|
True or False: Mendel's experiments involved a small sample size, which limited the credibility of his findings. |
Card: 3 / 120 |
|
False. Mendel's experiments involved a large sample size, lending greater credibility to his findings.
|
Card: 4 / 120 |
|
Mendel selected true-breeding lines that consistently produced offspring with ___ traits over many generations. |
Card: 5 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: Mendel proposed fundamental laws of inheritance based on his experiments conducted between ___ and ___. |
Card: 9 / 120 |
|
What was the significance of Mendel applying statistical analysis to biological problems? |
Card: 11 / 120 |
|
It allowed for a more rigorous and objective examination of inheritance patterns, leading to reliable conclusions.
|
Card: 12 / 120 |
|
True or False: Mendel's conclusions were mere conjectures and did not reflect general rules of inheritance. |
Card: 13 / 120 |
|
False. Mendel's conclusions reflected general rules of inheritance based on systematic experiments. |
Card: 14 / 120 |
|
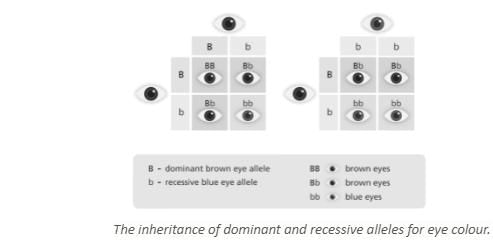
Homozygous refers to having two identical alleles for a trait, while heterozygous refers to having two different alleles for a trait. 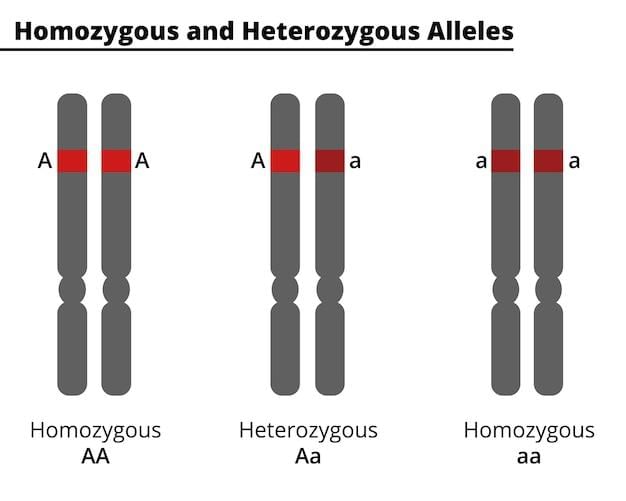 |
Card: 18 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: A dominant trait appears in the phenotype even when ___ allele is present. |
Card: 19 / 120 |
|
False; the phenotype refers to the observable traits, while the genotype refers to the genetic makeup. |
Card: 22 / 120 |
|
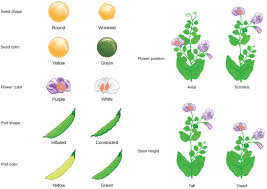
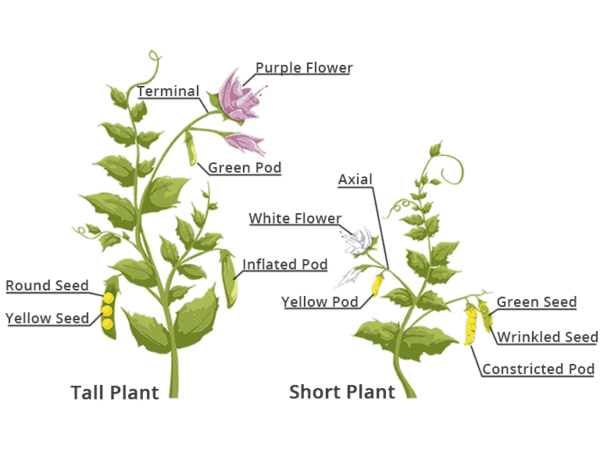
What were the parental traits that Mendel used in his hybridization experiment? |
Card: 23 / 120 |
|
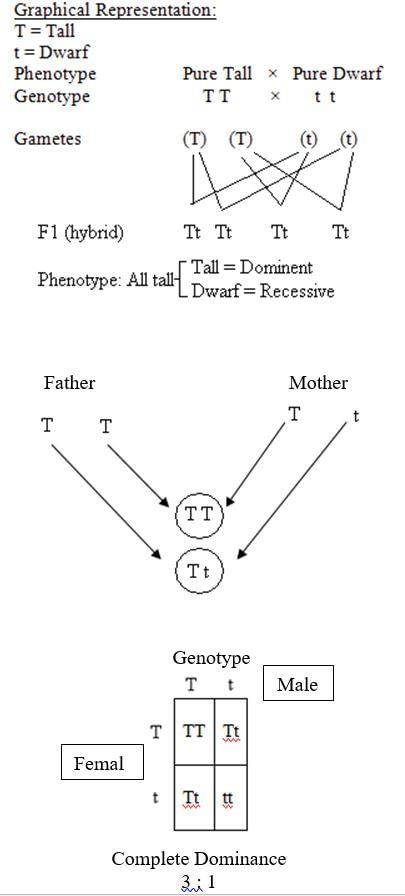
Mendel crossed tall and dwarf pea plants to study the inheritance of one gene. 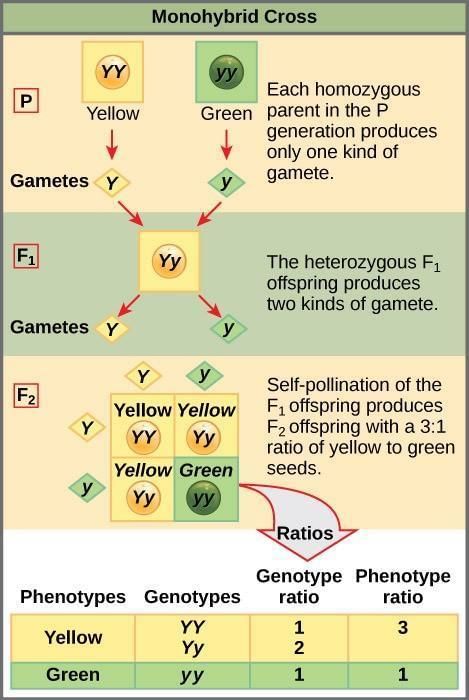 |
Card: 24 / 120 |
|
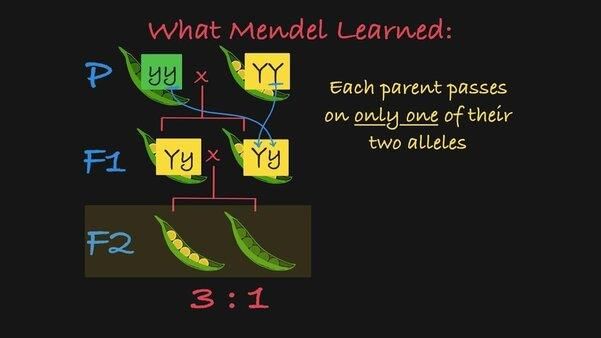
Fill in the blank: The first hybrid generation produced by Mendel's cross is known as the ___ progeny. |
Card: 25 / 120 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following traits represents a recessive trait in Mendel's experiments? A) Blue flowers B) White flowers C) Tall plants D) Dwarf plants |
Card: 27 / 120 |
|
An allele is a variant form of a gene that determines a specific trait, such as the gene for flower color having different alleles for blue or white colors. 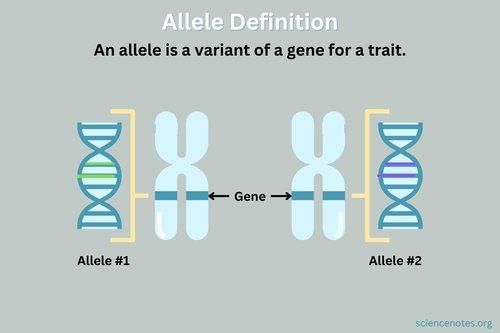 |
