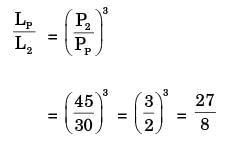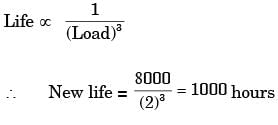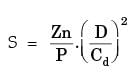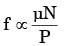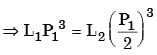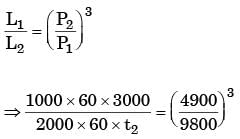GATE Past Year Questions: Bearings | Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: For a ball bearing, the fatigue life in millions or revolutions is given by L = (c/P)n, where P is the constant applied load and c is the basic dynamic load rating. Which one of the following statements is TRUE? [GATE ME 2024]
(a) n = 3, assuming that the inner racing is fixed and outer racing is revolving.
(b) n = 1/3, assuming that the outer racing is fixed and the inner racing is revolving
(c) n = 3, assuming that the outer racing is fixed and inner racing is revolving
(d) n = 1/3, assuming that the inner racing is fixed and outer racing is revolving
Ans: (c)
L = (C/P)n x 106 rev
n = 3 for ball bearing
n = 10/3 for roller bearing
Q1: A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque Mz about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300N and T2 = 100N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The selfweights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of π available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places). [GATE ME 2022 SET-2]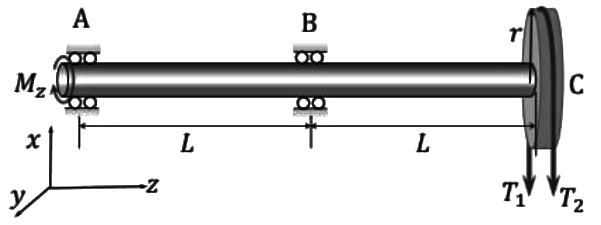 Ans: 23.6 to 24.2
Ans: 23.6 to 24.2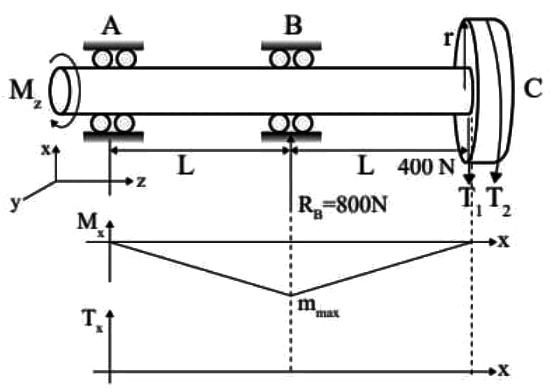
Mₘₐₓ = 400 × L = 400 × 0.5 × 10³
= 200 × 10³ N·mm
Tₘₐₓ = Mz
= (T₁ - T₁) × r
= (200 × 0.4) × 10³
Tₘₐₓ = 80 × 10³ N·mm
Here section-B is critical due to loading,
Critical particle :
According to maximum shear stress theory,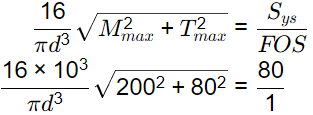
⇒ d = 23.94 mm
Q2: A shaft of length L is made of two materials, one in the inner core and the other in the outer rim, and the two are perfectly joined together (no slip at the interface) along the entire length of the shaft. The diameter of the inner core is di and the external diameter of the rim is do, as shown in the figure. The modulus of rigidity of the core and rim materials are Gi and Go, respectively. It is given that do do = 2di and Gi = 3Go. When the shaft is twisted by application of a torque along the shaft axis, the maximum shear stress developed in the outer rim and the inner core turn out to be τo and τi, respectively. All the deformations are in the elastic range and stress strain relations are linear. Then the ratio τi/τo is ______ (round off to 2 decimal places). [GATE ME 2022 SET-2]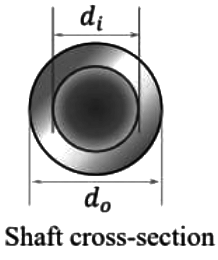 Ans: Given Gi = 3Go, do = 2di, li = lo, θi = θo (It is a rigid joint)
Ans: Given Gi = 3Go, do = 2di, li = lo, θi = θo (It is a rigid joint)
Find Ti/To =?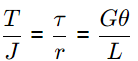
τmax(in core) = 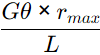
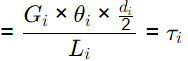
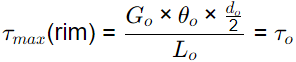
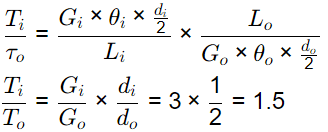
[2016,Set-3]
[2011]
[2010]
[2008]
[2007]
[2007]
[2005]
[2005]
[1997]
[1997]
[1996]
[1992]
[1992]
[1988]
[1987]
|
51 videos|102 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Bearings - Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What are the different types of bearings used in mechanical engineering? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate the load capacity of bearings? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of bearing life in mechanical systems? |  |
| 4. What factors should be considered when selecting a bearing for a specific application? |  |
| 5. How can improper lubrication affect bearing performance? |  |