|
Card: 5 / 36 |
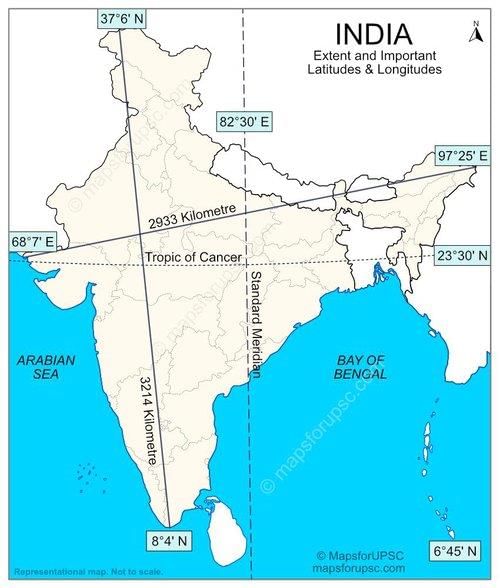
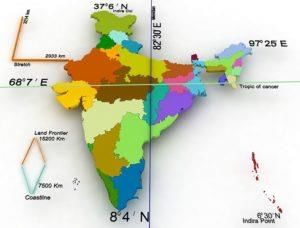
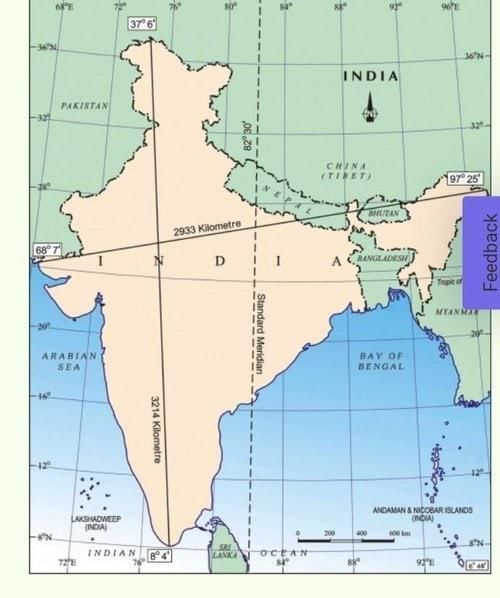
Fill in the blank: The southern boundary of India extends up to ___ N latitude in the Bay of Bengal. |
|
Card: 9 / 36 |
Fill in the blank: The distance from east to west across India is approximately ___ km. |
|
Card: 12 / 36 |
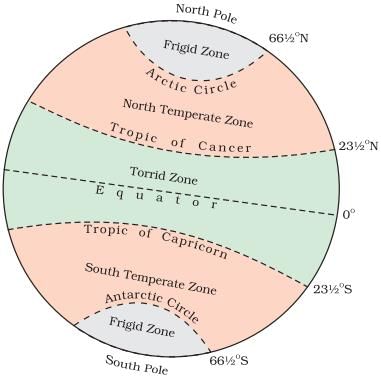
The southern part lies within the tropics, while the northern part lies in the sub-tropical zone or warm temperate zone.  |
|
Card: 14 / 36 |
The Indian subcontinent is bounded by the Himalayas, Hindukush, Purvachal hills, and the Indian Ocean. 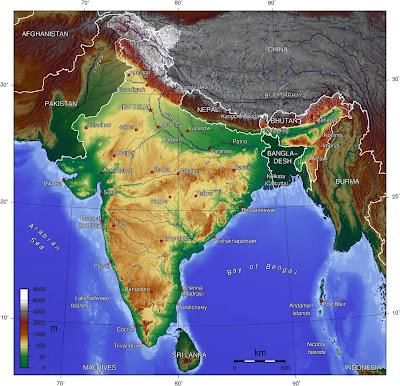 |
|
Card: 20 / 36 |
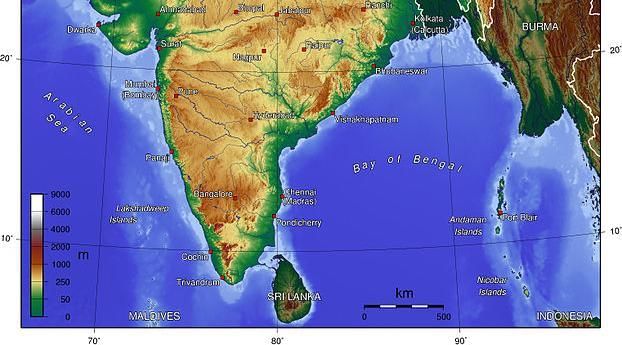
The major rivers include Ganga, Brahmaputra, Mahanadi, Krishna, Godavari, and Kaveri. 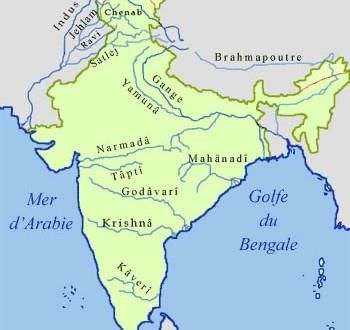 |
|
Card: 21 / 36 |
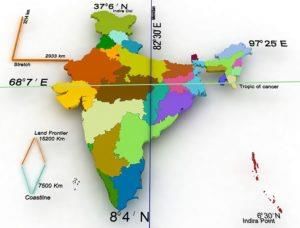
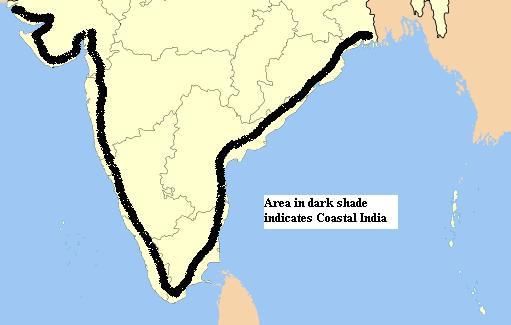