Card: 30 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: The observable physical or physiological traits of an organism are referred to as its ___. |
Card: 31 / 120 |
|
Mendel's F1 progeny plants were all tall, indicating that the tall trait is ___ over the dwarf trait. |
Card: 33 / 120 |
|
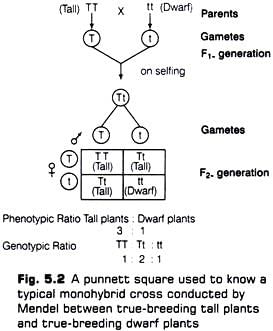
In the F2 generation, the phenotypic ratio of tall to dwarf plants is ___:___. |
Card: 35 / 120 |
|
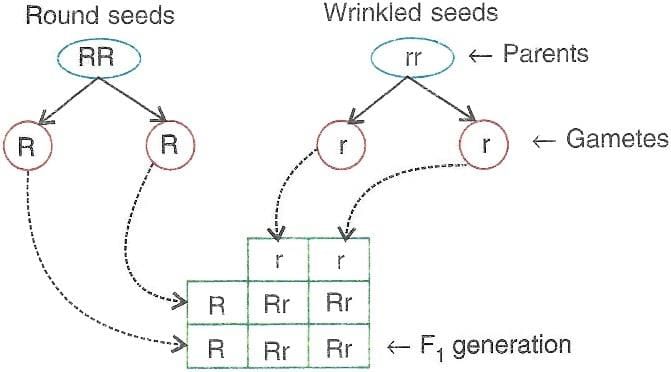
What term is used to describe the genetic makeup of an organism, such as TT, Tt, or tt? |
Card: 37 / 120 |
|
True or False: In a monohybrid cross between TT and tt, all offspring will show the dwarf phenotype. |
Card: 39 / 120 |
|
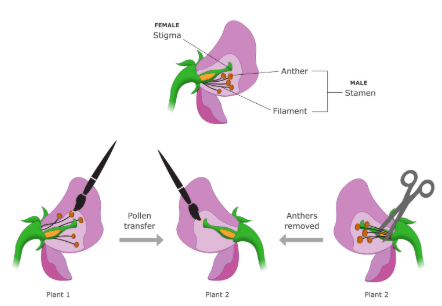
When performing a test cross, a tall plant is crossed with a ___ plant to determine its genotype. |
Card: 41 / 120 |
|
The tool used to predict the probability of different genotypes in offspring is called a ___ ___. |
Card: 43 / 120 |
|
The principle of segregation states that alleles segregate randomly into gametes during meiosis. |
Card: 46 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: The genotypic ratio observed in the F2 generation is ___:___:___ for TT:Tt:tt. |
Card: 47 / 120 |
|
What are the contrasting forms of a gene that determine specific traits called? |
Card: 49 / 120 |
|
In Mendel's experiments, what did the presence of dwarf plants in the F2 generation indicate about inheritance? |
Card: 51 / 120 |
|
It indicated that the dwarf trait was recessive and could reappear in subsequent generations. |
Card: 52 / 120 |
|
What are the two fundamental rules formulated by Mendel regarding inheritance? |
Card: 53 / 120 |
|
The two fundamental rules are the First Law (Law of Dominance) and the Second Law (Law of Segregation). |
Card: 54 / 120 |
|
In a monohybrid cross, what is the phenotypic ratio observed in the F2 generation? |
Card: 55 / 120 |
|
True or False: In the F1 generation of a monohybrid cross, both parental characters are expressed. |
Card: 59 / 120 |
|
False. In the F1 generation, only one parental character is expressed due to dominance. 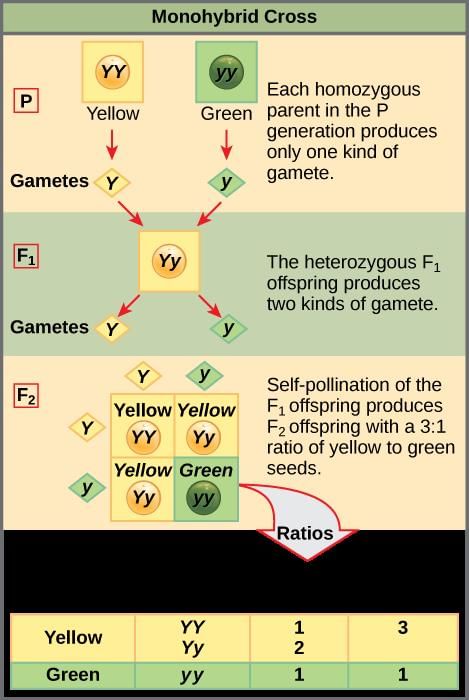 |
Card: 60 / 120 |
 Unlock all Flashcards with EduRev Infinity Plan Starting from @ ₹99 only
|
|
What happens to alleles during gamete formation according to Mendel's Second Law? |
Card: 61 / 120 |
|
During gamete formation, the alleles of a pair segregate from each other, so each gamete receives only one of the two alleles. |
Card: 62 / 120 |
|
