of memory is primarily involved in performing tasks such as driving a car? A) Semantic Memory B) Procedural Memory C) Episodic Memory D) Declarative Memory |
Card: 43 / 48 |
|
What are the two main reasons identified for forgetting information stored in long-term memory? |
Card: 45 / 48 |
|
Insufficient memorization of the information and incorrect encoding of the information. 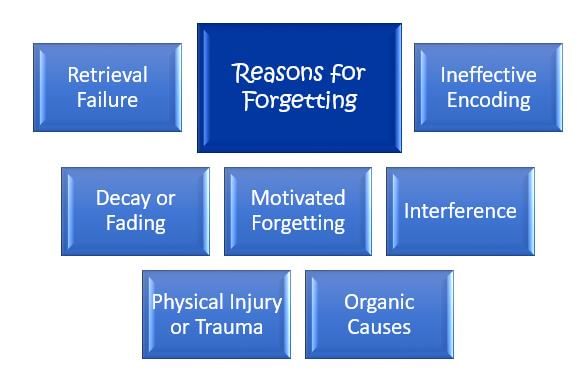 |
Card: 46 / 48 |