Fuels and Fossil Fuels | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Fuel |

|
| Fossil Fuels |

|
| Exhaustible Natural Resources |

|
Introduction
Fuel is a combustible substance primarily made up of carbon. When properly burned in the presence of air, fuel releases a significant amount of energy as heat and light. Fuels can be classified into natural and artificial types. They provide substantial energy, economically utilized for various domestic and industrial purposes.
For example, when we burn a piece of paper with a matchstick, the flame produces light. This light energy results from the matchstick’s heat energy being transformed into light energy. Humans need specific materials to convert one form of energy into another to perform numerous tasks. These materials are called fuels. In this article, we will explore fuel and its properties in detail.
Types of Fuel
Based on occurrence, fuel can be categorized into two types:
- Natural or Primary fuel (e.g., coal, wood, crude oil, natural gas, etc.)
- Artificial or Secondary fuel (e.g., kerosene, charcoal, petrol, water gas, etc.)
Another way to classify fuel is by their physical state:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
Fuels possess distinct characteristics like ignition temperature and calorific value. These properties determine their applications in various aspects of daily life.
- Fuel plays a vital role in our daily activities including powering vehicles, generating electricity, and operating industries.
- Due to the escalating demand for fuel, there is a risk of overexploitation of non-renewable resources like coal, petroleum, and natural gas.
- Overuse of these resources could lead to their depletion.
- Hence, transitioning to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power is imperative.
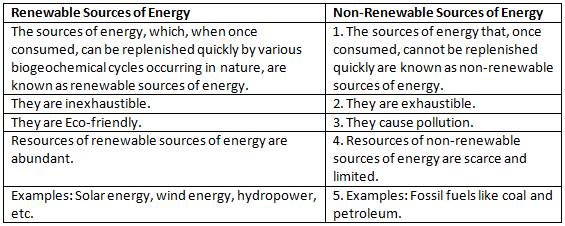
Renewable Vs Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
The difference between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy are explained below:
Fuels can be classified based on their occurrence and state. Based on occurrence, they are divided into:
Natural or Primary Fuels: These are naturally obtained and can be extracted, filtered, cleaned, or graded without significant energy expenditure. Primary fuels are generally non-renewable. Examples include coal, wood, crude oil, natural gas, and peat.
Artificial or Secondary Fuels: These are derived from primary fuels through chemical or physical processes that purify or remove impurities. Secondary fuels are processed forms of primary fuels. Examples include kerosene, charcoal, petrol, diesel, water gas, and biogas.
Based on the State of Aggregation
Fuels are also classified by the state in which they exist:
Solid Fuels: These exist in a solid state. Examples include coal, bituminous, anthracite, peat, wood, coke, and charcoal.
Liquid Fuels: These exist in a liquid state. Examples include diesel, petrol, kerosene, and crude oil.
Gaseous Fuels: These exist in a gaseous state. Examples include natural gas, biogas, and water gas. Gaseous fuels can be derived from natural gas (near coal and petroleum deposits) and other processes like biomass fermentation and petroleum refining.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are formed from the decomposition of dead plants and animals, primarily consisting of carbon and hydrogen, and are found in the Earth's crust. Examples include coal, petroleum, and crude oil. The formation process of coal, known as 'metamorphism,' involves the decomposition of organic material into peat, which, over millions of years under high pressure and temperature, transforms into coal.
Formation of Coal
- Millions of years ago, deceased plants and animals were buried deep in the ground.
- Initially, these expired natural materials rotted into peat.
- Over time, with immense pressure and heat, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen were extracted, leaving behind only carbon, which turned into coal.
- Coal, a type of natural fuel from the earth, is obtained through mining and serves as a significant energy source.
- The transformation of buried plants into coal due to decomposing processes is termed as 'Metamorphism'.
Exhaustible Natural Resources
Fossil fuels form slowly over millions of years and will take another million years to replenish once fully used. - Human consumption of fossil fuels is rapid compared to their natural formation rate. - Fossil fuels are limited and exhaustible energy resources.
- The creation of fossil fuels is a lengthy process, spanning millions of years. Consequently, it would require an additional million years to regenerate them after full depletion.
- This implies that the speed at which humans consume fossil fuels greatly surpasses how quickly they are naturally produced.
