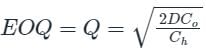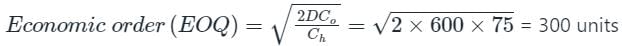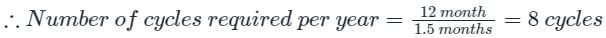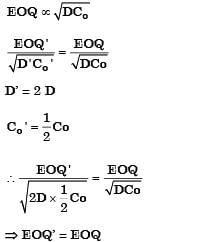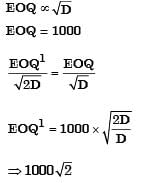GATE Past Year Questions: Inventory Control | Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering PDF Download
Q1: A company orders gears in conditions identical to those considered in the economic order quantity (EOQ) model in inventory control. The annual demand is 8000 gears, the cost per order is 300 rupees, and the holding cost is 12 rupees per month per gear. The company uses an order size that is 25% more than the optimal order quantity determined by the EOQ model. The percentage change in the total cost of ordering and holding inventory from that associated with the optimal order quantity is [GATE ME 2024]
(a) 2.5
(b) 5
(c) 0
(d) 12.5
Ans: (a)
D = 8000 gear/year
C0 = 300
Ch = 12/ month =144/ year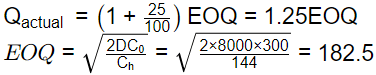
Qactual = 1.25 × EOQ = 1.25 × 182.5
= 1.25 × 182.5 = 228.125
Total cost at EOQ
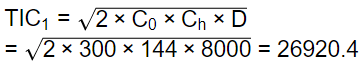
Total cost at actual order (Qactual)
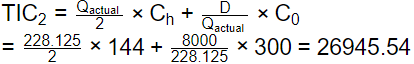
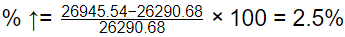
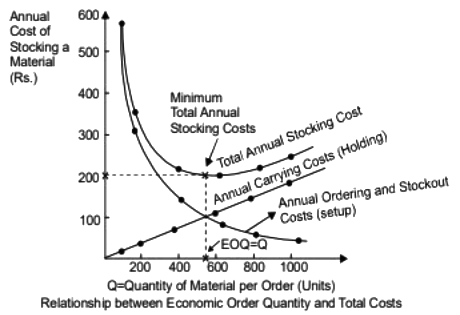
Q1: With reference to the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) model, which one of the options given is correct? [GATE ME 2023]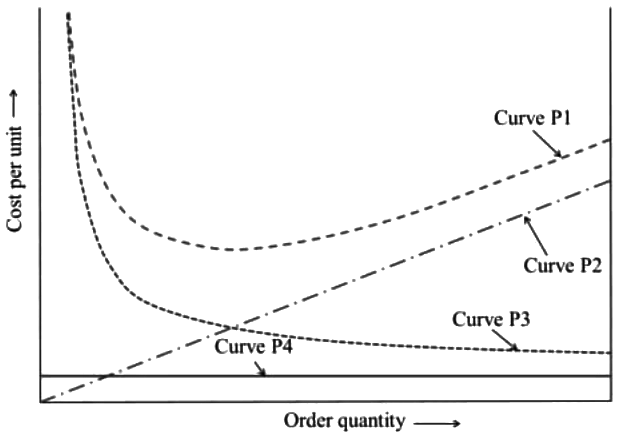 (a) Curve P1: Total cost, Curve P2: Holding cost, Curve P3: Setup cost, and Curve P4: Production cost.
(a) Curve P1: Total cost, Curve P2: Holding cost, Curve P3: Setup cost, and Curve P4: Production cost.
(b) Curve P1: Holding cost, Curve P2: Setup cost, Curve P3: Production cost, and Curve P4: Total cost.
(c) Curve P1: Production cost, Curve P2: Holding cost, Curve P3: Total cost, and Curve P4: Setup cost.
(d) Curve P1: Total cost, Curve P2: Production cost, Curve P3: Holding cost, and Curve P4: Setup cost.
