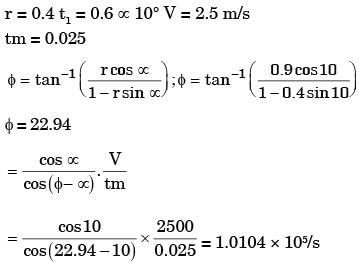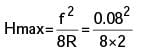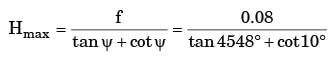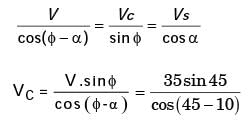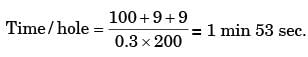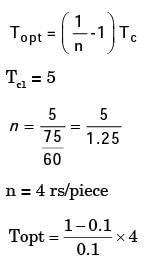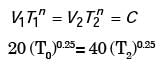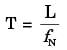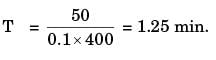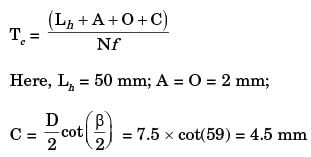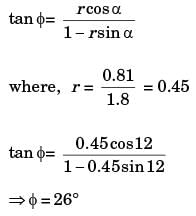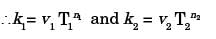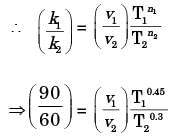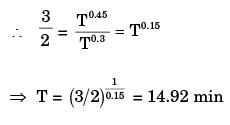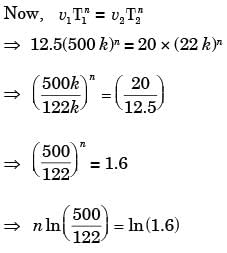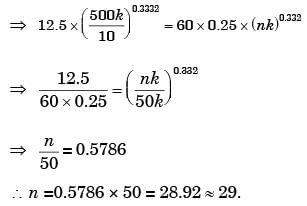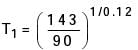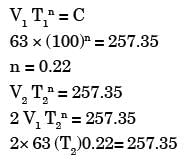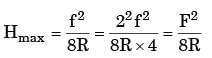Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a shaping process, the number of double strokes per minute is 30 and the quick return ratio is 0.6. If the length of the stroke is 250 mm, the average cutting velocity in mm/min.
[PI 2012]
Explanation
Number of Double stroke = 30
Quick Return Ratio = 0.6 = M
Length of Strike = 250 mm = L
Average cutting velocity = L.N (1 + 19)
= 30 × 250 (1 + 0.6) = 12 m /min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Details pertaining to an orthogonal metal cutting process are given below:
Chip thickness ratio 0.4
Undeformed thickness 0.6 mm
Rake angle +10°
Cutting speed 2.5 m/s
Mean thickness of primary shear zone 25 microns
The shear strain rate in s-1 during the process is
[PI 2012]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Two identical cylindrical jobs are turned using (a) a round nosed tool of nose radius 2 mm and (b) a sharp corner tool having principal cutting edge angle = 45° and auxiliary cutting edge angle = 10°. If the operation is carried out of the feed of 0.08 mm/rev, the height at micro irregularities on the machined surfaces (in mm) in the two cases will be
[PI 2004]
Explanation
ASA Signature
ψ = 45°, ψ =10°
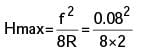
ORS signature = 0.0004 mm
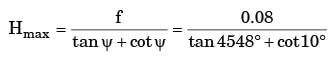
Hmax = 0.012 mm
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:The rake angle of a cutting tool is 15°, shear angle 45° and cutting velocity 35 m/min. What is the velocity of chip along the tool face?
