|
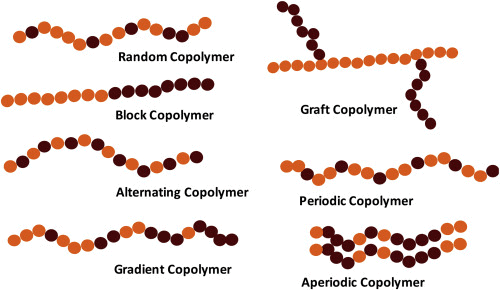
Homopolymers are made up of only one type of monomer, while copolymers consist of two or more different types of monomers. |
Card: 2 / 32 |
|
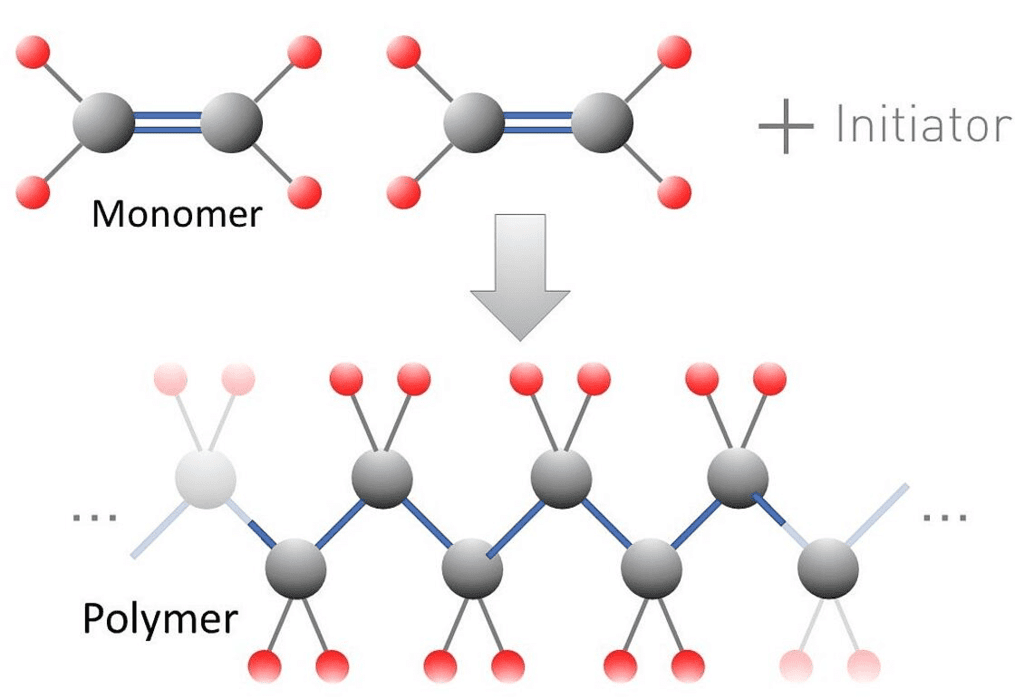
Fill in the blank: The process by which monomers are joined to form polymers is called ___. |
Card: 3 / 32 |
|
True or False: All copolymers have a perfectly alternating arrangement of monomer units. |
Card: 5 / 32 |
|
False. Most copolymers tend more towards an alternating type but have many random imperfections. |
Card: 6 / 32 |
|
What type of copolymer features monomer units that are distributed randomly throughout the polymer chain? |
Card: 7 / 32 |
|
Fill in the blank: Polymers that consist of branched chains typically have ___ melting points compared to linear polymers. |
Card: 9 / 32 |
|
What are the characteristics of cross-linked or three-dimensional network polymers? |
Card: 11 / 32 |
|
They are hard, rigid, and brittle due to the joining of linear polymeric chains into a three-dimensional structure. |
Card: 12 / 32 |
|
Graft copolymers are formed by irradiating a homopolymer chain in the presence of a second monomer, which generates radical sites for polymerization. |
Card: 14 / 32 |
|
True or False: Synthetic polymers are always designed to mimic natural polymers. |
Card: 15 / 32 |
|
False. Synthetic polymers are man-made and can have properties distinct from natural polymers. |
Card: 16 / 32 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
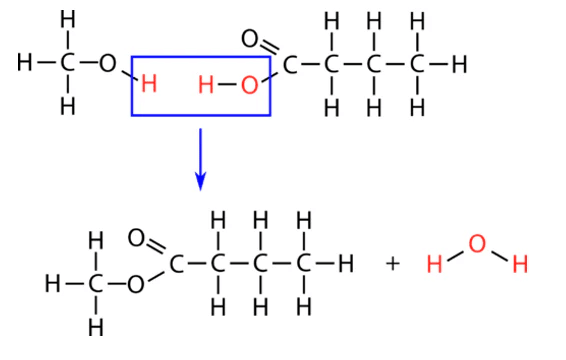
What type of polymerization involves the loss of small molecules during the formation of polymers? |
Card: 17 / 32 |
|
What distinguishes semi-synthetic polymers from natural and synthetic polymers? |
Card: 19 / 32 |
|
Semi-synthetic polymers are derived from natural polymers, typically modified for enhanced properties. |
Card: 20 / 32 |
|
Branched chain polymers do not pack well, leading to lower melting points, densities, and tensile strengths compared to linear polymers. |
Card: 22 / 32 |
|
What is the role of functional groups in the formation of condensation polymers? |
Card: 23 / 32 |
|
Functional groups must be present for polymerization, and at least two functional groups are required to form linear or cross-linked structures. |
Card: 24 / 32 |
|
What type of polymer is formed when monomers with three functional groups are used? |
Card: 27 / 32 |
|
The terminal units determine the nature of the linkages and influence the physical properties of the polymer. |
Card: 30 / 32 |
|
Synthetic polymers are man-made, often designed for specific applications, and can have unique properties not found in natural polymers. |
Card: 32 / 32 |