- These depletable energy resources exist in finite amounts, making fossil fuels exhaustible natural reserves.
Burning Fossil Fuels
The burning of fossil fuels refers to burning coal, crude oil, and natural gas to generate energy. This energy is used to generate electricity and other industrial activities. Petrol, diesel, and CNG are widely used as fuels for running vehicles that help transportation. Coal was firstly used around the as a fuel in fired steam engines. With time, the burning of fossil fuels has steadily increased. Each year, all across the world, fossil fuels are burned to produce around million tonnes of carbon dioxide, which is a significant reason for global warming. Along with carbon dioxide, other gases such as nitrogen oxides, sulphur, and many other harmful gases are released into the atmosphere that adversely affects our environment. This combustion of fossil fuels can be explained by the chemical equation given below: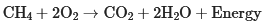
Alternatives to Fossil Fuels
- Renewable Energy Sources:
To prevent environmental pollution, it's better to choose renewable energy sources like wind and solar power instead of fossil fuels. These energy sources are abundant and always available.
- Wind Energy:
Wind energy is commonly used to generate electricity through windmills.
- Solar Energy:
Solar energy is a significant renewable energy source on Earth. Solar cells and panels are used to create electricity.
- Hydroelectricity:
Hydropower plants utilize water as an energy source.
- Biofuel:
Biodiesel, derived from sources like vegetable oils and animal fats, serves as a clean substitute for diesel fuel. It's non-toxic and biodegradable.
- Nuclear Fuel:
Nuclear fuels like Uranium and Plutonium are used in reactors to produce vast amounts of energy. They cause minimal air pollution.
- Hydrogen Fuel:
Hydrogen fuel, found in hydrocarbons and organic matter, is becoming a popular alternative to traditional fuels due to its efficiency and high energy content.
- Hydrogen is naturally available in the environment.
- It's more efficient than other energy sources.
- Hydrogen fuel is environmentally friendly as it will produce only water vapour on burning..
Properties of an Ideal Fuel
- Calorific Value: It's how much heat a fuel makes when it burns. The main job of fuel is to change as much of its chemical energy into heat and other types of energy when it burns. The higher the calorific value, the better the fuel.
- Ignition Temperature: This is the lowest temperature at which a material catches fire. A good fuel should catch fire easily at a low temperature.
- Rate of Combustion: An ideal fuel burns steadily and at a normal speed. If a fuel burns too fast and explodes, it's not ideal.
- Environmental Friendly: When we use fuel, we worry about how it affects the environment. A good fuel should burn completely with little residue left behind, so it doesn't pollute the air with particles. Examples include CNG and LPG.
- Readily available: An ideal fuel should be easy to find when you need it and shouldn't cost a lot.
- Handling: Fuel should be simple to store and move around. This makes it easier to reach, prevents waste, and protects the environment.
Summary
Fuel is defined as a material that produces heat and energy upon combustion.
Fuels are used in various applications: petrol and diesel power vehicles, coal is used in power plants for electricity generation, and natural gas is another type of fuel used to generate energy.
- Fuels can be classified based on their occurrence into natural or primary fuels and artificial or secondary fuels.
- They can also be classified by the state in which they exist: solid, liquid, and gas.
Most natural fuels are fossil fuels, including coal, bituminous, anthracite, peat, wood, coke, charcoal, diesel, petrol, kerosene, crude oil, natural gas, biogas, and water gas.
- A good fuel should have a moderate ignition temperature and a high calorific value.
- Although fossil fuels are very effective for energy generation, they are non-renewable and significantly pollute the environment.
- Therefore, we should transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydro energy.
- These renewable sources can help protect our natural resources to a great extent.
|
477 videos|1443 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Fuels and Fossil Fuels - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the different types of fuel? |  |
| 2. What are fossil fuels and why are they considered exhaustible natural resources? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of using fossil fuels as a source of energy? |  |
| 4. How are fossil fuels extracted and processed for use as energy sources? |  |
| 5. What are some alternative sources of energy to fossil fuels? |  |




















