|
Card: 2 / 48 |
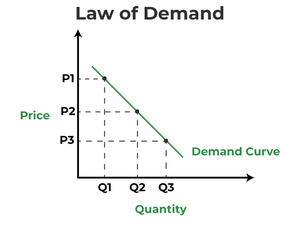
Elasticity of demand measures how much the quantity demanded of a commodity responds to changes in its own price, while keeping other factors constant. 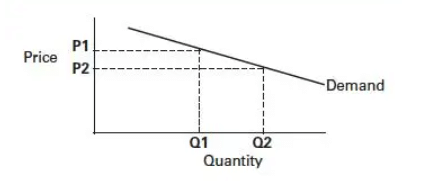
|
|
Card: 3 / 48 |
If the quantity demanded for good X increases more than for good Y when prices decrease, good X is considered to be ___ to price changes. |
|
Card: 7 / 48 |
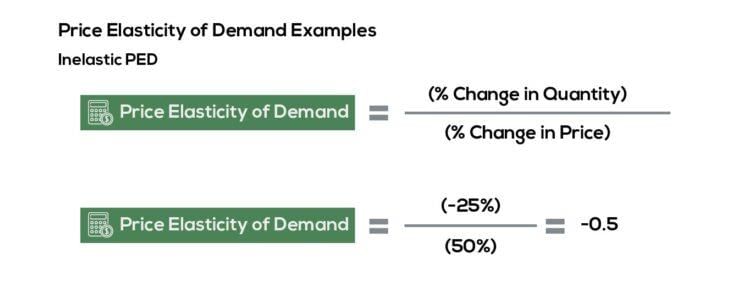
Fill in the blank: The formula for calculating price elasticity of demand is EP = |ΔQ / ΔP|, where ΔQ is the change in ___ and ΔP is the change in ___. |
|
Card: 9 / 48 |
What happens to the price elasticity of demand when the price of a good decreases and the quantity demanded increases? |
|
Card: 10 / 48 |
It indicates a higher responsiveness of demand, thus suggesting that the good is elastic. 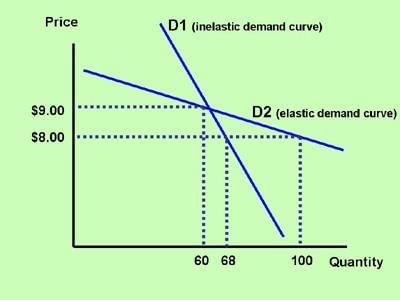 |
|
Card: 11 / 48 |
Riddle: I measure how sensitive demand is to price changes, but I am not a price tag. What am I? |
|
Card: 13 / 48 |
What does a higher absolute value of price elasticity of demand indicate about a product? |
