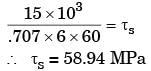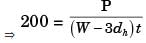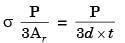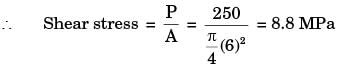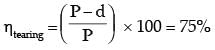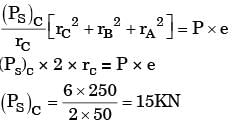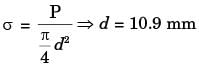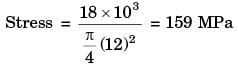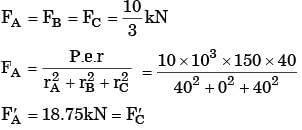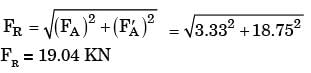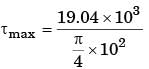GATE Past Year Questions: Bolted, Riveted & Welded Joint | Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: A bracket is attached to a vertical column by means of two identical rivets U and V separated by a distance of 2 a = 100 mm , as shown in the figure. The permissible shear stress of the rivet material is 50MPa. If a load P = 10 kN is applied at an eccentricity e = 3 √7 a , the minimum crosssectional area of each of the rivets to avoid failure is ___________ mm2 [GATE ME 2022, SET-1]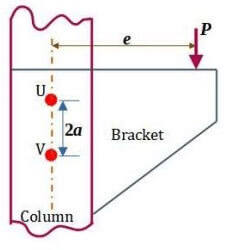 (a) 800
(a) 800
(b) 25
(c) 100√7
(d) 200
Ans: (a)
The given load is eccentric lateral load which results in
(i) primary shear due to direct loading
(ii) secondary shear due to eccentricity
(i) Primary shear: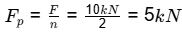
(ii) Secondary shear:
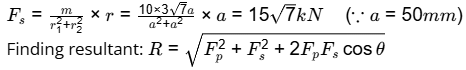
Here, θ is 90°
As secondary load is same on both rivets. Both are critical due to loading.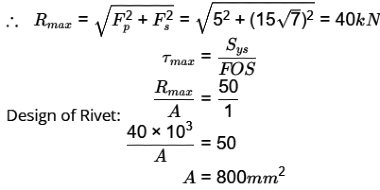
As FOS is considered as 1, A represents the minimum cross section area required.
Q2: A square threaded screw is used to lift a load W by applying a force F. Efficiency of square threaded screw is expressed as [GATE ME 2022, SET-1]
(a) The ratio of work done by W per revolution to work done by F per revolution
(b) W/F
(c) F/W
(d) The ratio of work done by F per revolution to work done by W per revolution
Ans: (a)
Screw efficiency= Work done in lifting the load/rev/Work done by the applied force/rev
Efficiency of screw jack η = tan α/tan ( α + ϕ )
Q1: A cantilever beam of rectangular cross-section is welded to a support by means of two fillet welds as shown in figure. A vertical load of 2 kN acts at free end of the beam. [GATE ME 2021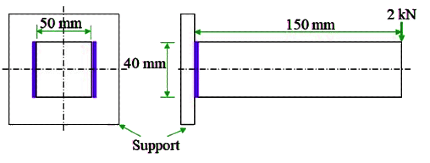
Considering that the allowable shear stress in weld is 60 N/mm 2 , the minimum size (leg) of the weld required is _______-mm (round off to one decimal place).
