Flow & Error Control Technique | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
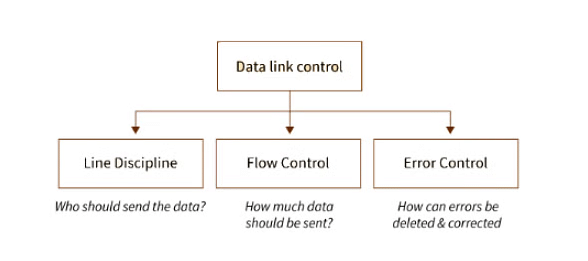
Data Link Layer is responsible for reliable point-to-point data transfer over a physical medium. To implement this data link layer provides three functions :
- Line Discipline
Line discipline is the functionality used to establish coordination between link systems. It decides which device sends data and when. - Flow Control
Flow control is an essential function that coordinates the amount of data the sender can send before waiting for acknowledgment from the receiver. - Error Control
Error control is functionality used to detect erroneous transmissions in data frames and retransmit them.
What is Flow Control in the Data Link Layer?
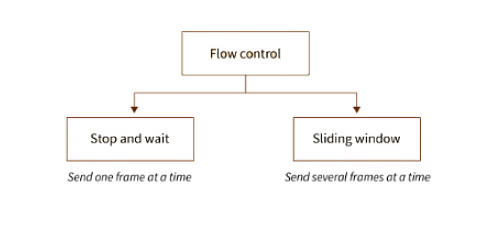
Flow control is a set of procedures that restrict the amount of data a sender should send before it waits for some acknowledgment from the receiver.
- Flow Control is an essential function of the data link layer.
- It determines the amount of data that a sender can send.
- It makes the sender wait until an acknowledgment is received from the receiver’s end.
- Methods of Flow Control are Stop-and-wait , and Sliding window.
Purpose of Flow Control
- The device on the receiving end has a limited amount of memory (to store incoming data) and limited speed (to process incoming data). The receiver might get overwhelmed if the rate at which the sender sends data is faster or the amount of data sent is more than its capacity.
- Buffers are blocks in the memory that store data until it is processed. If the buffer is overloaded and there is more incoming data, then the receiver will start losing frames.
- The flow control mechanism was devised to avoid this loss and wastage of frames. Following this mechanism, the receiver, as per its capacity, sends an acknowledgment to send fewer frames or temporarily halt the transmission until it can receive again.
- Thus, flow control is the method of controlling the rate of transmission of data to a value that the receiver can handle.
Methods to Control the Flow of Data
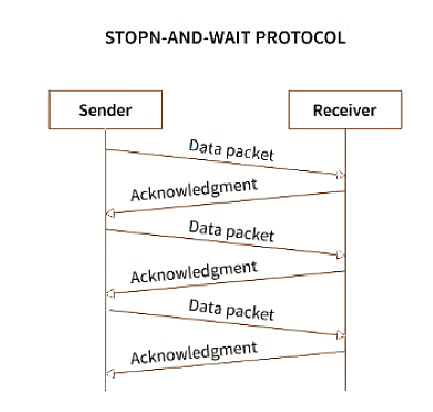
Stop-and-wait Protocol
Stop-and-wait protocol works under the assumption that the communication channel is noiseless and transmissions are error-free.
Working:
- The sender sends data to the receiver.
- The sender stops and waits for the acknowledgment.
- The receiver receives the data and processes it.
- The receiver sends an acknowledgment for the above data to the sender.
- The sender sends data to the receiver after receiving the acknowledgment of previously sent data.
- The process is unidirectional and continues until the sender sends the End of Transmission (EoT) frame.
Sliding Window Protocol
The sliding window protocol is the flow control protocol for noisy channels that allows the sender to send multiple frames even before acknowledgments are received. It is called a Sliding window because the sender slides its window upon receiving the acknowledgments for the sent frames.
Working:
- The sender and receiver have a “window” of frames. A window is a space that consists of multiple bytes. The size of the window on the receiver side is always 1.
- Each frame is sequentially numbered from 0 to n - 1, where n is the window size at the sender side.
- The sender sends as many frames as would fit in a window.
- After receiving the desired number of frames, the receiver sends an acknowledgment. The acknowledgment (ACK) includes the number of the next expected frame.
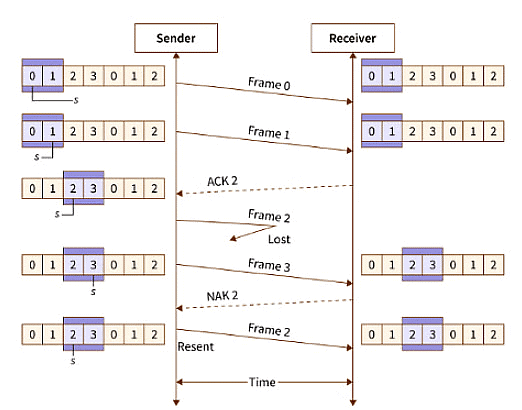
The sender sends the frames 0 and 1 from the first window (because the window size is 2).
