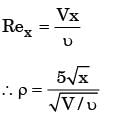GATE Past Year Questions: Boundary Layer Theory | Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: The figure shows two fluids held by a hinged gate. The atmospheric pressure is Pa = 100 k Pa. The moment per unit width about the base of the hinge is ________ kNm/m. (Rounded off to one decimal place)
Take the acceleration due to gravity to be g = 9.8 m/s2 [GATE ME 2023]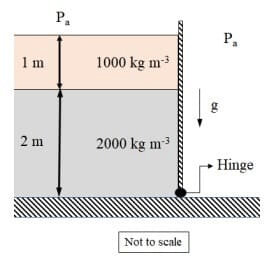
Ans: (55.9 to 58.5]
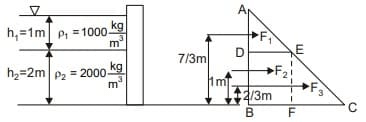 Forces from Pressure diagram
Forces from Pressure diagram
F1 = Area of △ A D E × △ADE × width
F1 = 1/2 x AD x DE x width
= 1/2 × 1 × 9810 × 1
F1 = 4905 N
F2 = Area of rectangle DEBF × width
F2 = 2 × 9810 × 1
F2 = 19620 N
F3 = Area of triangle ΔEFC
= 1/2 × EF × FC × width
= 1/2 x 2 x 39240 x 1
F3 = 39240 N
Location of forces from top
F1 → 2/3 x = 2/3 m
F2 → (1m + 2m/2) = 2m
F3 → 1m + 2m x 2/3 = 7/3m
Pressure at depth 1 m =ρ1 gh1
1000 × 9.81 × 1=9810 N/m2
DE = 9810 N/m2
BF = 9810 N/m2
Pressure at depth 3 m
P1gh1 + P2gh2
9810 + 2000 × 9.81 × 2
9810 + 39240 = 49050 N/m2
(BF) + (FC) = BC
Location of forces from bottom hinge
F1 → 3m - 2/3 m = 7/3 m
F2 → 3m - 2m = 1m
F3 → 3m - 7/3 m = 2/3 m
Moment about hinge F1 × 7/3 + F2 × 1 + F3 × 2 /3
4905 × 7/3 + 19620 + 39240 × 2/3
⇒ 57225Nm = 57.22kNm/m
Q1: A uniform wooden rod (specific gravity = 0.6, diameter = 4 cm and length = 8 m) is immersed in the water and is hinged without friction at point A on the waterline as shown in the figure. A solid spherical ball made of lead (specific gravity = 11.4) is attached to the free end of the rod to keep the assembly in static equilibrium inside the water. For simplicity, assume that the radius of the ball is much smaller than the length of the rod. [GATE ME 2022, SET-2]
Assume density of water = 103kg/m3 and π = 3.14
Radius of the ball is _______ cm (round off to 2 decimal places).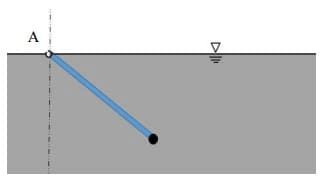 Ans: (3.48 to 3.7)
Ans: (3.48 to 3.7)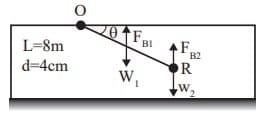 As the system is in equilibrium,
As the system is in equilibrium,
Σ M o = 0 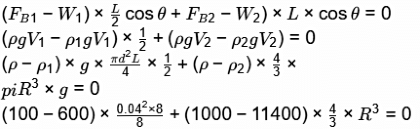
⇒ R = 0.03587m = 3.59cm
Q2: Consider a steady flow through a horizontal divergent channel, as shown in the figure, with supersonic flow at the inlet. The direction of flow is from left to right. [GATE ME 2022, SET-2]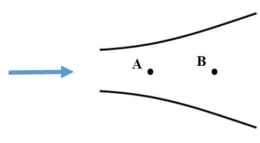
Pressure at location B is observed to be higher than that at an upstream location A. Which among the following options can be the reason?
(a) Since volume flow rate is constant, velocity at B is lower than velocity at A
(b) Normal shock
(c) Viscous effect
(d) Boundary layer separation
Ans: (a, b)
If the supersonic flow enters to the diverging duct, it will act as nozzle the pressure of the flow is decreases in the nozzle. But it is given the pressure of the flow at B is more than that A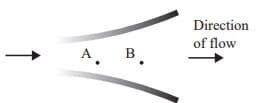
It will happen only with the development of normal shoot in the diverging flow (the normal shock wave is the characteristic of only supersonic flow) Because of normal shock wave in the diverging nozzle pressure increases and velocity decreases. But mass flow rate remains unchanged.