Ans:(a)
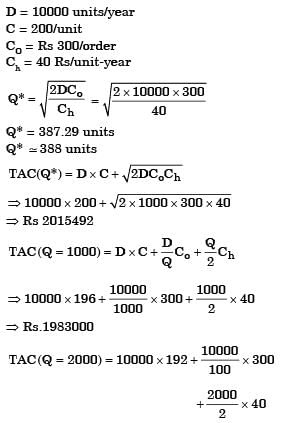
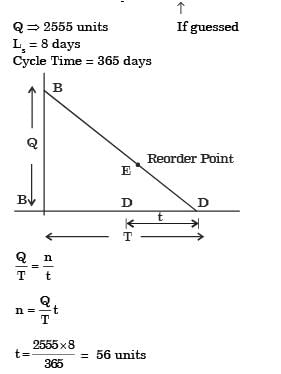
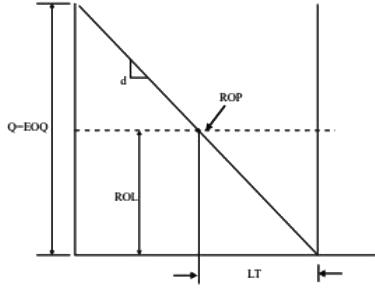
Q1: The demand of a certain part is 1000 parts/year and its cost is Rs. 1000/part. The orders are placed based on the economic order quantity (EOQ). The cost of ordering is Rs. 100/order and the lead time for receiving the orders is 5 days. If the holding cost is Rs. 20/part/year, the inventory level for placing the orders is ________ parts (round off to the nearest integer). [GATE ME 2022 SET-2]
Ans:13 to 15
Inventory control:
Annual demand (D) = 1000 units
Lead time (LT) = 5 days
Inventory level for placing the order = Re-order level (ROL)
Rate of consumption (d) = D/365
ROL = d × LT = (1000/365) x 5 = 13.69 ≈ 14 units
Q2: The product structure diagram shows the number of different components required at each level to produce one unit of the final product P. If there are 50 units of on-hand inventory of component A, the number of additional units of component A needed to produce 10 units of product P is _________ (in integer). [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]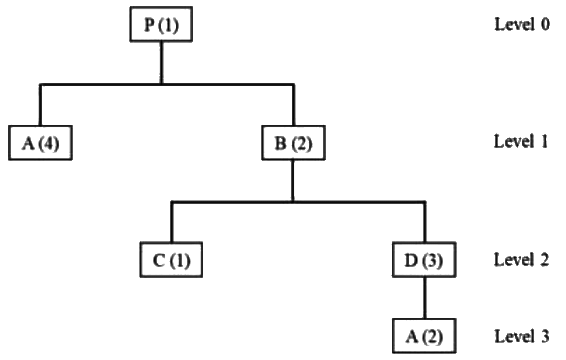 Ans:110 to 110
Ans:110 to 110
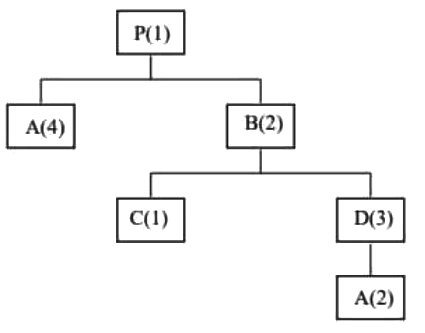 To produce 10 units of 'P'
To produce 10 units of 'P'
No. of units of 'A' required = (4 x 10) + (2 x 3 x 2 x 10) = 160 units
Net requirement of 'A' = 160 - 50 = 110 units
Q3: Which one of the following is NOT a form of inventory? [GATE ME 2022 SET-1]
(a) Raw materials
(b) Work-in-process materials
(c) Finished goods
(d) CNC Milling Machines
Ans: (d)
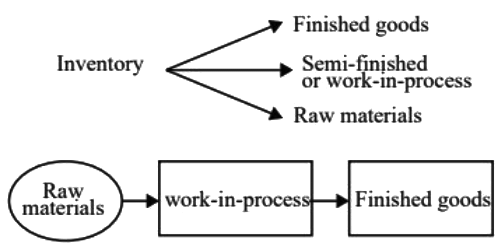 CNC milling machines will not be treated as inventory.