[PI 2005]
Explanation
α = 15°
ϕ = 45°
V = 35 m/min
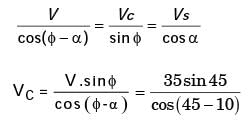
Vc = 25.58 m/min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A cylinder of 25 mm diameter and 100 mm length is turned with a tool, for which the relation VT0.25 = 55 is applicable. The cutting velocity is 22 m/min. For a tool feed of 0.046 mm/rev, the number of tool regrinds required to produce 425 cylinders is
[PI 2003]
Explanation
D = 25 mm,
h = 100 mm
VT0.25= 55
V = 22 m/min, f = 0.046 mm/ rev

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A 31.8 MM HSS drill is used to drill a hole in cast iron block 100 mm thick at cutting speed of 20 m/min and feed 0.3 mm/rev. If the over travel of drill is 4 mm and approach 9 mm, the time required to drill the hole is
[PI 2002]
Explanation
D = 31.8mm, t = 100 mm, V = 20m /min
f = 0.3 mm/rev,
Approach length = 4 mm
Over Travel = 9 mm
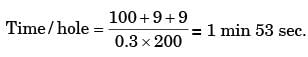
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Two different tools A and B having nose radius of 0.6 mm and 0.33 mm respectively are used to machine C-45 steel employing feed rate of 0.2 mm/rev and 0.1 mm/rev respectively. The tool that gives better finish and the value of ideal surface roughness are
[PI 2002]
Explanation
RA = 0.6 mm. RB = 0.33 mm
FA = 0.2 mm/rev FB = 0.1 mm/rev

Tool B have higher surface finish them A.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a single pass turning operation the cutting speed is the only variable based on the cutting time cost and the cutting edge cost. The tool life for minimum cost given that cost of 1 cutting edge is Rs. 5, operator wages including the machine tool cost is Rs. 75/hour and tool life equation is VT0.1 is 100
[PI 1995]
Explanation
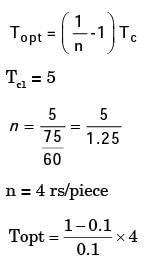
Topt = 36 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A workpiece of 2000 mm length and 300 mm width was machined by a planning operation with the feed set at 0.3 mm/stroke. If the machine tool executes 10 double strokes/min, the planning time for a single pass will be
[PI 1993]
Explanation
l = 2000 mm
w = 300 mm
f = 0.3 mm/ stroke
No. of stroke = 2 × 10
= 20 stroke / min {double stroke}
2000 „„„
Total Machining time= 2000/20 =100 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a cutting test with 0.3 mm flank wear as tool failure criterion, a tool life of 10 min was obtained at a cutting velocity of 20 m/min. Taking tool life exponent as 0.25, the tool life in minutes at 40 m/min of cutting velocity will be
[PI 1993]
Explanation
n = 0.25 V1 = 20m /min, T1 = 10 min
V2 = 40m/min , T2 = ?
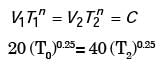
T2 = 0.625 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A single point cutting tool with 12° rake angle is used for orthogonal machining of a ductile material. The shear plane angle for the theoretically minimum possible shear strain to occur
[PI 1990]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:lf the number of double strokes per minute in a shaper is calculated by (0.643 × Cutting speed in mm/min)/length of the stroke in m. Then the return speed is faster than the cutting speed by
[PI 1989]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Feed rate in slab milling operation is equal to
[ME 2018,Set-2]
Explanation
Table feed or Feed rate
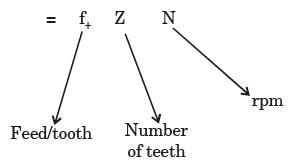
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:The preferred option for holding an odd-shaped workpiece in a centre lathe is
[ME 2018,Set-2]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A hole of 20 mm diameter is to be drilled in a steel block of 40 mm thickness. The drilling is performed at rotational speed of 400 rpm and feed rate of 0.1 mm/rev. The required approach and over run of the drill together, is equal to the radius of drill. The drilling time (in minute) is
