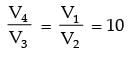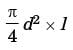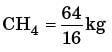Q1: A furnace can supply heat steadily at 1200 K at a rate of 24000 kJ/min. The maximum amount of power (in kW) that can by using the heat supplied by the furnace in an environment at 300 K is [GATE ME 2024]
(a) 300
(b) 150
(c) 18000
(d) 0
Ans: (a)
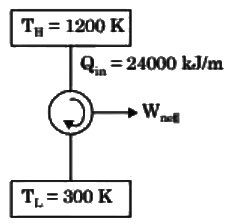
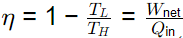
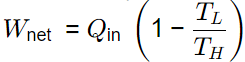
on 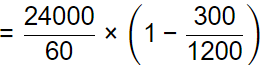
= 300 kW
Q1: An engine running on an air standard Otto cycle has a displacement volume 250 cm3 and a clearance volume 35.7 cm3. The pressure and temperature at the beginning of the compression process are 100 kPa and 300 K, respectively. Heat transfer during constant-volume heat addition process is 800 kJ/kg. The specific heat at constant volume is 0.718 kJ/kg.K and the ratio of specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume is 1.4. Assume the specific heats to remain constant during the cycle. The maximum pressure in the cycle is ______ kPa (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
Ans: 4780 to 4825
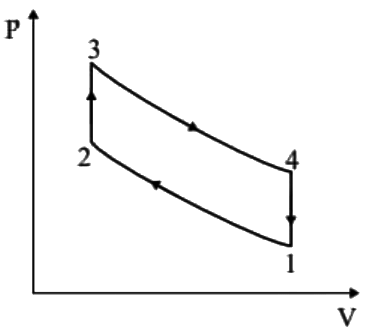 VS = 250 cm3
VS = 250 cm3
VC = 35.7 cm3
T1 = 300 K
P1 = 100 kPa
QS = 800 kJ/kg
Cv = 0.718 kJ/kgK
γ = 1.4
P3 = ___ kPa
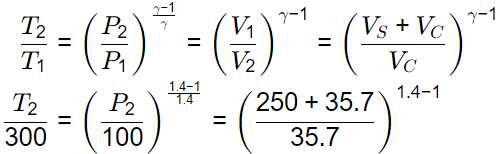
T2 = 689.31 K
P2 = 1838.82 kPa
QS = cv x (T3 - T2)
800 = 0.718 (T3 - 689.31)
T3 = 1803.516 K
For Process 2-3 (Volume is constant)
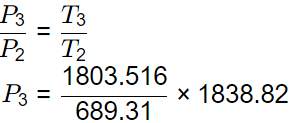
P3 = 4811 kPa
Q1: For an air-standard Diesel cycle, [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]
(a) heat addition is at constant volume and heat rejection is at constant pressure
(b) heat addition is at constant pressure and heat rejection is at constant pressure
(c) heat addition is at constant pressure and heat rejection is at constant volume
(d) heat addition is at constant volume and heat rejection is at constant volume
Ans: (c)
Heat addition is at constant pressure and heat rejection is at constant volume.
Q2: The indicated power developed by an engine with compression ratio of 8, is calculated using an air-standard Otto cycle {constant properties). The rate of heat addition is 10 kW. The ratio of specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume is 1.4. The mechanical efficiency of the engine is 80 percent.
The brake power output of the engine is ________ kW (round off to one decimal place). [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
Ans: 4.4 to 4.6
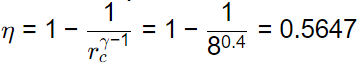
W/Q1 = 0.5647
W = 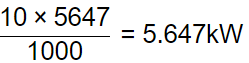
BP = ηm x W = 0.8 x 5.647
= 4.5175 kW
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself: In air standard Ottocycle the terminal pressures at the end of compression, heat release and expansion are respectively P2, P3 and P4. If the corresponding values are P2, P3, and P4, taking into account the effect of variable specific heat and dissociation of the working fluid, then
'[1989 : 2 Marks]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:An air standard diesel cycle consists of
[1990]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:With increasing temperature of intake air, CI engine efficiency
[1998]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:An IC engine has a bore and stroke of 2 units each. The area to calculate heat loss can be taken as
[1998]
Explanation
Total area for heat loss = surface area of cylinder = πdl = π x 2 x 2 = 4π
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:An air breathing air craft is flying at an altitude where the air density is half the value at ground level. With reference to the ground level, the air- fuel ratio at this altitude will be
Explanation
A/F ratio = ma/ mf
where ma – mass of air,
mf – mass of fuel.
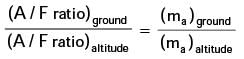
as mf is same at both places.
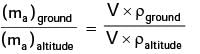
where 'V' is the volume of air taken in.
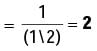
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:In a spark ignition engine working on the ideal Otto cycle, the compression ratio is 5.5. The work output per cycle (i.e., area of the P – V diagram) is equal to 23.625 × 105 × VcJ, where VC is the clearance volume in m3. The indicated mean effective pressure is
[2001]
Explanation
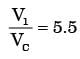
V1 = 5.5 vc
Vs = V1 – Vc
Vs = 4.5
Vc work output = 23.625 × 105 ×VC Joules.
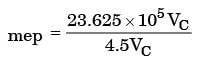
= 5.25 × 105Pa
= 5.250 bar
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:An ideal air standard Otto cycle has a compression ratio of 8.5. If the ratio of the specific heats of air (g) is 1.4, what is the thermal efficiency (in percentage) of the Otto cycle?
