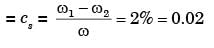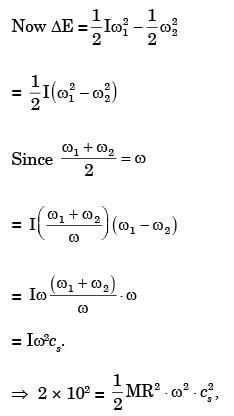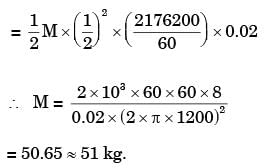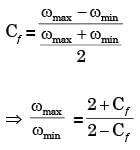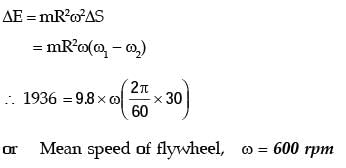GATE Past Year Questions: Flywheel | Theory of Machines (TOM) - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: The torque provided by an engine is given by T(θ) = 12000 + 2500sin(2θ) N.m, where θ is the angle turned by the crank from inner dead center. The mean speed of the engine is 200 rpm and it drives a machine that provides a constant resisting torque. If variation of the speed from the mean speed is not to exceed ±0.5, the minimum mass moment of inertia of the flywheel should be _______ kg.m2 (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
Ans: 560 to 580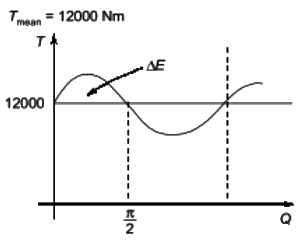
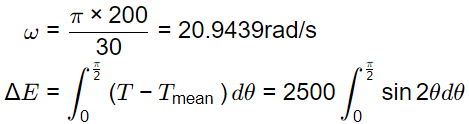
= 2500 × 1 = 2500 J
ΔE = Iω2Cs
2500 = I x 20.94392 x 0.01
I = 569.934 kgm2 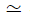 570 kg.m2
570 kg.m2
Q2: The controlling force curves P, Q and R for a spring controlled governor are shown in the figure, where r1 and r2 are any two radii of rotation.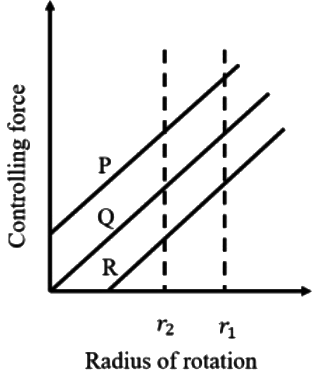 The characteristics shown by the curves are [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
The characteristics shown by the curves are [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
(a) P - Unstable; Q - Stable; R - Isochronous
(b) P - Unstable; Q - Isochronous; R - Stable
(c) P- Stable; Q - Isochronous; R - Unstable
(d) P - Stable; Q - Unstable; R - Isochronous
Ans: (b)
F(r)∣P = ar + b → Unstable
F(r)∣Q = ar + b → Isochronous
F(r)∣R = ar − b → Stable
Q1: The turning moment diagram of a flywheel fitted to a fictitious engine is shown in the figure.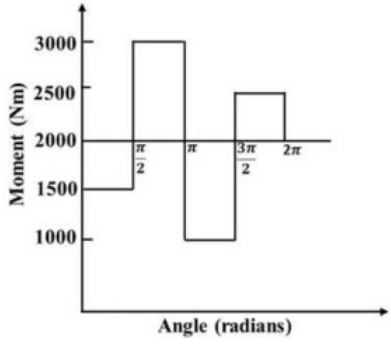 The mean turning moment is 2000 Nm. The average engine speed is 1000 rpm. For fluctuation in the speed to be within ±2% of the average speed, the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel is _________ kgm2. [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]
The mean turning moment is 2000 Nm. The average engine speed is 1000 rpm. For fluctuation in the speed to be within ±2% of the average speed, the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel is _________ kgm2. [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]
Ans: 3.55 to 3.65
N = 1000 rpm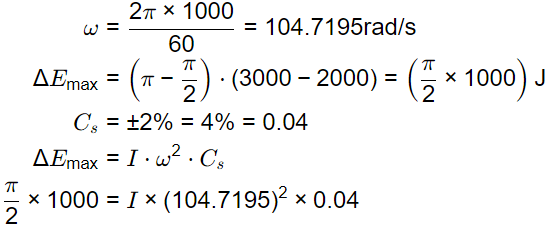
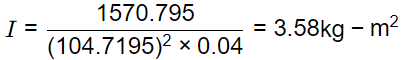
Q2: A flywheel is attached to an engine to keep its rotational speed between 100 rad/s and 110 rad/s. If the energy fluctuation in the flywheel between these two speeds is 1.05 kJ then the moment of inertia of the flywheel is _________________kg.m2 (round off to 2 decimal places). [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
Ans: 0.98 to 1.02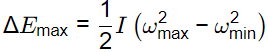
∴ 1.05 × 103 × 2 = I(1102 − 1002)
I = 1 kg.m2
[2007]
[2003]
[2006]
[2001]
[1998]
|
87 videos|76 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Flywheel - Theory of Machines (TOM) - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is a flywheel and how does it function in mechanical systems? |  |
| 2. What are the key advantages of using a flywheel in mechanical engineering applications? |  |
| 3. How does the moment of inertia affect the performance of a flywheel? |  |
| 4. What calculations are involved in determining the energy stored in a flywheel? |  |
| 5. What are typical applications of flywheels in mechanical engineering? |  |