Flip-Flops & Its Types | Digital Logic - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
Introduction
- A flip-flop in digital electronics is a circuit with two stable states that can be used to store binary data. The stored data can be changed by applying varying inputs. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Both are used as data storage elements.
- It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. But first, let’s clarify the difference between a latch and flip-flops.
Flip-Flop v/s Latch
- The primary difference between a latch and a flip-flop is a gating or clocking mechanism.
- In Simple words. Flip Flops are edge-triggered and a latch is level-triggered.
- If you are confused between latch and flip-flop, then you should check this detailed article where we discussed the difference between Latch and Flip Flop.
- For example, let us talk about SR latch and SR flip-flops. In this circuit when you Set S as active, the output Q will be high and Q’ will be Low. This is irrespective of anything else. (This is an active-low circuit; so active here means low, but for an active high circuit, active would mean high)
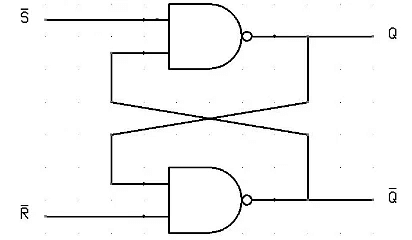
- A flip-flop, on the other hand, is a synchronous Circuit and is also known as a gated or clocked SR latch.
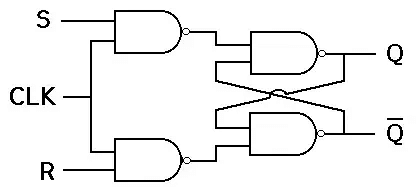
- In this circuit diagram, the output is changed (i.e. the stored data is changed) only when you give an active clock signal. Otherwise, even if the S or R is active, the data will not change.
Let’s understand the flip-flop in detail with the truth table and circuits.
Types
There are basically 4 types of flip-flops:
- SR Flip-Flop
- JK Flip-Flop
- D Flip-Flop
- T Flip-Flop
1. SR Flip Flop
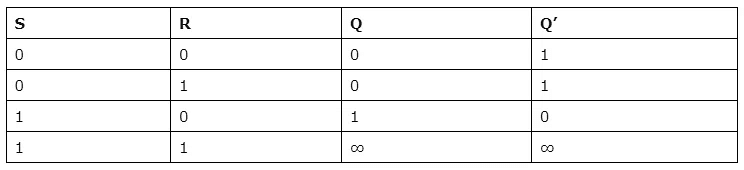
This is the most common flip-flop among all. This simple flip-flop circuit has a set input (S) and a reset input (R). In this system, when you Set “S” as active, the output “Q” would be high, and “Q‘” would be low. Once the outputs are established, the wiring of the circuit is maintained until “S” or “R” go high, or power is turned off.
As shown above, it is the simplest and easiest to understand. The two outputs, as shown above, are the inverse of each other. The truth table of SR Flip-Flop is highlighted below.
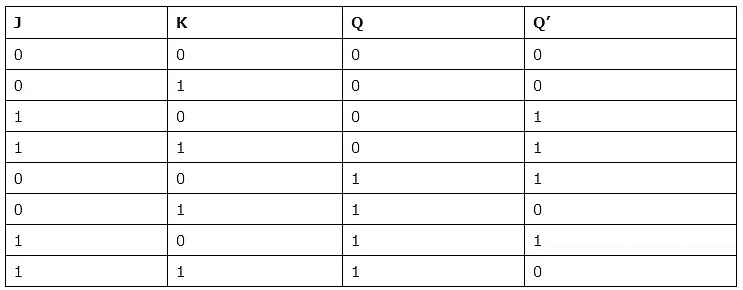
2. JK Flip-Flop
- Due to the undefined state in the SR flip-flops, another flip-flop is required in electronics. The JK flip-flop is an improvement on the SR flip-flop where S=R=1 is not a problem.
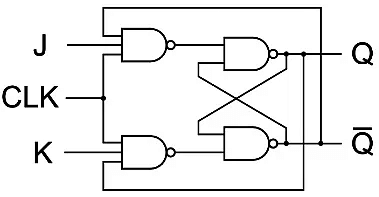
- The input condition of J=K=1, gives an output inverting the output state. However, the outputs are the same when one tests the circuit practically.
- In simple words, If J and K data input are different (i.e. high and low), then the output Q takes the value of J at the next clock edge. If J and K are both low, then no change occurs. If J and K are both high at the clock edge, then the output will toggle from one state to the other. JK Flip-Flops can function as Set or Reset Flip-flops.
Truth Table:
 3. D Flip-Flop
3. D Flip-Flop
- D flip-flop is a better alternative that is very popular with digital electronics. They are commonly used for counters and shift registers and input synchronization.
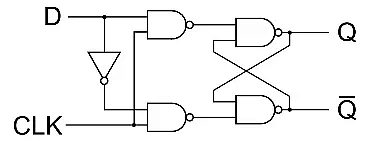
- In the D flip-flops, the output can only be changed at the clock edge, and if the input changes at other times, the output will be unaffected.
Truth Table: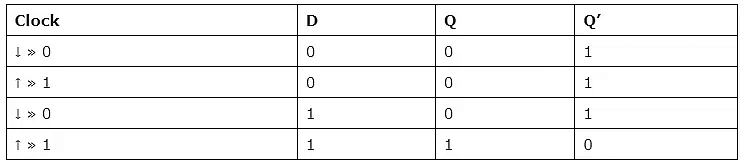
The change of state of the output is dependent on the rising edge of the clock. The output (Q) is the same as the input and can only change at the rising edge of the clock.
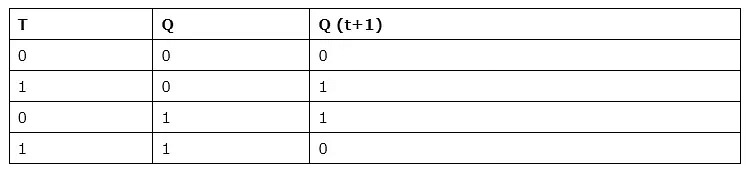
4. T Flip-Flop
- A T flip-flop is like a JK flip-flop. These are basically single-input versions of JK flip-flops. This modified form of the JK is obtained by connecting inputs J and K together. It has only one input along with the clock input.
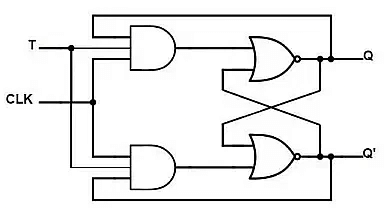
- These flip-flops are called T flip-flops because of their ability to complement their state i.e. Toggle, hence they are named Toggle flip-flops.
Truth Table:
Applications
These are the various types of flip-flops being used in digital electronic circuits and the applications of Flip-flops are as specified below.
- Counters
- Frequency Dividers
- Shift Registers
- Storage Registers
|
53 docs|15 tests
|





