Ans: (6.4 to 6.9)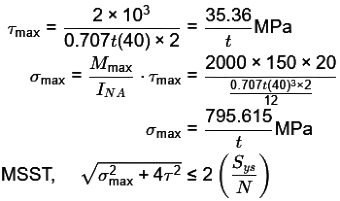
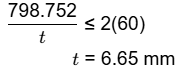
Q1: A bolt head has to be made at the end of a rod of diameter d = 12 mm by localized forging (upsetting) operation. The length of the unsupported portion of the rod is 40 mm. To avoid buckling of the rod, a closed forging operation has to be performed with a maximum die diameter of ________ mm. [GATE ME 2020, SET-2]
Ans: (18 to 19.5)
If l >3d then
Die dia =1.5d
=1.5 (12)
=18mm
Q2: A rectangular steel bar of length 500 mm, width 100 mm, and thickness 15 mm is cantilevered to a 200 mm steel channel using 4 bolts, as shown. [GATE ME 2020, SET-1]
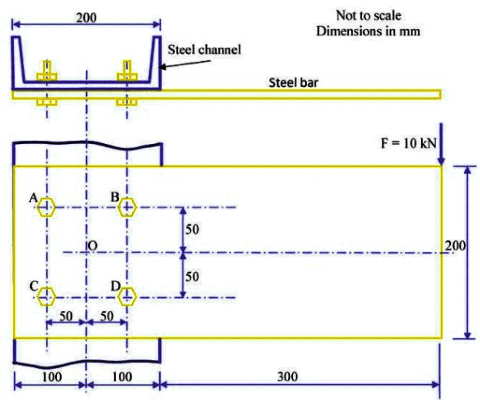
Ans: (15.9 to 16.1)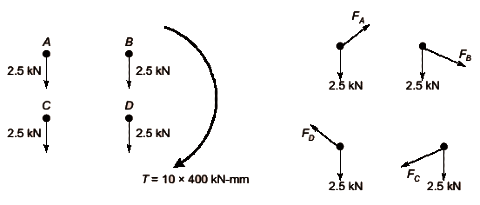
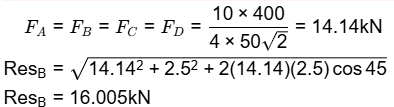
The factor of safety is [2006]
[1987]
If the plates are to be designed to avoid tearing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kN is [2013]
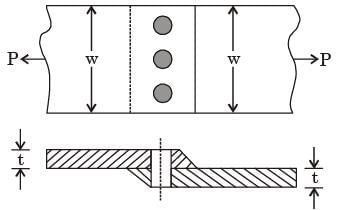
width of the plate ω = 200 mm, thickness of the plate t = 5 mm, number of rivets n = 3, diameter of the rivet dr = 10 mm, diameter of the rivet hole dr = 11 M mm, allowable tensile stress of the plate σp = 200 MPa, allowable shear stress of the rivet σs = 100 MPa and allowable bearing stress of the rivet σc = 150 MPa.
If the rivets are to be designed to avoid crushing failure, the maximum permissible load P in kN is [2013]
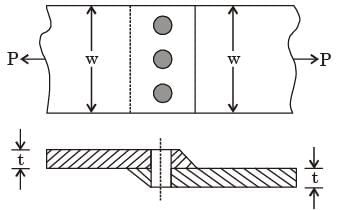
width of the plate ω = 200 mm, thickness of the plate t = 5 mm, number of rivets n = 3, diameter of the rivet dr = 10 mm, diameter of the rivet hole dr = 11 M mm, allowable tensile stress of the plate σp = 200 MPa, allowable shear stress of the rivet σs = 100 MPa and allowable bearing stress of the rivet σc = 150 MPa.
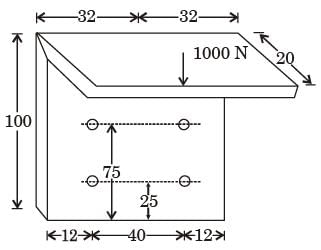
Direct shear stress (in MPa) in the most heavily loaded rivet is
[1996]
[2018, Set-2]
[2017, Set-2]
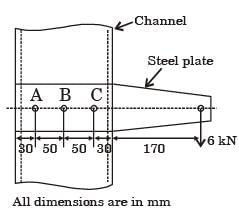
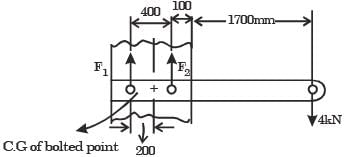
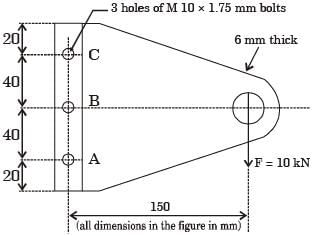
Considering the effect of direct load and moment, the magnitude of resultant shear force (in kN) on bolt C is
[2014, Set-2]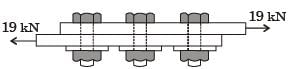
The resultant shear stress on bolt P is closest to: [2008]
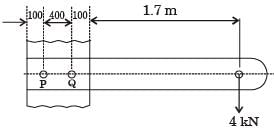
The primary and secondary shear loads on bolt P, respectively, are

[2007]
[2004]
[1998]
[1996]
|
49 videos|107 docs|77 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Bolted, Riveted & Welded Joint - Design of Machine Elements - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is the difference between a bolted joint and a riveted joint? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using a welded joint over a bolted or riveted joint? |  |
| 3. How can the strength of a bolted joint be improved? |  |
| 4. What are the limitations of a riveted joint? |  |
| 5. Can a bolted joint be converted to a welded joint? |  |