CNC milling machines will not be treated as inventory.
Q1: A factory produces m(i = 1, 2, ... m) products, each of which requires processing on n(j = 1, 2, ... n) workstations. Let aij be the amount of processing time that one unit of the ith product requires on the jth workstation. Let the revenue from selling one unit of the ith product be ri and hi be the holding cost per unit per time period for the ith product. The planning horizon consists of T(t = 1, 2, ... T) time periods. The minimum demand that must be satisfied in time period t is dit, and the capacity of the jth workstation in time period t is cjt. Consider the aggregate planning formulation below, with decision variables Sit (amount of product i sold in time period t), Xit (amount of product i manufactured in time period t) and Iit (amount of product i held in inventory at the end of time period t.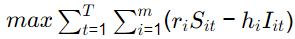
subject to
Sit ≥ dit ∀i, t
< capacity constraint >
< inventory balance constraint >
Xit, Sit, Iit ≥ 0; Ii0 = 0
The capacity constraints and inventory balance constraints for this formulation are [GATE ME 2021 SET-2]
(a) 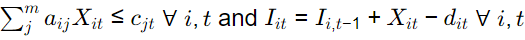
(b) 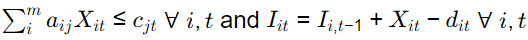
(c) 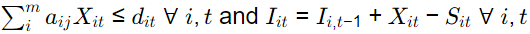
(d) 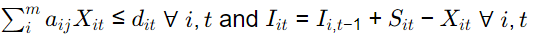
Ans:(a)
m → i ... m ← product
n → i ... n ← workstation
ri → selling price
hi→ holding cost
T → t = 1, 2, … T
dit → demand of product in time t
cjt → capacity of workstation in time t
Sit → Number of product sold in time t
xit → Number of product produced in time t
Iit → Number of product i hold in inventory at end of period t
Capacity constraint
aij xit ≤ cjt
Inventory constraint
lit = Ii,t−1 + xit − Sit
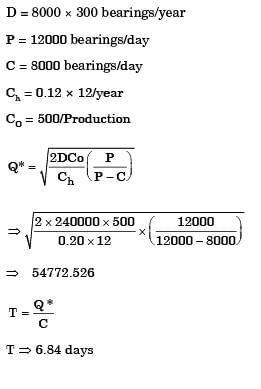
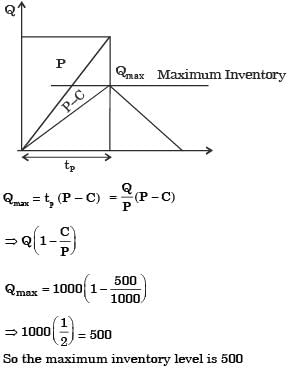
Q1: For a single item inventory system, the demand is continuous, which is 10000 per year. The replacement is instantaneous and backorders (S units) per cycle are allowed as shown in the figure.