True or False: India has a total coastline of approximately 7,517 km, including its islands. |
|
Card: 24 / 36 |
India's diverse physical landscape supports varied ecosystems, including fertile river plains, mineral-rich mountains, and coastal fisheries.  |
|
Card: 27 / 36 |
Fill in the blank: India's area is approximately ___ million square kilometers. |
|
Card: 29 / 36 |
Short answer: What natural barrier contributes to the regional identity of the Indian subcontinent? |
|
Card: 31 / 36 |
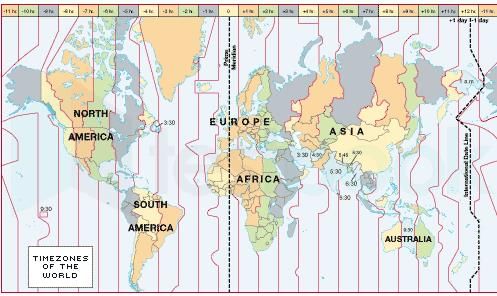
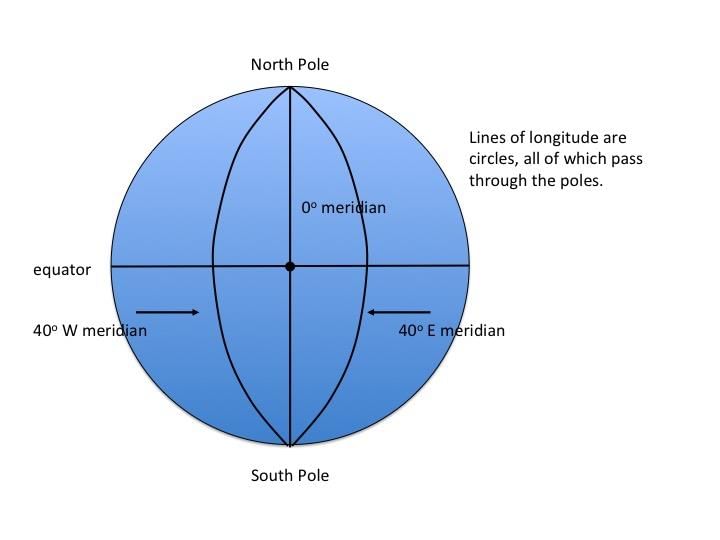
True or False: The distance between longitudes remains constant as one moves towards the poles. |
|
Card: 35 / 36 |
True or False: The standard time of a region is influenced by the height of the sun. |
|
Card: 36 / 36 |
False. Standard time is based on the central meridian of an area and has no relation to the height of the sun. 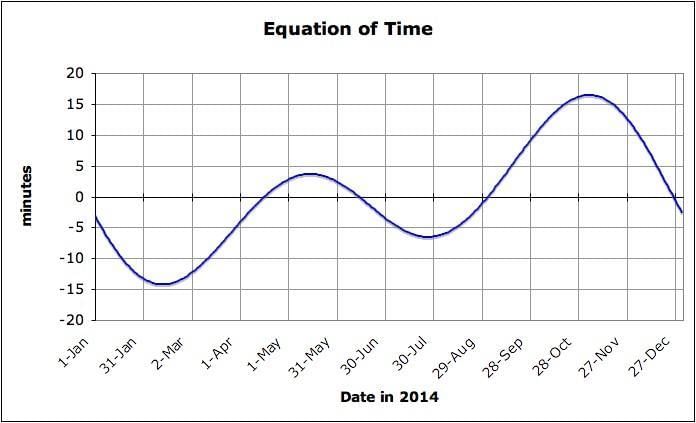 |