[ME 2014,Set-2]
Explanation
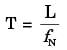
L = t + Ap1
Ap1 = 0.5 D (holes diameter)
= 10 mm
t = 40 mm
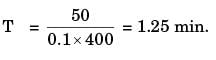
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a single pass drilling operation, a through hole of 15 mm diameter is to be drilled in a steel plate of 50 mm thickness. Drill spindle speed is 500 rpm, feed is 0.2 mm/rev and drill point angle is 118°, Assuming 2 mm clearance at approach and exit, the total drill time (in seconds) is
[ME 2012]
Explanation
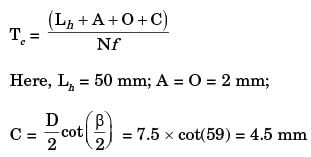
N = 500 rpm; f = 0.2 mm/rev
Tc = 0.585 min or 35.1 seconds
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
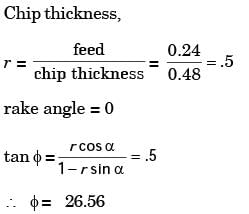
Try yourself:A single-point cutting tool with 12° rake angle is used to machine a steel work-piece. The depth of cut, i.e. uncut thickness is 0.81 mm. The chip thickness under orthogonal machining condition is 1.8 mm. The shear angle is approximately
[ME 2011]
Explanation
Relation between shear angle (ϕ), chip thickness ratio (r) and rake angle (α) is given by
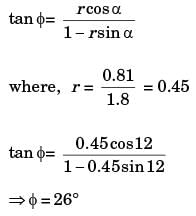
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:For tool A, Taylor's tool life exponent (n) is 0.45 and constant (K) is 90. Similarly for tool B, n = 0.3 and K = 60. The cutting speed (in 'm/ min) above which tool A will have a higher tool life than tool B is
[ME 2010]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Friction at the tool-chip interface can be reduced by
[ME 2009]
Explanation
By increasing the cutting speed. Heat dissipation is increased hence there is lower temperature & lower friction coefficient.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a single point turning tool, the side rake angle and orthogonal rake angle are equal. ϕ is the principal cutting edge angle and its range is 0° ≤ f ≤ 90°. The chip flows in the orthogonal plane. The value of ϕ is closest to
[ME 2008]
Explanation
Side rake angle is equal to orthogonal rake angle when principle cutting edge angle become 90° and corresponding approach angle SCEA = 0°
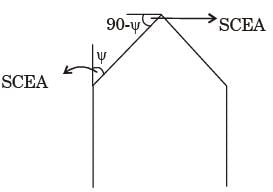
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In orthogonal turning of low carbon steel pipe with principal cutting edge angle of 90°, the main cutting force is 1000 N and the feed force is 800 N. The shear angle is 25° and orthogonal rake angle is zero. Employing Merchants theory, the ratio of friction force to normal force acting on the cutting tool is
[ME 2007]
Explanation
Here, ϕ = shear angle = 25º
λ = Friction angle,
α = rake angle = 0º
From Merchant''s theory, 2ϕ + λ - α = 90º
∴ λ = 90º - 50º = 40º

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In orthogonal turning of medium carbon steel, the specific machining energy is 2.0 J/mm3. The cutting velocity, feed and depth of cut are 120 m/min, 0.2 mm/rev and 2 mm respectively.The main cutting force in N is
[ME 2007]
Explanation
FC = Cutting force;
V = Cutting velocity
Specific machining energy = 2.0 J/mm3
∴ FC × V =2 × MRR
⇒ FC = 2 × .2 × 10–3 × 2 × 103 = 800 N
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In orthogonal turning of a low carbon steel bar of diameter 150 mm with uncoated carbide tool, the cutting velocity is 90 m/min. The feed is 0.24 mm/rev and the depth of cut is 2 mm. The chip thickness obtained is 0.48 mm. If the orthogonal rake angle is zero and the principal cutting edge angle is 90°, the shear angle in degree is
[ME 2007]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A 600 mm x 30 mm flat surface of a plate is to be finish machined on a shaper. The plate has been fixed with the 600 mm side along the tool travel direction. If the tool over-travel at each end of the plate is 20 mm, average cutting speed is 8 m/min, feed rate is 0.3 mm/stroke and the ratio of return time to cutting time of the tool is 1 : 2, the time required for machining will be