The receiver after receiving the sent frames, sends an acknowledgment for frame 2 (as frame 2 is the next expected frame).
The sender then sends frames 2 and 3. Since frame 2 is lost on the way, the receiver sends back a “NAK” signal (a non-acknowledgment) to inform the sender that frame 2 has been lost. So, the sender retransmits frame 2.
What is Error Control in the Data Link Layer?
Error Control is a combination of both error detection and error correction. It ensures that the data received at the receiver end is the same as the one sent by the sender.
Error detection is the process by which the receiver informs the sender about any erroneous frame (damaged or lost) sent during transmission.
Error correction refers to the retransmission of those frames by the sender.
Purpose of Error Control
Error control is a vital function of the data link layer that detects errors in transmitted frames and retransmits all the erroneous frames. Error discovery and amendment deal with data frames damaged or lost in transit and the acknowledgment frames lost during transmission. The method used in noisy channels to control these errors is ARQ or Automatic Repeat Request.
Categories of Error Control
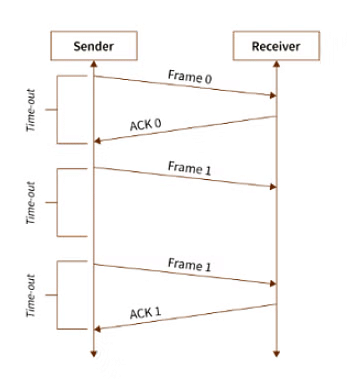
Stop-and-wait ARQ
- In the case of stop-and-wait ARQ after the frame is sent, the sender maintains a timeout counter.
- If acknowledgment of the frame comes in time, the sender transmits the next frame in the queue.
- Else, the sender retransmits the frame and starts the timeout counter.
- In case the receiver receives a negative acknowledgment, the sender retransmits the frame.
Sliding Window ARQ
To deal with the retransmission of lost or damaged frames, a few changes are made to the sliding window mechanism used in flow control.
Go-Back-N ARQ :
In Go-Back-N ARQ, if the sent frames are suspected or damaged, all the frames are re-transmitted from the lost packet to the last packet transmitted.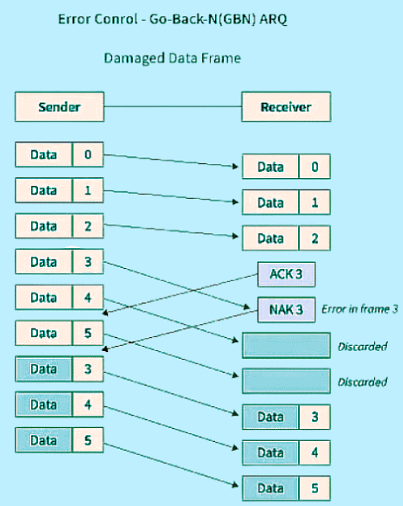
Selective Repeat ARQ:
Selective repeat ARQ/ Selective Reject ARQ is a type of Sliding Window ARQ in which only the suspected or damaged frames are re-transmitted.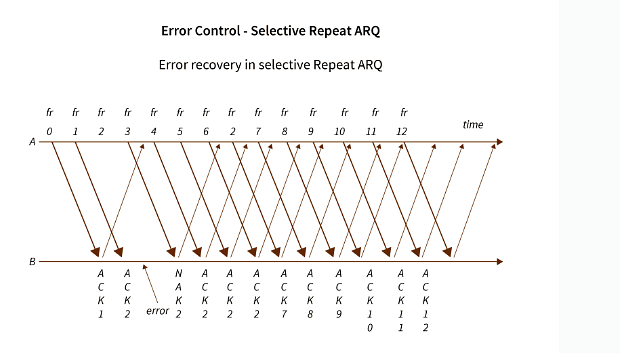
Difference Between Flow Control & Error Control
| Flow Control | Error Control |
|
|
Approaches For Flow Control:
| Approaches for error detection are
|
|
|
| Examples of Flow control technique are 1.Stop and Wait protocol 2.Sliding Window Protocol | Example of Error Control 1.Stop and wait for ARQ 2.Slidingf window ARQ |
|
23 videos|171 docs|81 tests
|
FAQs on Flow & Error Control Technique - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What is flow control in networking? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of flow control techniques? |  |
| 3. How does error control help in data transmission? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between flow control and error control? |  |
| 5. Why is flow and error control important in networking? |  |

