Q3: A solid spherical bead of lead (uniform density = 11000 kg/ m3 ) of diameter d = 0.1 mm sinks with a constant velocity V in a large stagnant pool of a liquid (dynamic viscosity = 1.1 × 1 0 − 3 k g . m − 1 . s − 1 ) The coefficient of drag is given by CD = 24/Re where the Reynolds number (Re) is defined on the basis of the diameter of the bead. The drag force acting on the bead is expressed as D = (C D )(0.5ρV 2 )( πd 2/4 ), where p is the density of the liquid. Neglect the buoyancy force. Using g = 10 m/s 2 , the velocity V is __________ m/s. [GATE ME 2022, SET-1]
(a) 1/24
(b) 1/6
(c) 1/18
(d) 1/12
Ans: (c)
As buoyancy force is neglected we can neglect density of fluid () in the following equation.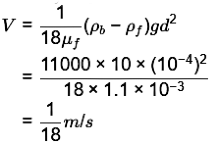
Q4: The figure shows a purely convergent nozzle with a steady, inviscid compressible flow of an ideal gas with constant thermophysical properties operating under choked condition. The exit plane shown in the figure is located within the nozzle. If the inlet pressure ( P 0 ) is increased while keeping the back pressure (P back ) unchanged, which of the following statements is/are true? [GATE ME 2022, SET-1]
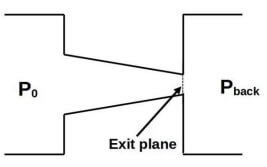
(a) Mass flow rate through the nozzle will remain unchanged.
(b) Mach number at the exit plane of the nozzle will remain unchanged at unity
(c) Mass flow rate through the nozzle will increase.
(d) Mach number at the exit plane of the nozzle will become more than unity.
Ans: (b, c)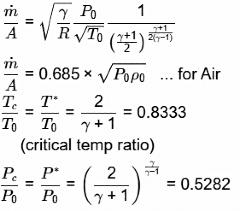
(critical temp ratio)
where γ = Adiabatic index = 1.4
If P0 increases , mass flow rate increases. Mach number at the exit plane of the nozzle will remain unchanged at unity. Since the maximum expected velocity from the converging nozzle is sound velocity.
Q5: In the following two-dimensional momentum equation for natural convection over a surface immersed in a quiescent fluid at temperature T ∞ (g is the gravitational acceleration, β β is the volumetric thermal expansion coefficient, v v is the kinematic viscosity, u u and v are the velocities in x and y directions, respectively, and T is the temperature) [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
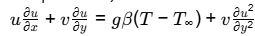
the term g β ( T − T ∞ ) represents
(a) Ratio of inertial force to viscous force.
(b) Ratio of buoyancy force to viscous force.
(c) Viscous force per unit mass.
(d) Buoyancy force per unit mass.
Ans: (d) 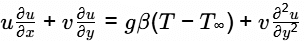
This is the equation that governs the fluid motion in the boundary layer due to effect of Buoyancy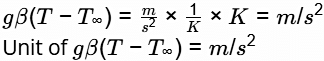
Buoyancy force is due to density difference and gravitational effect
g β (T − T ∞ ) represents Buoyancy force per unit mass.
Q1: Which of the following is responsible for eddy viscosity (or turbulent viscosity) in a turbulent boundary layer on a flat plate? [GATE ME 2021, SET-2]
(a) Nikuradse stresses
(b) Reynolds stresses
(c) Boussinesq stresses
(d) Prandtl stresses
Ans: (b)
Reynolds stresses are responsible for eddy viscosity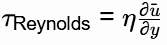
where η= Eddy viscosity.