What is the significance of the recessive factor in Mendel's Law of Dominance? |
Card: 65 / 120 |
|
The recessive factor is masked by the dominant factor and is not expressed in the F1 generation, but it can appear in the F2 generation due to segregation. |
Card: 66 / 120 |
|
Multiple Choice: Which of the following statements reflects the essence of the Law of Segregation? A) Factors blend together, B) Factors exist in pairs, C) Only dominant factors are expressed, D) All factors are recessive. |
Card: 67 / 120 |
|
What is the primary characteristic of incomplete dominance as observed in the F1 generation of snapdragons? |
Card: 69 / 120 |
|
The F1 generation exhibits a phenotype that is a blend of the two parental traits, rather than resembling either parent exactly. |
Card: 70 / 120 |
|
In the cross between true-breeding red-flowered plants (RR) and true-breeding white-flowered plants (rr), what phenotype is displayed by the F1 generation? |
Card: 71 / 120 |
|
Incomplete dominance results in a phenotypic ratio of ___ in the F2 generation from a cross of F1 snapdragons. |
Card: 73 / 120 |
|
True or False: In incomplete dominance, the red allele (R) is completely dominant over the white allele (r). |
Card: 75 / 120 |
|
False. The red allele (R) is not completely dominant over the white allele (r), allowing the heterozygous (Rr) phenotype to be distinctively pink. |
Card: 76 / 120 |
|
Dominance refers to the relationship between alleles and how they influence the expression of traits, where some alleles are dominant while others are recessive. |
Card: 78 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: A gene carries the information necessary to express a specific ___ and in diploid organisms, there are ___ copies of each gene. |
Card: 79 / 120 |
|
What happens to the phenotype when one allele produces a non-functional enzyme? |
Card: 81 / 120 |
|
The phenotype will depend on the functioning of the unmodified allele, which is considered the dominant allele, while the modified allele is typically the recessive one.  |
Card: 82 / 120 |
|
True or False: All alleles produce equal effects on the expression of traits. |
Card: 83 / 120 |
|
False. Some alleles are dominant and produce stronger effects, while others are recessive and may not manifest unless in a homozygous state. |
Card: 84 / 120 |
|
Co-dominance is a genetic phenomenon where offspring exhibit traits from both parents equally, instead of resembling just one parent or showing a blend of traits. |
