Class 2 Exam > Class 2 Notes > Year 2 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) > Forces and movement
Forces and movement | Year 2 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 2 PDF Download
What is a Force?
- A force is an interaction between objects that causes them to move.
- Forces can either be a push or a pull.
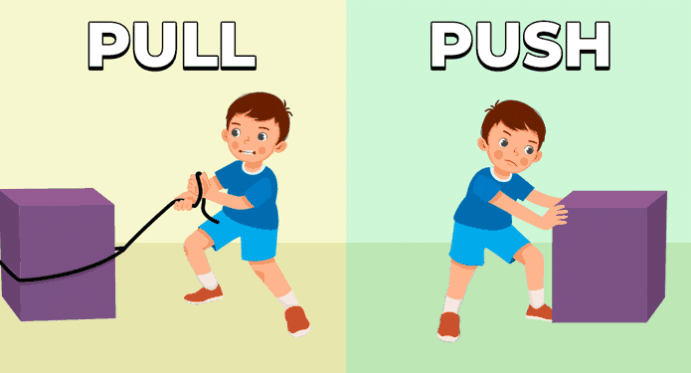
Push Forces
- Definition: A push force moves objects away from you.
- Examples:
- Shopping Trolley: When you go grocery shopping, you push the trolley away from you to move it.
- Volleyball: Players push the ball away from them to pass it to others or to score.
Pull Forces
- Definition: A pull force brings objects closer to you.
- Examples:
- Flying a Kite: When flying a kite, you pull on the rope to keep the kite from flying away.
- Harvesting Fruits and Vegetables: You pull the fruit or vegetable away from the plant to pick it.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Types of Forces: What are the two types of forces?
Ans: Push and Pull
Example 2: Defining a Push: How can you define a push?
Ans: A motion that moves objects away from you.
Example 3: Playing a Piano: What force is being used when playing a piano?
Ans: Push
Example 4: Golfing: What force is being used by a golfer?
Ans: Push
Example 5: Defining a Pull: What is the best way to describe a pull?
Ans: A motion that moves objects towards you.
Examples in Real Life
- Push:
- Moving a door open.
- Sliding a toy car forward.
- Pull:
- Opening a drawer.
- Tugging on a rope in a game of tug-of-war.
Summary
- Forces cause motion and can either push objects away or pull them closer.
- Understanding push and pull helps us see how we interact with the world around us.
Question for Forces and movementTry yourself: Which force is being used when a person is swimming in a pool?View Solution
The document Forces and movement | Year 2 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 2 is a part of the Class 2 Course Year 2 Science IGCSE (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 2 at this link: Class 2
|
6 videos|24 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Forces and movement - Year 2 Science IGCSE (Cambridge) - Class 2
| 1. What are the different types of forces that affect movement? |  |
Ans. The different types of forces that affect movement include gravitational force, frictional force, air resistance, tension force, and normal force.
| 2. How does friction affect an object's movement? |  |
Ans. Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object. It can cause objects to slow down or come to a stop, as it acts in the opposite direction to the object's motion.
| 3. What is the relationship between force and acceleration? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's second law of motion, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. This means that a greater force will result in a greater acceleration, while a greater mass will result in a smaller acceleration for the same force.
| 4. How does air resistance impact the movement of objects? |  |
Ans. Air resistance is a type of frictional force that acts on objects as they move through the air. It can slow down the movement of objects, especially those with large surface areas like parachutes or feathers.
| 5. Can forces change the direction of an object's movement? |  |
Ans. Yes, forces can change the direction of an object's movement. For example, when a ball is kicked, the force applied causes it to change direction and move towards a different location.
Related Searches
