[2002]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:For an engine operating on air standard Otto cycle, the clearance volume is 10% of the swept volume. The specific heat ratio of air is 1.4.The air standard cycle efficiency is
[2003]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:An engine working on air standard Otto cycle has a cylinder diameter of 10 cm and stroke length of 15 cm. The ratio of specific heats for air is 1.4. If the clearance volume is 196.3 cc and the heat supplied per kg of air per cycle is 1800 kJ/kg, the work output per cycle per kg of air is
[2004]
Explanation
Given: Vc = V2 = 196.3 cm3 = 0.0001963 m3 stroke volume,
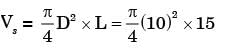
= 1178.09 cc
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:The stroke and bore of a four stroke spark ignition engine are 250 mm and 200 mm respectively. The clearance volume is 0.001 m3.If the specific heat ratio g = 1.4, the air-standard cycle efficiency of the engine is
[2007]
Explanation
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:Which one of the following is NOT a necessary assumption for the air-standard Otto cycle?
[2008]
Explanation
In take process is the constant volume h eat addition process Hence (b) is not the right assumption
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:In an air-standard Otto cycle, the compression ratio is 10. The condition at the beginning of the compression process is 100 kPa and 27°C.Heat added at constant volume is 1500 kJ/kg, while 700 kJ/kg of heat is rejected during the other constant volume process in the cycle.Specific gas constant for air = 0.287 kJ/kgK.The mean effective pressure (in kPa) of the cycle is
[2009]
Explanation
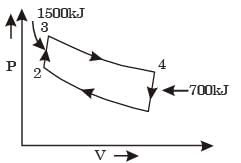 Here, P1 = 100 kPa
Here, P1 = 100 kPa
T1 = 27°C
Cv = 0.287 kJ/kgK
Pm ´ (V1 - V2)= work done
= h1 - h2
= 1500 - 700
= 800 kJ
Now P1V1 = mRT1
or 100 x 103 x V1 = 1 x 0.287 ´x 103 x 300
or V1 = 0.861
∴ V2 = 0.0861
Now Pm ( 0.861 – 0.0861) = 800
∴
Pm = 1032 kPa
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:The crank radius of a single-cylinder IC engine is 60 mm and the diameter of the cylinder is 80 mm. The swept volume of the cylinder in cm3 is
[2011]
Explanation
Stroke of the cylinder, l = 2r = 2 x 60 = 120 mm.
Swept volume = 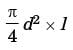
= π/4 x 802 x 120 = 603cm3
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:For the same values of peak pressure, peak temperature and heat rejection, the correct order of efficiencies for Otto, Duel and Diesel cycles is
[2015]
Explanation
For same values of peak pressure and temperature. Diesel cycle is most efficient and Otto cycle is least. Efficiency of dual cycle lies in between.nDiesel > nDual > nOtto.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:The power output from a spark ignition engine is varied by
[1990]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:For determining the ignition quality of compression ignition engine fuels, the reference fuels used are
[1991]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:If air fuel ratio of the mixture in petrol engine is more than 15:1
[1991]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:Alcohols are unsuitable at diesel engine fuels because
[1992]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:Knocking tendency in a Sl engine reduces with increasing
[1993]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:In order to burn 1 kilogram of CH4 completely, the minimum number of kilograms of oxygen needed is (take atomic weights of H, C and O as 1, 12 and 16 respectively)
[1995]
Explanation
CH4 + 2C2 → CO2 + 242O
16 kg 24 kg 44 kg 36 kg
1kg 64/16 kg
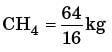
from above balance reactionmass of O2 for complete com bu st i on of 1 k g → mass of oxygen = 4 kg]
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:The silencer of an internal combustion engine
[1999]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:A diesel engine is usually more efficient than a spark ignition engine because
[2003]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:At the time of starting, idling and low speed operation, the carburettor supplies a mixture which can be termed as
[2004]
Explanation
Very rich mixtur e is provided during starting, idling and peak power to ensure burning due to low supply of air, low temperature etc.
Report a problem
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:BHP of a diesel engine can be increased by
[1991]
Question for GATE Past Year Questions: Internal Combustion Engine
Try yourself:Brake thermal efficiency of the three basic types of reciprocating engines commonly used in road vehicles are given in the increasing order as
[1992]

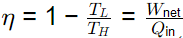
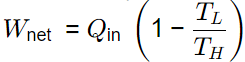
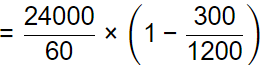
 VS = 250 cm3
VS = 250 cm3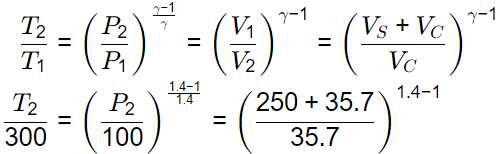
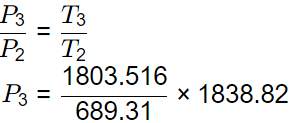
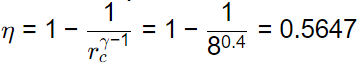
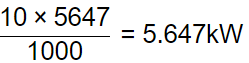







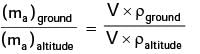
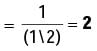
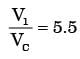
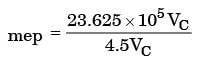
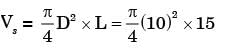
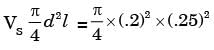
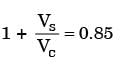
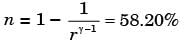
 Here, P1 = 100 kPa
Here, P1 = 100 kPa