Q2: Consider fully developed, steady state incompressible laminar flow of a viscous fluid between two large parallel horizontal plates. The bottom plate is fixed and the top plate moves with a constant velocity of U = 4 m/s. Separation between the plates is 5 mm. There is no pressure gradient in the direction of flow. The density of fluid is 800 kg/m3, and the kinematic viscosity is 1.25 × 1 − 4 m2/s The average shear stress in the fluid is ________Pa (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2021, SET-1]
Ans: (79 to 81)
V = 4m/s
p = 800 kg/m3
v =1.25 × 10 −4 m2/s
h = 5 mm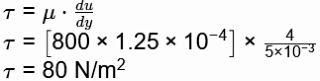
= 80 Pa
Q1: Water (density 1000 k g/m3) flows through an inclined pipe of uniform diameter. The velocity, pressure and elevation at section A are VA = 3.2 m/s, pA = 186 kPa and zA = 24.5 m respectively, and those at section B are VB = 3.2 m/s, pB = 260 k P and zB = 9.1 m , respectively. If acceleration due to gravity is 10 m/s2 then the head lost due to friction is _________ m (round off to one decimal place). [GATE ME 2020, SET-2]
Ans: (7.9 to 8.1)
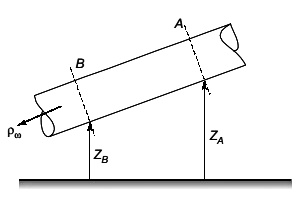
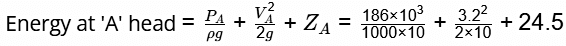
=18.6 + 0.512+ 24.5 = 43.612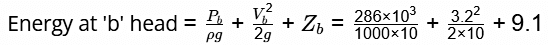
=26 + 0.512 + 9.1=35.612
EA > EB ′ so flow from 'A' to 'B'
Heat loss = EA − EB = 43.612 − 35.612 = 8 m = of water head
Q2: Consider steady, viscous, fully developed flow of a fluid through a circular pipe of internal diameter D. We know that the velocity profile forms a paraboloid about the pipe center line, given by: V = -C (r2 - D2/4) m/s, where C is a constant. The rate of kinetic energy (in J/s) at the control surface A-B, as shown in the figure, is proportional to Dn. The value of n is________. [GATE ME 2020, SET-1]
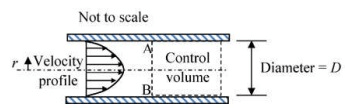
Ans: (8 to 8)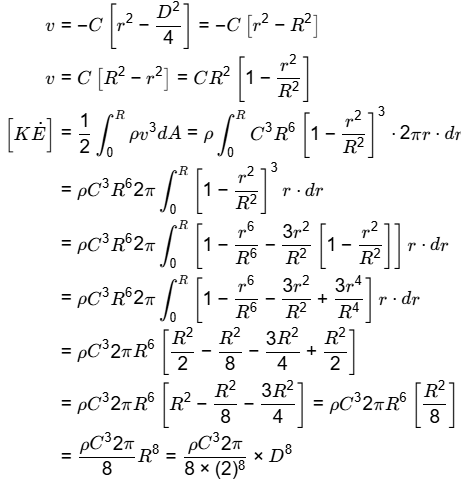
n = 8
Q3: Match the following non-dimensional numbers with the corresponding definitions: [GATE ME 2020, SET-1]
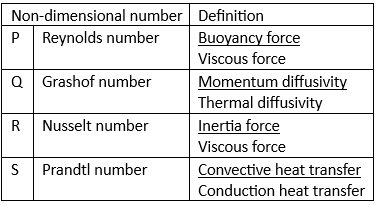 (a) P-1, Q-3, R-2, S-4
(a) P-1, Q-3, R-2, S-4
(b) P-3, Q-1, R-2, S-4
(c) P-4, Q-3, R-1, S-2
(d) P-3, Q-1, R-4, S-2
Ans: (d)
Q4: Froude number is the ratio of [GATE ME 2020, SET-1]
(a) buoyancy forces to viscous forces
(b) inertia forces to viscous forces
(c) buoyancy forces to inertia forces
(d) inertia forces to gravity forces
Ans: (c)
[2012]
[2007]
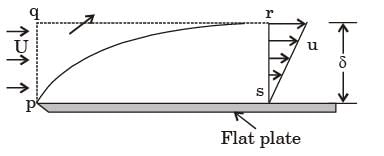
The integrated drag force (in N) on the plate, between p – s, is
[2006 ]
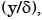 , at the section r-s, where y is the height from plate.
, at the section r-s, where y is the height from plate.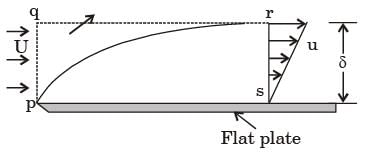
The mass flow rate (in kg/s) across the section q – r is
[2006]
[2002]
[2002]
[1990]
u(x, y, z, t) =
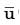 (x, y, z) + u'(x, y, z, t) The time average of the fluctuating velocity u (x, y, z, t) is
(x, y, z) + u'(x, y, z, t) The time average of the fluctuating velocity u (x, y, z, t) is
[2016]
.I. The fluid is well-mixed
II. The fluid is unmixed
III.ReD < 2300
IV. ReD > 2300
[2014]
P: Compressible flow U: Reynolds number
Q: Free surface flow V: Nusselt number
R: Boundary layer flow W: Weber number
S: Pipe flow X: Froude number
T: Heat convection Y: Mach number
Z: Skin friction coefficient
[2010]
[1994]
[1988]
[Question:504379]
|
56 videos|106 docs|75 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Boundary Layer Theory - Fluid Mechanics for Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is the boundary layer theory in fluid mechanics? |  |
| 2. What are the key assumptions of the boundary layer theory? |  |
| 3. How do you determine the boundary layer thickness? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Reynolds number in boundary layer theory? |  |
| 5. How does boundary layer separation occur and why is it important? |  |

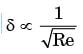
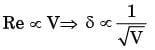
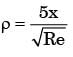 for laminar flow
for laminar flow