Four Spheres of Earth | General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Lithosphere |

|
| The Hydrosphere |

|
| The Biosphere |

|
| The Atmosphere |

|
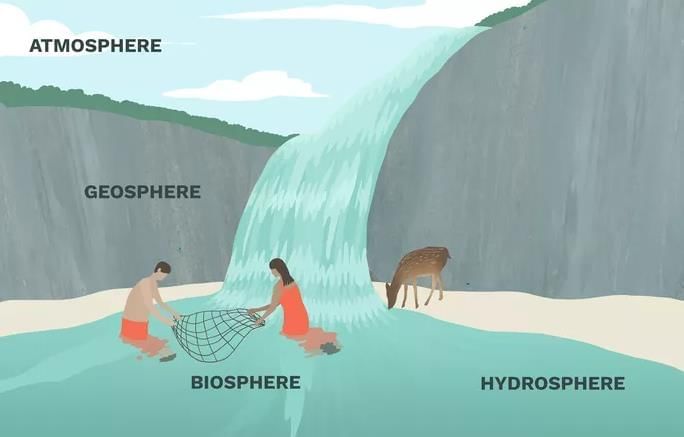
The Earth's boundary consists of four interconnected spheres: the lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere. These spheres represent different aspects of the Earth and are essential for studying the planet's organic and inorganic materials.
The Lithosphere
- The lithosphere, also known as the geosphere, includes all of the Earth's rocks, such as the mantle and crust, which are the outermost layers of the planet.
- This sphere encompasses features like the boulders of Mount Everest, the sands of Miami Beach, and lava from volcanoes like Mount Kilauea in Hawaii.
- The lithosphere varies in thickness from approximately 40 km to 280 km. It extends to the point where the minerals in the Earth's crust start to behave in a viscous or fluid manner.
- The exact depth at which this occurs depends on the Earth's chemical composition, as well as the heat and pressure acting on the material.
- The lithosphere is made up of about 12 major tectonic plates and several minor ones that fit together like a puzzle.
- These plates include the Eurasian, Indo-Australian, Philippine, Antarctic, Pacific, Cocos, Juan de Fuca, North American, Caribbean, South American, Scotia, and African plates.
- These tectonic plates are not static; they are slowly moving. The friction generated when these plates push against each other leads to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of mountains and ocean trenches.
The Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere includes all the water found on or near the Earth's surface, such as in oceans, rivers, lakes, underground aquifers, and the moisture present in the atmosphere. Scientists believe that the total amount of water on Earth is approximately 1.3 billion cubic kilometers.
- More than 97% of this water is located in the oceans.
- The remaining water is freshwater, with two-thirds of it frozen in polar regions and mountain snowpacks.
- Despite covering most of the planet's surface, water constitutes only 0.023% of the Earth's total mass.
The Earth's water is not stationary; it continuously changes form as it moves through the hydrological cycle. This cycle involves various processes:
- Water falls to the Earth as rain, seeps into underground aquifers, and can rise to the surface through springs or seep from porous rock.
- It flows from small streams into larger rivers, which eventually empty into lakes, seas, and oceans.
- From these bodies of water, some water evaporates back into the atmosphere, starting the cycle all over again.
The Biosphere
The biosphere includes all living organisms, such as plants, animals, and single-celled organisms. Most of the life on land is found in a zone that extends from three meters below the ground to 30 meters above it. In the oceans and seas, most marine life is found in a zone that stretches from the surface down to about 200 meters.
However, some creatures can live far outside these typical ranges:
- Birds have been observed flying as high as 7,000 meters above the Earth under certain conditions.
- The Mariana snailfish has been discovered living at depths greater than 6,000 meters in the Marianas Trench.
- Microorganisms are known to survive in extreme conditions well beyond these ranges.
The biosphere is made up of biomes, which are areas where similar types of plants and animals are found together. For example, a desert with its cacti, sand, and lizards is one type of biome, while a coral reef is another.
The Atmosphere
- The atmosphere is made up of gases that surround our planet, held in place by Earth's gravity. Most of this atmosphere is found close to the surface of the planet, where it is densest. The air consists of 79% nitrogen and just under 21% oxygen, with small amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, and other trace gases.
- The atmosphere extends about 10,000 kilometers into space and is divided into four main zones:
- Troposphere: This is the lowest layer, containing about three-quarters of the atmosphere's mass. It stretches from about 8 to 14.5 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- Stratosphere: Above the troposphere, the stratosphere extends up to 50 kilometers above the planet.
- Mesosphere: This layer reaches up to about 85 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- Thermosphere: The thermosphere extends to about 600 kilometers above the Earth.
- Exosphere: This is the outermost layer of the atmosphere. Beyond the exosphere is outer space.
Conclusion
- All four spheres of the Earth—lithosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and atmosphere—can exist together in a single location. For instance, in a piece of soil, there are minerals from the lithosphere, moisture from the hydrosphere, living organisms like insects and plants from the biosphere, and pockets of air from the atmosphere.
- This interconnected system is essential for supporting life as we know it on our planet.
|
64 videos|153 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Four Spheres of Earth - General Knowledge for Young Learners - Class 1
| 1. What are the four spheres of Earth, and how do they interact with each other? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the Lithosphere in Earth's system? |  |
| 3. How does the Hydrosphere contribute to weather and climate? |  |
| 4. In what ways does the Biosphere depend on the Atmosphere? |  |
| 5. What are some human impacts on the four spheres of Earth? |  |




