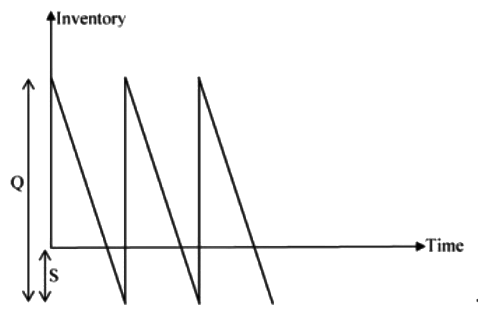 As soon as the quantity (Q units) ordered from the supplier is received, the backordered quantity is issued to the customers. The ordering cost is Rs. 300 per order. The carrying cost is Rs. 4 per unit per year. The cost of backordering is Rs. 25 per unit per year. Based on the total cost minimization criteria, the maximum inventory reached in the system is ________ (round off to nearest integer). [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]
As soon as the quantity (Q units) ordered from the supplier is received, the backordered quantity is issued to the customers. The ordering cost is Rs. 300 per order. The carrying cost is Rs. 4 per unit per year. The cost of backordering is Rs. 25 per unit per year. Based on the total cost minimization criteria, the maximum inventory reached in the system is ________ (round off to nearest integer). [GATE ME 2020 SET-2]Ans:1130 to 1140
Given data: D = 10000 items/year, Co = Rs. 300/order,
Ch = Rs. 4/unit/year, Cb = Rs. 25/unit/year,
For minimum tool cost
Quantity ordered,
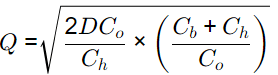
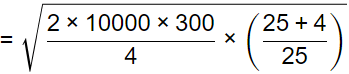
Q = 1319.09 unit
Now, for minimum cost, optimum units backordered
(Q − S) × Ch =(S) x Cb
S(Cb + Ch) = Q x Ch
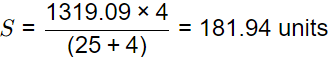
Maximum inventory in the system, Qmax = Q − S
=1319.09 − 181.94
=1137.15 unit
≈1137 units
Alternate:
Maximum inventory in system 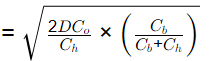
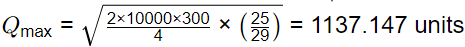
Q2: Consider two cases as below.
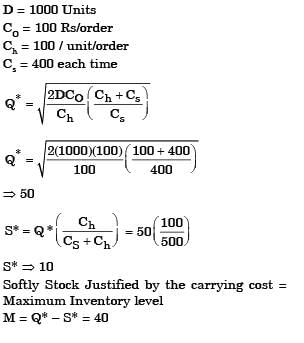
Case 1: A company buys 1000 pieces per year of a certain part from vendor 'X'. The changeover time is 2 hours and the price is Rs. 10 per piece. The holding cost rate per part is 10% per year.
Case 2: For the same part, another vendor 'Y' offers a design where the changeover time is 6 minutes, with a price of Rs. 5 per piece, and a holding cost rate per part of 100% per year. The order size is 800 pieces per year from 'X' and 200 pieces per year from 'Y'.
Assume the cost of downtime as Rs. 200 per hour. The percentage reduction in the annual cost for Case 2, as compared to Case 1 is___________ (round off to 2 decimal places). [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
Ans:8.19 to 8.23
Given, for case (i)
Q = 1000, C = Rs110,. r = 10% and Cost of downtime = 200/hr, Change over time = 2hrs
Then,
Ch = 10 × (10/100) = Rs1/ unit/year
Cd = 200 × 2 = 400/ order
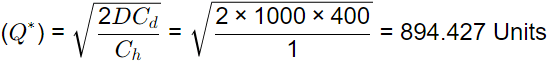
Total cost for Case 1
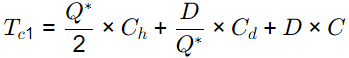
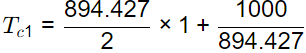 x 400 + 1000 x 10 = Rs. 10894.427
x 400 + 1000 x 10 = Rs. 10894.427
Case (ii)
800 units are ordered from vendor X then total cost from vendor X, only the units will change other conditions (holding and downtime cost) will remain the same as the vendor is the same