Card: 86 / 120 |
|
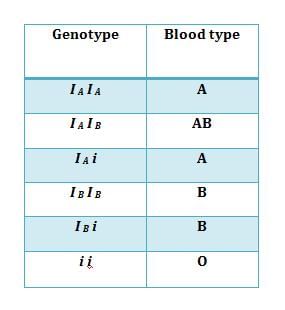
The ABO blood groups are determined by the gene I, which has three alleles: IA, IB, and i. |
Card: 88 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blanks: The IA and IB alleles produce different ___ on the surface of red blood cells. |
Card: 89 / 120 |
|
How many possible genotypes can result from the three alleles of the ABO blood group system? |
Card: 93 / 120 |
|
There are six possible combinations of the alleles, leading to six different genotypes. 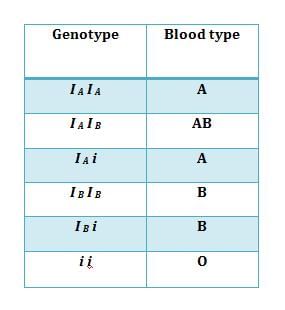 |
Card: 94 / 120 |
|
When both IA and IB are present, both sugars are produced, resulting in the AB blood type. |
Card: 96 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: The ABO blood group system illustrates the concept of ___ alleles. |
Card: 97 / 120 |
|
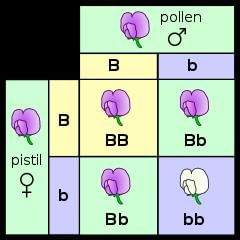
Starch synthesis in pea seeds is controlled by one gene with two alleles (B and b). |
Card: 100 / 120 |
|
Short Answer: What phenotype do BB homozygotes produce in the starch synthesis example? |
Card: 101 / 120 |
|
True or False: Heterozygotes (Bb) produce the same size starch grains as homozygotes (bb). |
Card: 103 / 120 |
|
What are the dominant traits identified by Mendel in his experiments with pea plants? |
Card: 105 / 120 |
|
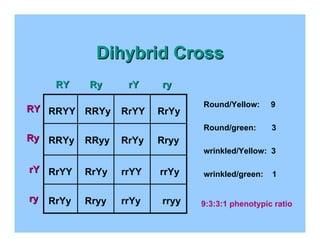
The dominant traits identified by Mendel are yellow seed color (Y) and round seed shape (R). |
Card: 106 / 120 |
|
In Mendel's experiment, the genotypes of the parent plants were RRYY and rryy. What does RRYY represent? |
Card: 107 / 120 |
|
The F1 generation of Mendel's cross exhibited the genotype RrYy. What does this genotype indicate? |
Card: 109 / 120 |
|
The genotype RrYy indicates that the F1 generation is heterozygous for both traits, showing a combination of traits from both parent plants. 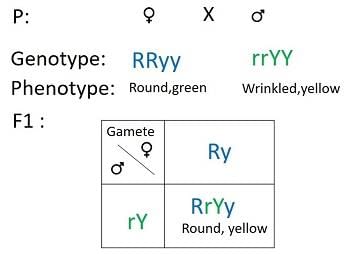 |
Card: 110 / 120 |
|
After Mendel self-hybridized the F1 plants, what segregation ratio did he observe for yellow to green seeds in the F2 generation? |
Card: 111 / 120 |
|
Mendel observed a segregation ratio of 3:1 for yellow to green seeds in the F2 generation. |
Card: 112 / 120 |
|
True or False: The traits for seed color and seed shape in Mendel's experiments segregated independently. |
Card: 113 / 120 |
|
Fill in the blank: The recessive traits identified by Mendel were ___ and ___. |
Card: 115 / 120 |
|
What gametes were produced by the parent plants RRYY and rryy during Mendel's crossing? |
Card: 117 / 120 |