|
Card: 14 / 48 |
A higher absolute value indicates that the product is more elastic, meaning that its quantity demanded changes significantly with price changes.
|
|
Card: 16 / 48 |
EP = |(Percentage change in quantity demanded) / (Percentage change in price)| |
|
Card: 17 / 48 |
Elastic demand is characterized by an elasticity coefficient greater than ___ and indicates that the quantity demanded is ___ responsive to price changes. |
|
Card: 19 / 48 |
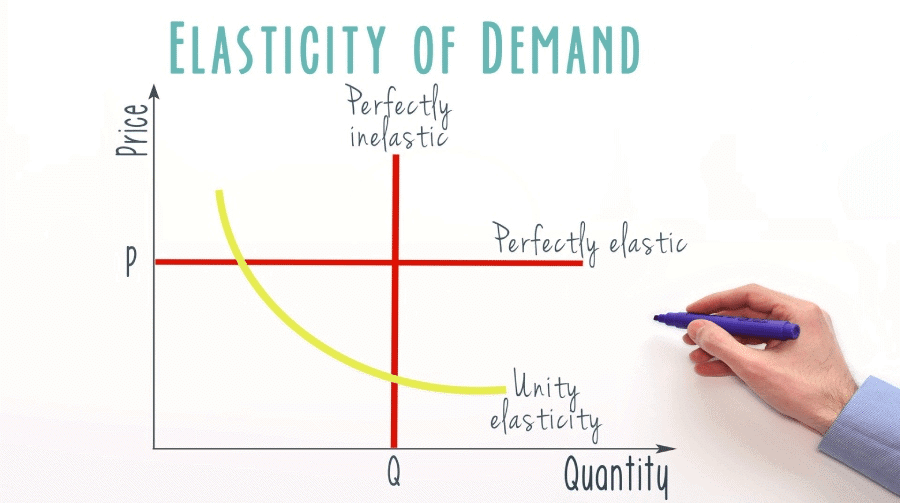
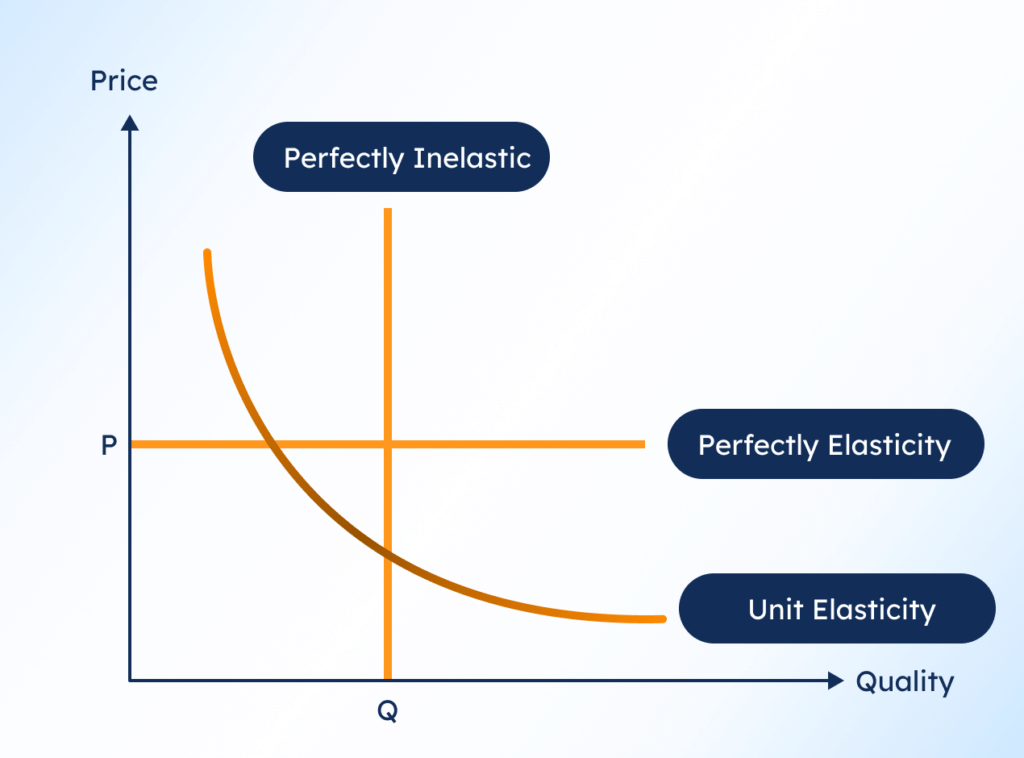
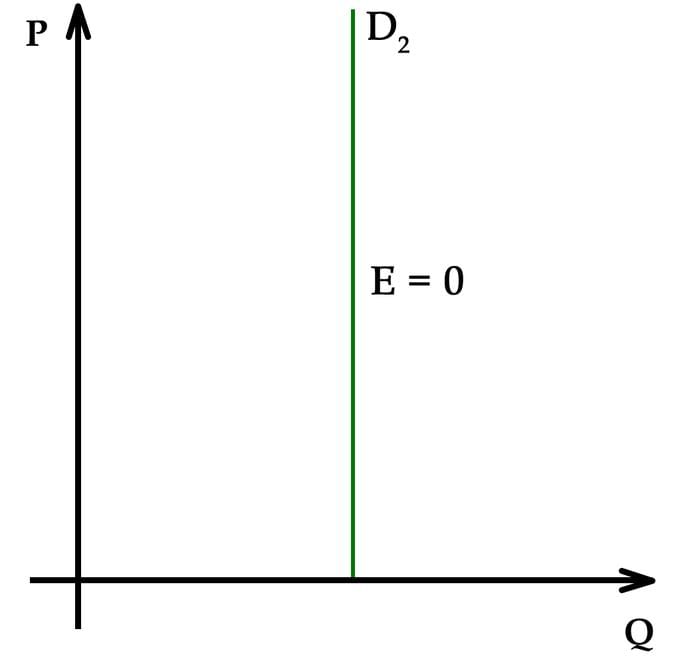
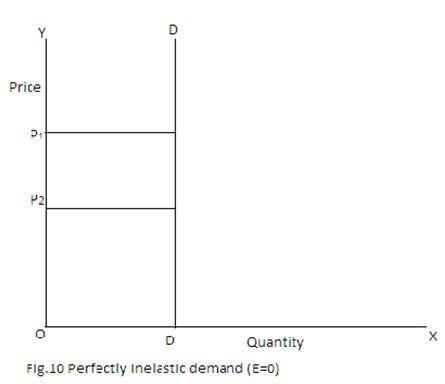
True or False: A perfectly inelastic demand curve is represented by a horizontal line. |
|
Card: 21 / 48 |
If the price of a luxury good decreases by 10% and the quantity demanded increases by more than 10%, the demand for this good is classified as ___. |
|
Card: 23 / 48 |
Riddle: I can change without a care, my quantity stays the same, no matter the price I declare. What am I? |
|
Card: 25 / 48 |
What happens to quantity demanded when the price of a necessary good decreases, if the demand is inelastic? |