For quantities ordered from the vendor x
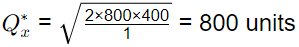
Total cost for vendor x
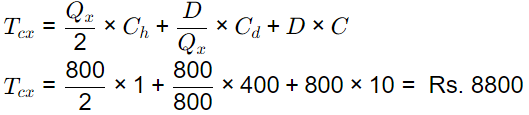
For vendor Y
Q = 200, C = Rs5,. r = 100% and Cost of downtime = 200/hr, Change over time = 6 minutes Then,
Ch = 5 × (100/100) = Rs 5/ unit / year
Cd = 200 × (6/60) = 20/ order
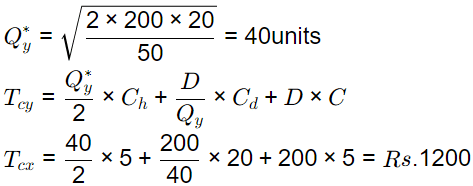
Total cost for the second case
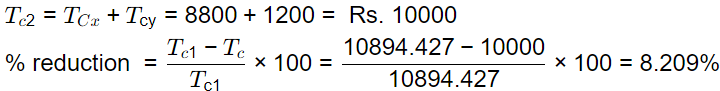
Q3: For an assembly line, the production rate was 4 pieces per hour and the average processing time was 60 minutes. The WIP inventory was calculated. Now, the production rate is kept the same, and the average processing time is brought down by 30 percent. As a result of this change in the processing time, the WIP inventory [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
(a) decreases by 25%
(b) increases by 25%
(c) decreases by 30%
(d) increases by 30%
Ans: (c)
WIP = Throughput rate x Processing time
(WIP)1 = 4 x 1 = 4 units
(Processing Time)2 = 1 x 0.7 = 0.7
Throughput rate = 4
(WIP)2 = 4 x 0.7 = 2.8
% decrease = 30%
Q4: In the Critical Path Method (CPM), the cost-time slope of an activity is given by [GATE ME 2020 SET-1]
(a) 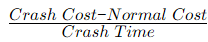
(b) 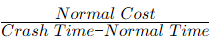
(c) 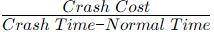
(d) 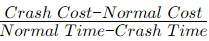
Ans: (d)
[2018]
[2014]
[2014]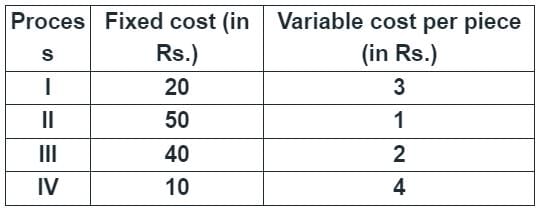
[2010]
[2009]
[2007]
[2007]
[2007 : 2 Marks]
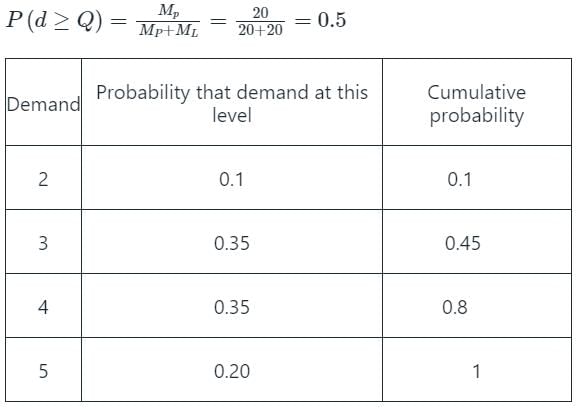
The stockist pays Rs. 70 for each item and he sells each at Rs. 90. If the stock is left unsold in any month, he can sell the item at Rs. 50 each. There is no penalty for unfulfilled demand. To maximize the expected profit, the optimal stock level is [2006]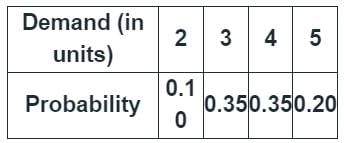
[2006]
[2004]
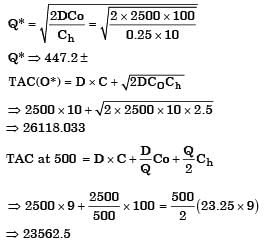
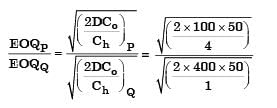
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) of products P and Q will be in the ratio? [2004]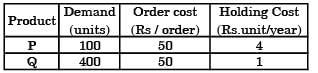
[2003]
[1999]
[1998]
[1995]
[1991]
[1989]
[1998]
[1997]
|
30 videos|65 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on GATE Past Year Questions: Inventory Control - Industrial Engineering - Mechanical Engineering
| 1. What is the significance of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) in inventory control? |  |
| 2. How do safety stock levels affect inventory management? |  |
| 3. What are the main types of inventory in manufacturing? |  |
| 4. What is the role of Inventory Turnover Ratio in assessing inventory performance? |  |
| 5. How can Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management benefit a manufacturing firm? |  |