Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
CTET & State TET Exam > Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation > Flashcards: Piaget, Kohlberg & Vygotsky Theories
|
67 videos|154 docs|41 tests
|
FAQs on Flashcards: Piaget, Kohlberg & Vygotsky Theories Flashcard - Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the main stages of Piaget's cognitive development theory? |  |
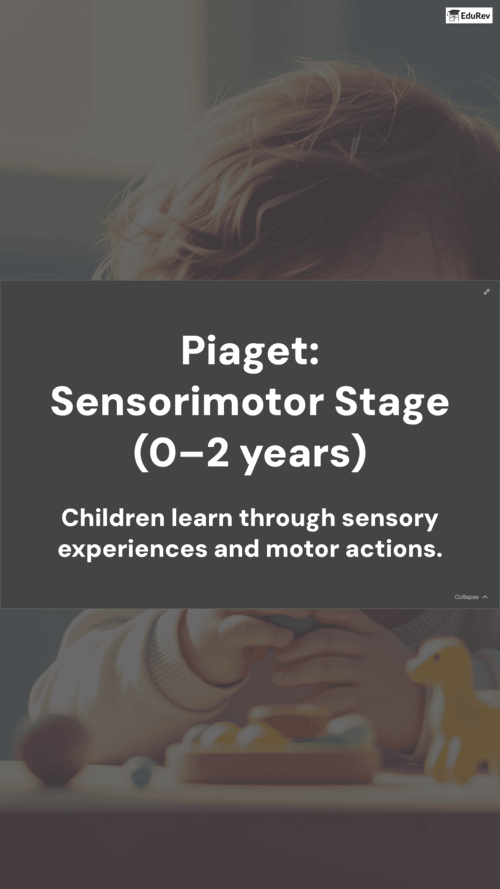
Ans. Piaget's cognitive development theory consists of four main stages: the Sensorimotor Stage (birth to 2 years), where infants learn through sensory experiences and motor actions; the Preoperational Stage (2 to 7 years), characterized by symbolic thinking and egocentrism; the Concrete Operational Stage (7 to 11 years), where logical reasoning develops but is limited to concrete objects; and the Formal Operational Stage (11 years and up), where abstract thinking and hypothetical reasoning emerge.
| 2. How does Kohlberg's theory of moral development differ from Piaget's cognitive development theory? |  |
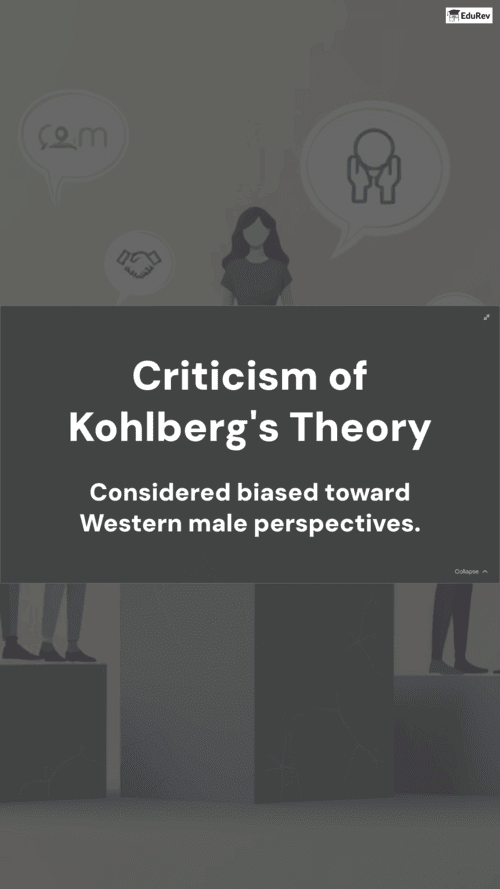
Ans. Kohlberg's theory of moral development builds on Piaget's ideas but focuses specifically on how individuals develop moral reasoning. While Piaget identified cognitive stages, Kohlberg proposed three levels of moral reasoning: Pre-conventional, Conventional, and Post-conventional, each with two stages. Kohlberg's theory emphasizes the evolution of moral understanding rather than cognitive abilities alone, showcasing how social and ethical considerations influence moral growth.
| 3. What role does Vygotsky's concept of the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) play in learning? |  |
Ans. Vygotsky's Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) is a key concept that describes the difference between what a learner can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance from a more knowledgeable other (like a teacher or peer). This concept emphasizes the importance of social interaction and scaffolding in the learning process, suggesting that effective teaching should target the ZPD to help students reach their full potential.
| 4. Can you explain the significance of social interaction in Vygotsky's theory compared to Piaget's? |  |
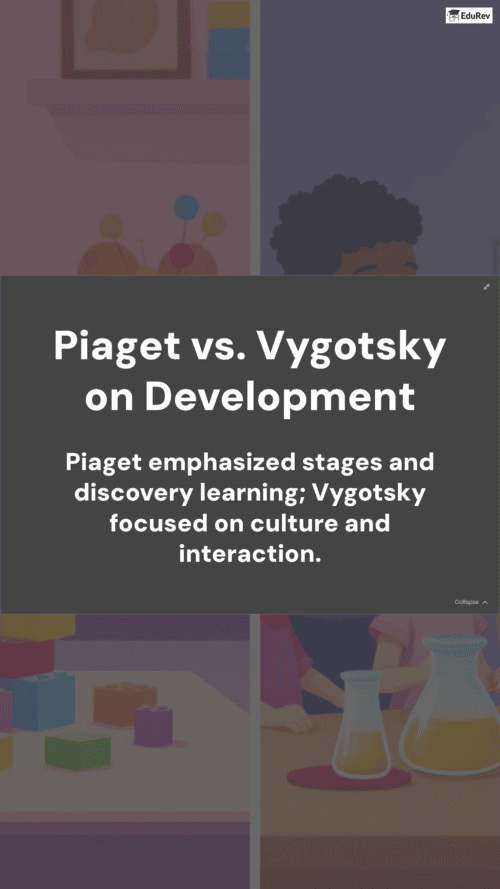
Ans. In Vygotsky's theory, social interaction is fundamental to cognitive development, as he believed that knowledge is co-constructed through collaboration and communication. In contrast, Piaget viewed social interaction as less critical, emphasizing that cognitive development primarily occurs through individual exploration and discovery. Thus, Vygotsky placed greater importance on cultural and social contexts in shaping cognitive processes.
| 5. How can educators apply Piaget, Kohlberg, and Vygotsky's theories in the classroom? |  |
Ans. Educators can apply Piaget's theory by providing developmentally appropriate activities that match students' cognitive stages, such as hands-on learning for younger children. From Kohlberg's perspective, teachers can facilitate discussions on moral dilemmas to enhance moral reasoning. Vygotsky's approach encourages collaborative learning opportunities and scaffolding, ensuring that students receive the support they need to advance within their ZPD, fostering both cognitive and social development.
Related Searches