|
Card: 26 / 48 |
The quantity demanded increases, but by a smaller percentage than the decrease in price. 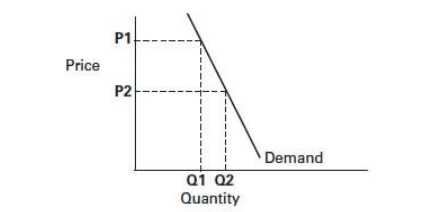 |
|
Card: 27 / 48 |
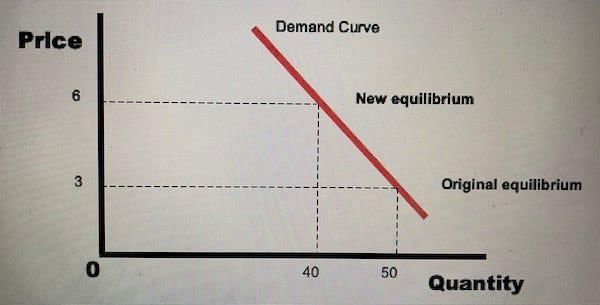
If the price of wheat drops from 40 paisa to 20 paisa and the demand rises from 1,600 kg to 2,000 kg, what is the price elasticity of demand? |
|
Card: 29 / 48 |
Fill in the blank: If a product has a price elasticity of demand equal to infinity, it is said to have ___ demand. |
|
Card: 31 / 48 |
How does the concept of unit elasticity of demand manifest in real-world scenarios? |
|
Card: 32 / 48 |
Unit elasticity occurs when a percentage change in price results in an equal percentage change in quantity demanded, such as a 10% price drop leading to a 10% increase in quantity demanded.  |
|
Card: 34 / 48 |
The Total Outlay (Revenue) Method, proposed by Alfred Marshall, assesses elasticity by analyzing the relationship between total revenue (TR) and price changes, calculated as TR = P × Q. |
|
Card: 35 / 48 |
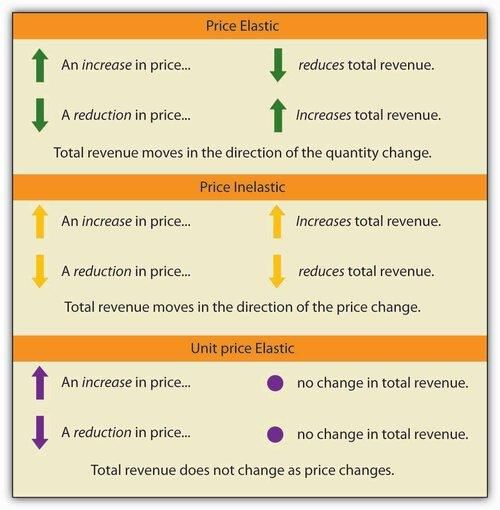