[ME 2005]
Explanation
Length travelled in forwarded stroke = 640 mm Number of strokes = 100
Time for cutting = 8 min
Return time = 4 min
Total time = 12 min.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In a machining operation, doubling the cutting speed reduces the tool life to 1/8th of the original value. The exponent n in Taylor's tool life equation VTn = C. is
[ME 2004]
Explanation
Taylor’s tool life equation,
VTn = C ...(i)
Where, V = cutting speed and T = tool life
When cutting speed is doubled and tool life

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Through holes of 10 mm diameter are to be drilled in a steel plate of 20 mm thickness. Drill spindle speed is 300 rpm, feed 0.2 mm/rev and drill point angle is 120°. Assuming drill over travel of 2 mm, the time for producing a hole will be
[ME 2004]
Explanation
Given: Diameter of hole,
d =10 mm
Thickness of steel plate, t = 20 mm

Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:A batch of 10 cutting tools could produce 500 components while working at 50 rpm with a tool feed of 0.25 mm/rev and depth of cut of 1 mm. A similar batch of 10 tools of the same specification could produce 122 components while working at 80 rpm with a feed of 0.25 mm/rev and 1 mm depth of cut. How many components can be produced with one cutting tool at 60 rpm?
[ME 2003]
Explanation
Velocity of first cutting tool,
v1 = 50 × 0.25 = 12.5 mm/min
Velocity of second cutting tool,
v2 = 0.25 × 80= 20 mm/min
Since tool life = number of component produce × tool constant
∴ Tool life for first tool = T1 = 500 × k
Took life for second tool = T21 = 122 × k
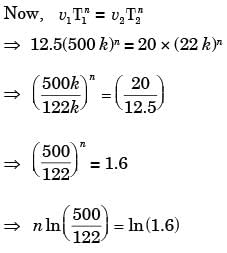
⇒ n = 0.3332 Hence number of components produced by one cutting tool at 60 rpm is:
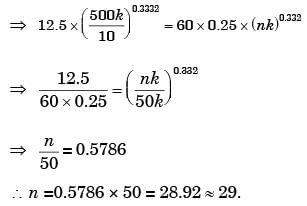
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Tool life testing on a lathe under dry cutting conditions gauge n and C of Taylor tool life equation as 0.12 and 130 m/min. respectively. When a coolant was used, C increased by 10%.The increased tool life with the use of coolant at a cutting speed of 90 m/min is
[ME 2001]
Explanation
n = 0.12, c = 130 m /min
C1 = 130 × 1.1 = 143 m/min
V1 = 90 m /min
V1 T1n = C1
90 (T1)n = 143
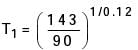
T1 = 47.4 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:For turning NiCr alloy steel at cutting speeds of 64 m/min and 100 m/min, the respective tool lives are 15 min-and 12 min. The tool life for a cutting speed of 144 m/min is
[ME 2001]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Helix angle of fast helix drill is normally
[ME 1997]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Tool life of a 10 hours is obtained when cutting with a single point tool at 63 m/min. If Taylor's constant C = 257.35, tool life on doubling the velocity will be
[ME 1996]
Explanation
V1 = 63m/min T1 = 60 hours = 600 min
C = 257.35
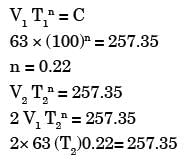
T2 = 25.6 min
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:The rake angle in drill
[ME 1996]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:The effect of rake angle on the mean friction angle in machining can be explained by
[ME 1992]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:In turning operation the feed rate could be doubled to increase the metal removal rate. To keep the same level of surface finish, the nose radius of the tool has to be
[ME 1989]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Cutting Tool Geometry & Tool Life
Try yourself:Cutting tools are provided with large positive rake angle mainly for
[ME 1987]
Explanation
As rake angle a increases, shear plane angle ϕ decreases. So less force is required for cutting.
Report a problem