Fill in the blank: Elastic demand occurs when a price decrease leads to a ___ in total revenue. |
|
Card: 37 / 48 |
True or False: If the price increases and total revenue increases, demand is considered elastic. |
|
Card: 38 / 48 |
False. If the price increases and total revenue increases, demand is considered inelastic. 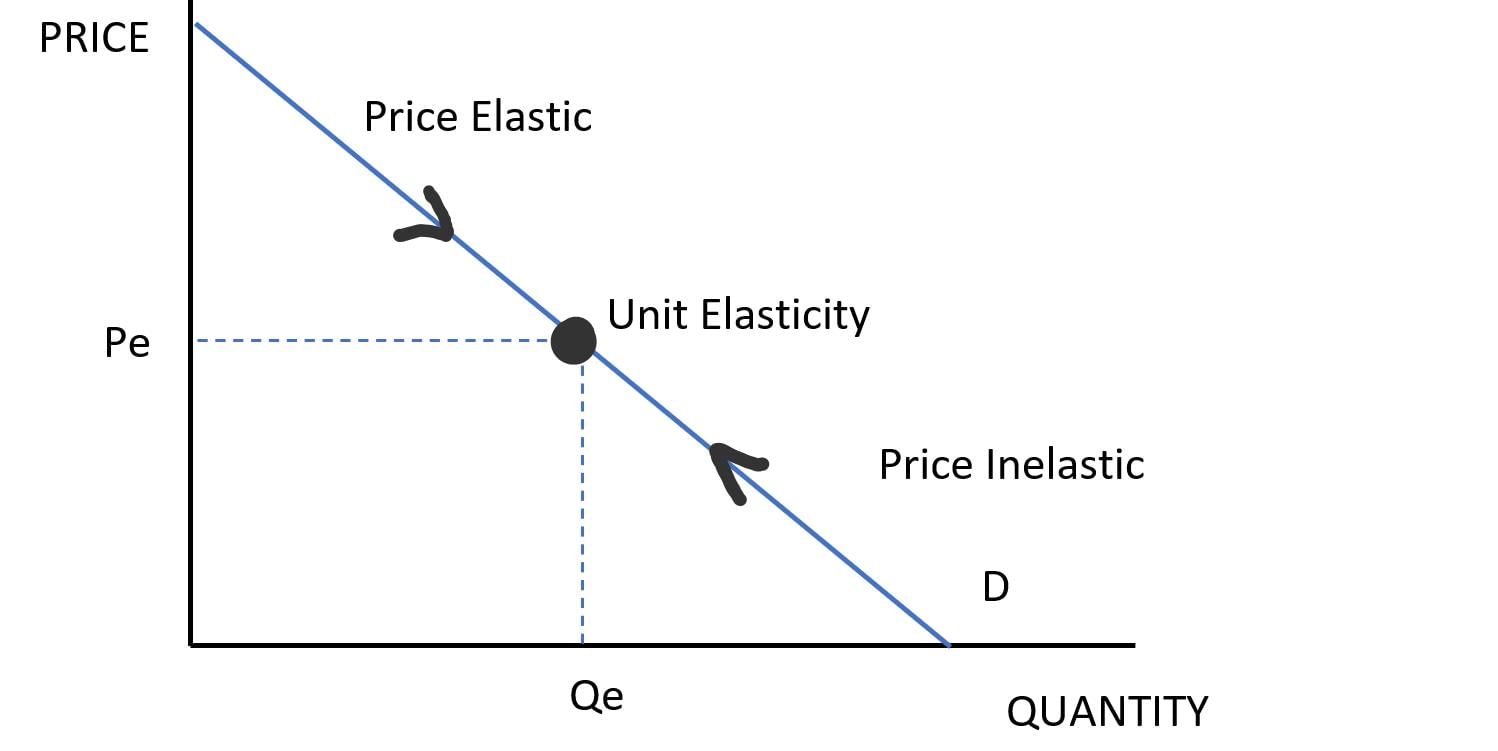 |
|
Card: 40 / 48 |
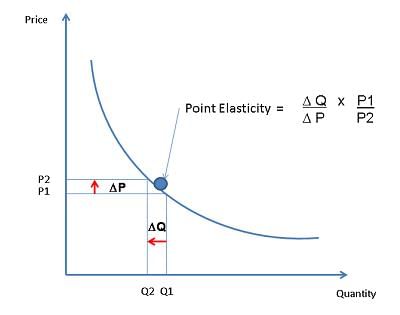
The formula EP = dQ/dP represents the elasticity of demand at a specific point on the demand curve, showing how quantity demanded changes with respect to price. |
|
Card: 41 / 48 |
Riddle: I help you understand how much demand changes with price, but I only do it at one specific point. What am I? |
|
Card: 44 / 48 |
The Arc Elasticity Method measures elasticity over a range of prices, providing an average elasticity between two points on the demand curve, which is useful for larger changes in price and quantity. 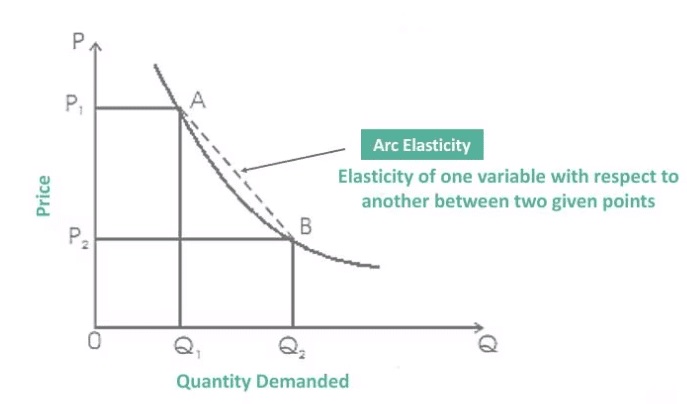 |
|
Card: 45 / 48 |
Fill in the blank: Inelastic demand is indicated when the price decreases and total revenue ___ . |